Amniotic fluid – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Amniotic fluid
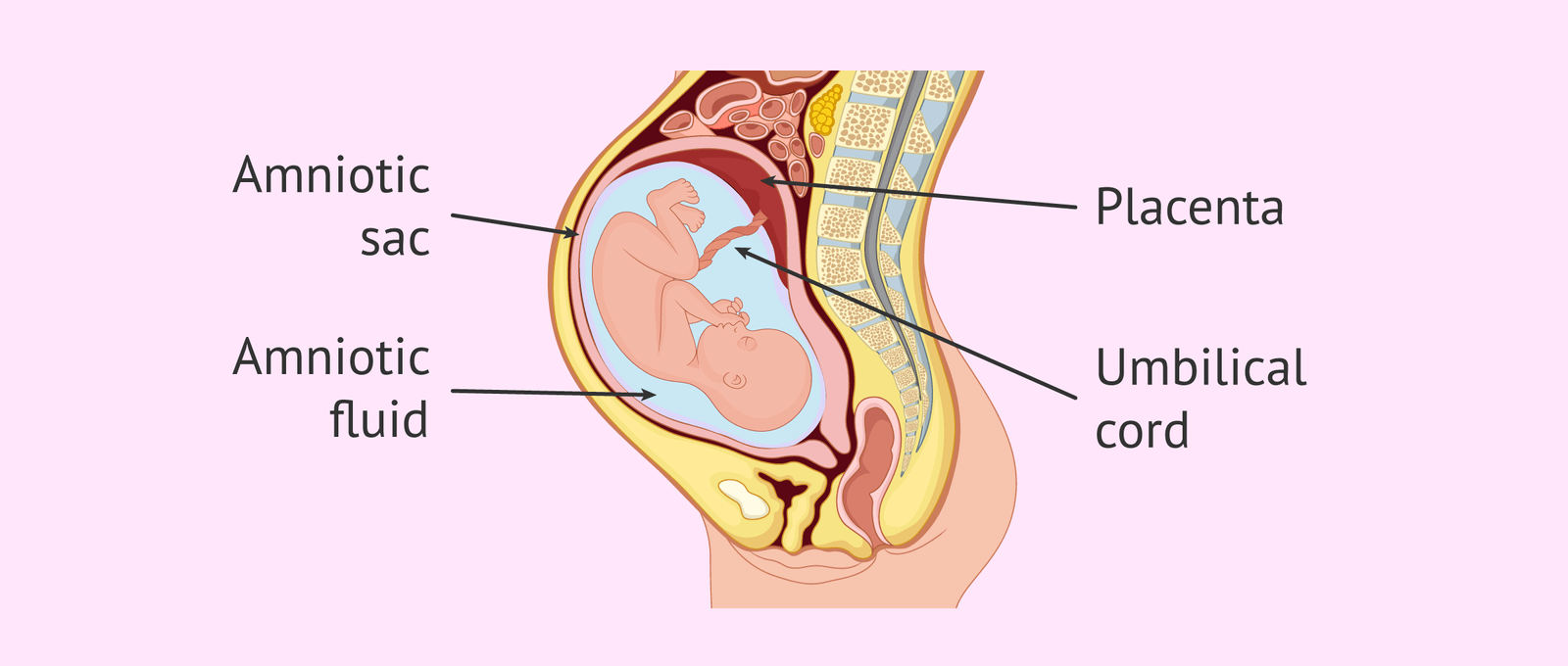
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac.
or
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid Amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus.
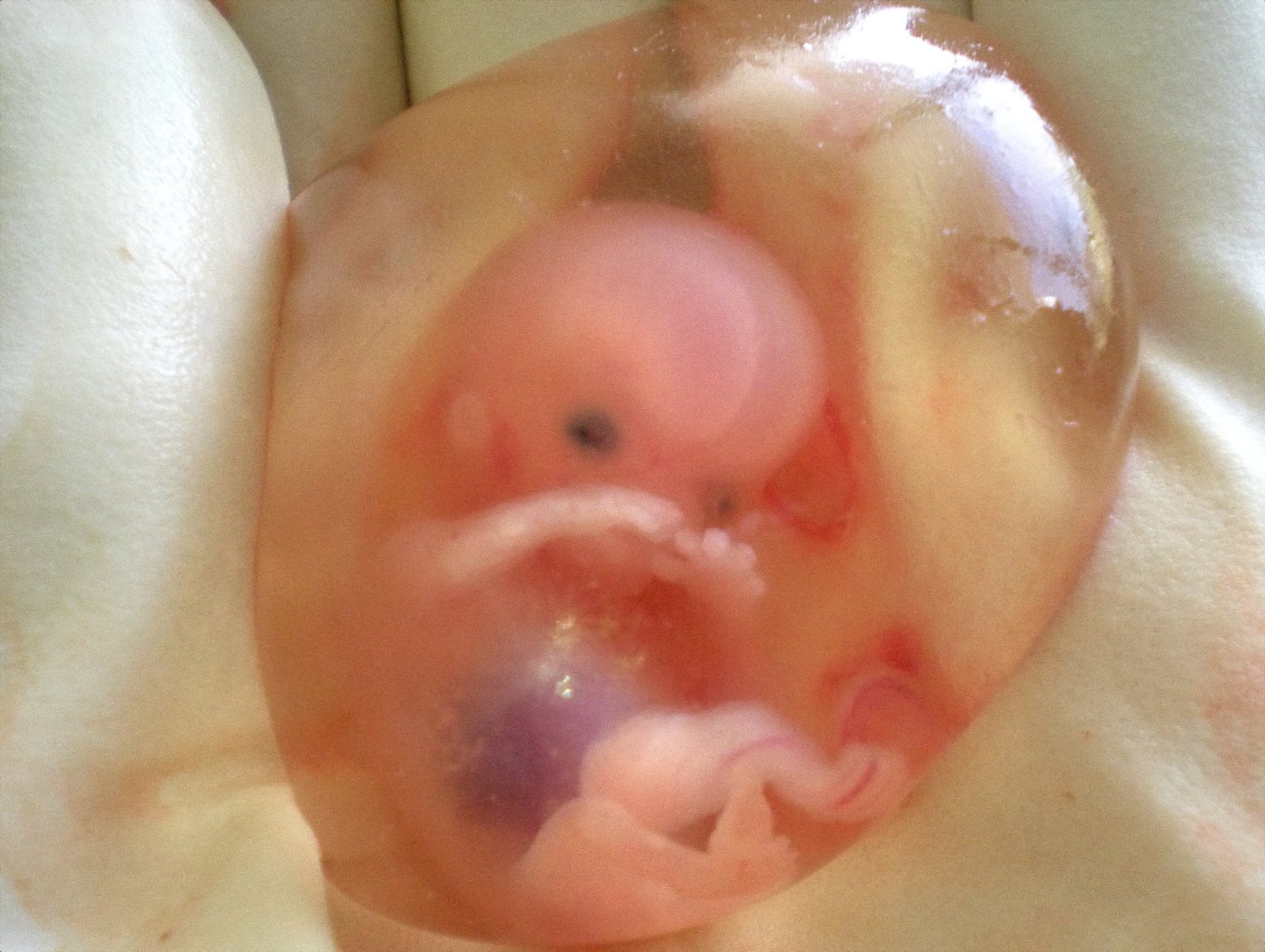
Figure: amniotic fluid
Sources/origin of amniotic fluid:
Amniotic fluid comes from both fetal and maternal origin
1. Transudation from the maternal serum across the placental membrane.
2. Transudation from fetal circulation across the umbilical cord or placental membranes.
3. Secretion from the amniotic epithelium.
4. Transudation of fetal plasma through highly permeable fetal skin before it is keratinized at 20th week.
5. Fetal urine- daily output at term is about 400-1200 ml
6. Fetal lung fluid that enters the amniotic cavity to add to its volume.
Composition of amniotic fluid:
A. Organic constituents
➤ Proteins-0.3 mg/dl
➤ Glucose- 20mg/dl
➤ Urea- 30 mg/dl
► Non protein nitrogen-30mg/dl
➤ Uric acid-4 mg/dl
➤ Creatinine-2 mg/dl
➤ Lipids-50 mg/dl
➤ Hormones- insulin,prolactin, rennin
B. Inorganic constituents- Na, K,Cl
C. Suspended particles- Lanugo, Desqamated fetal skin cells, vernix caseosa, shedded amniotic cells, cells from thr respiratory tract, GIT, Genitourinary tract.
Functions of amniotic fluid:
1. The fluid allows the baby to move around while it is developing. This movement allows for bone and muscle development.
2. The fetus breathes the fluid in and out, allowing it to practice breathing and to aid in lung development.
3. The fluid also helps to keep the fetus nice and warm by keeping heat in. It also helps to keep the temperature consistent.
4. The fluid offers protection from any blows that may come to the uterus area. It may cushion the blow if the mother falls.
