Aortic valve stenosis – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Aortic valve stenosis
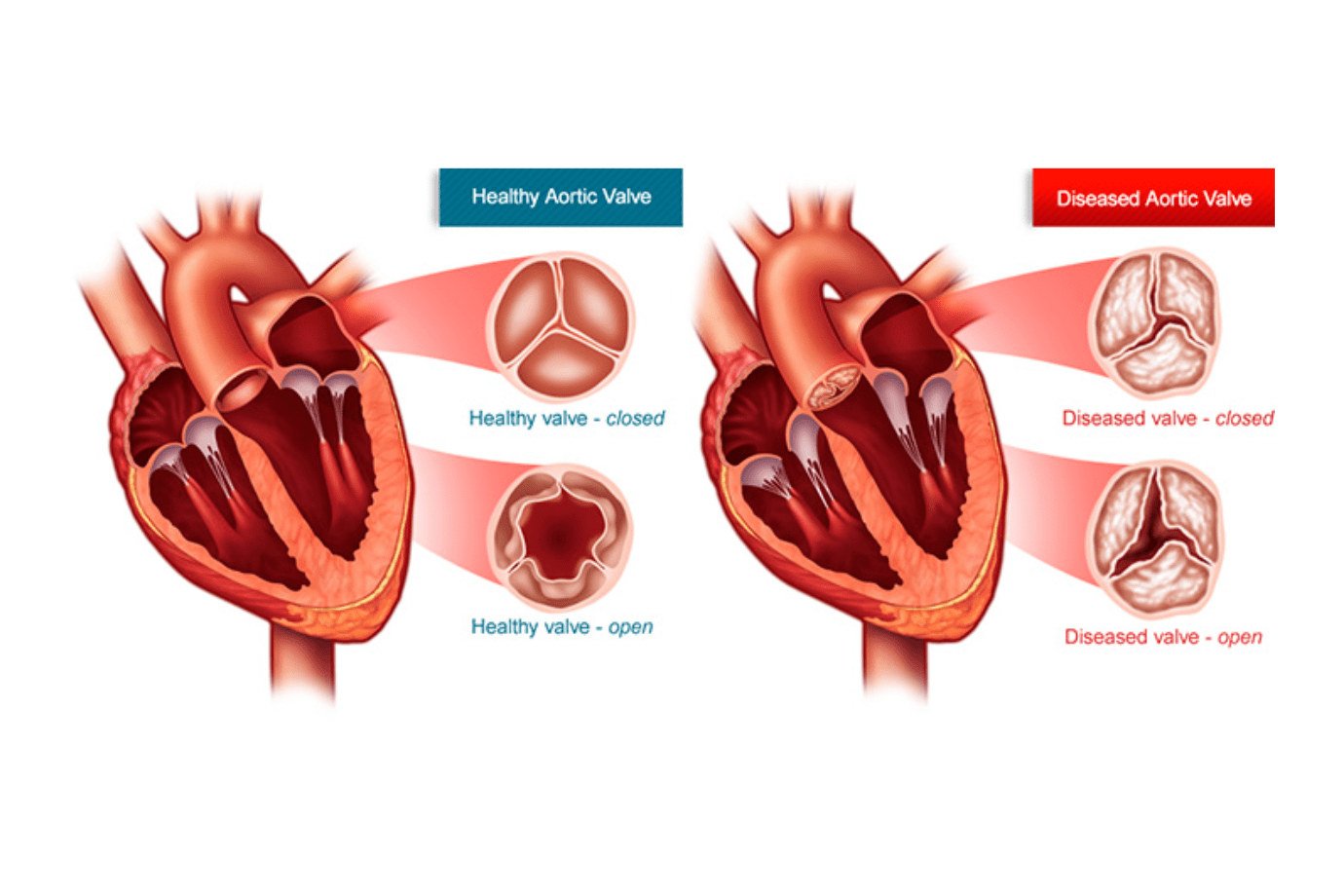 Aortic valve stenosis or aortic stenosis occurs when the heart’s aortic valve narrows. This narrowing prevents the valve from opening fully, which reduces or blocks blood flow from heart into the main artery to the body (aorta) and onward to the rest of the body.
Aortic valve stenosis or aortic stenosis occurs when the heart’s aortic valve narrows. This narrowing prevents the valve from opening fully, which reduces or blocks blood flow from heart into the main artery to the body (aorta) and onward to the rest of the body.
Causes of Aortic Stenosis:
i. Infants, children, adolescents:
- Congenital aortic stenosis
- Congenital subvalvular aortic stenosis
- Congenital supravalvular aortic stenosis
ii. Young adults to middle-aged:
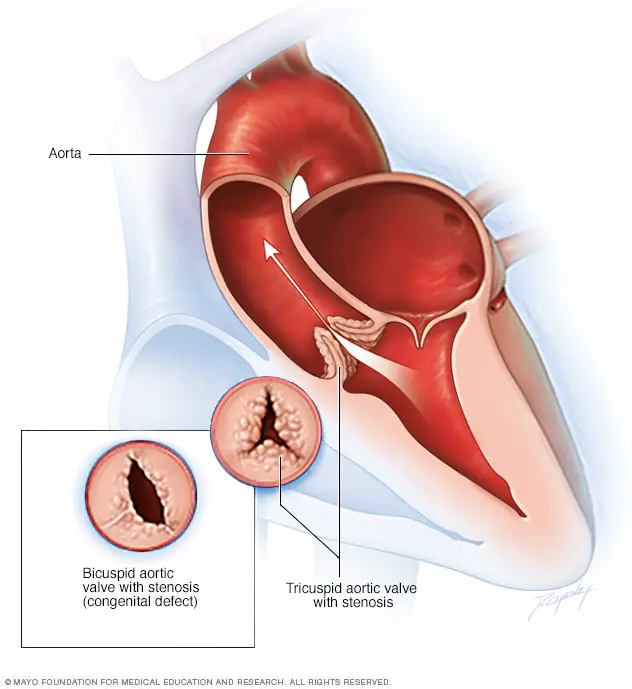
- Calcification and fibrosis of congenitally bicuspid aortic valve
- Rheumatic aortic stenosis
iii. Middle-aged to elderly:
- Senile degenerative aortic stenosis Calcification of bicuspid valve
- Rheumatic aortic stenosis
Management of Aortic stenosis
Clinical feature of Aortic stenosis:
Symptoms:
- Mild or moderate aortic stenosis is usually asymptomatic
- Exertional dyspnoea
- Angina
- Exertional syncope
- Sudden death
- Episodes of acute pulmonary oedema
Signs:
- Ejection systolic murmur
- Slow-rising carotid pulse
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Heaving apex beat (LV pressure overload)
- Signs of pulmonary venous congestion (e.g. crepitations)
Investigations:
i ECG:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (usually)
- Left bundle branch block
ii. Chest X-ray:
- May be normal. Sometimes enlarged left ventricle and dilated ascending aorta on PA view, calcified valve on lateral view
iii. Echo:
- Calcified valve with restricted opening, hypertrophied LV
iv. Doppler:
- Measurement of severity of stenosis
- Detection of associated aortic regurgitation
v. Cardiac catheterization:
- Mainly to identify associated coronary artery disease
- May be used to measure gradient between LV and aorta
(Ref: Davidson/23/522-523)