5. When the fetus swallows the amniotic- fluid, it is practicing using and developing the digestive system.
6. It keeps the umbilical cord from being squeezed too hard. A big squeeze could cut off the nutritional supply from the mother to the baby.
7. The amniotic- fluid act as lubricant. The fetus growing body parts are very fragile and could grow together, such as in the case of webbed fingers or toes.
8. Amniotic- fluid helps protect the baby from bumps and potential injury
9. Amniotic fluid also contains important nutrients, hormones and antibodies
Clinical significance of amniotic fluid:
1. Study of the amniotic fluid provides useful information about the wellbeing & also maturity of the fetus.
2. Intra- amniotic instillation of chemicals are used as method of induction of abortion.
3. Excess or less volume of liquor amnii is assessed by amniotic fluid index (AFI) which helps to diagnose polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
4. Rupture of membrane with drainage of liquor is a helpful method in induction of labour.
Clinical importance of colour of amniotic fluid:
1. Meconium stained (green): Suggestive of fetal distress in presentation other than the breech or transverse. Depending upon the degree and duration of the distress, it may be thin or thick or, pea soups (thick with flakes). Thick with presence of flakes suggests chronic fetal distress.
2. Golden colour in RH incompatibility is due to excessive haemolysis of the fetal RBC and production of excess bilirubin
3. Greenish yellow (saffron) in post maturity.
4. Dark color: Found in concealed accidental haemorrhage (due to contamination of blood).
5. Tobacco juice / dark brown color: Found in IUD. The dark color is due to frequent presence of old HbA
