Arthrodesis of wrist joint – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
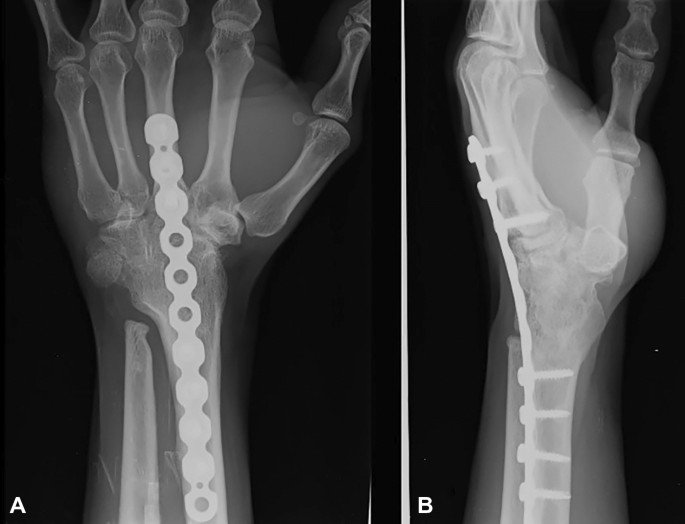
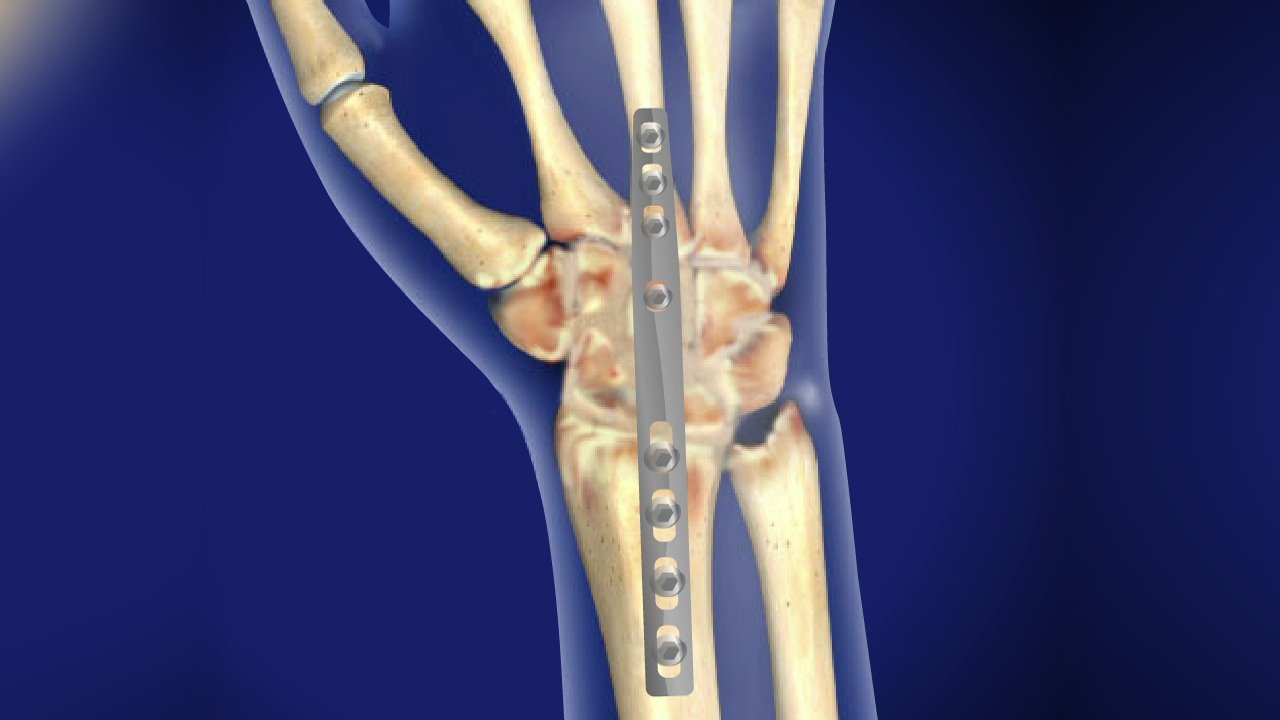
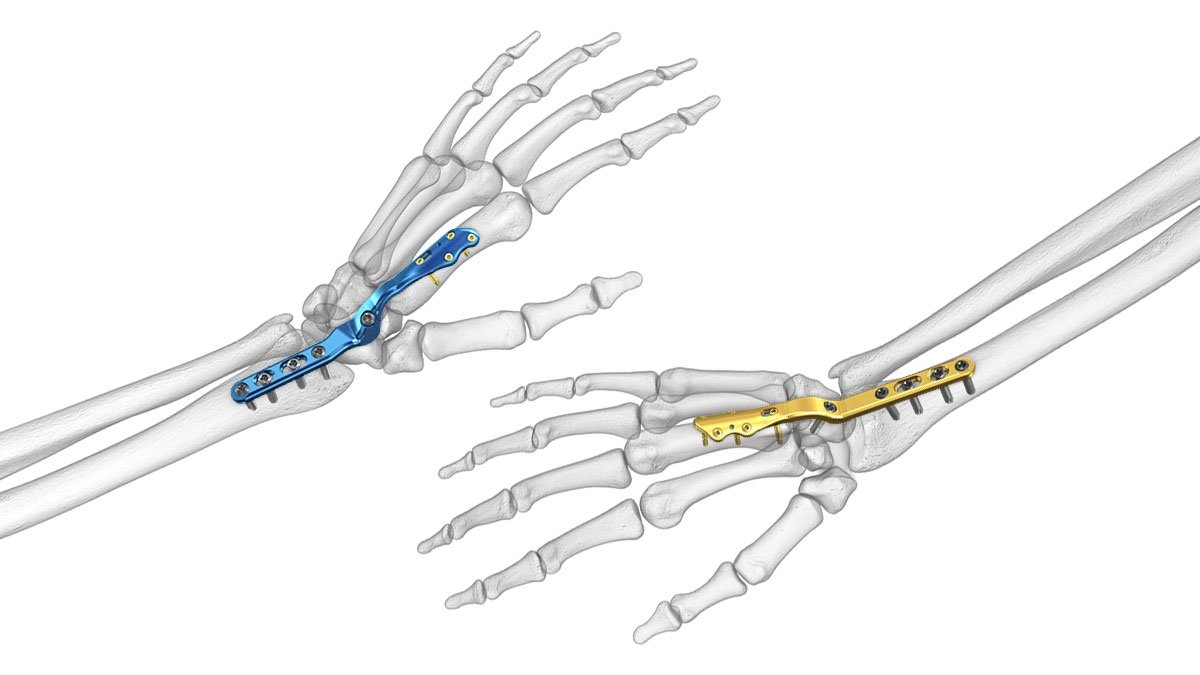
Arthrodesis of wrist joint
Arthrodesis of wrist
It may be defined as surgical fusion of the radiocarpal joint.
[Ref-Adult Orthpaedic nursing, Lippincott, P-388]
Indications of Wrist arthrodesis:
1. When their is gross bone and cartilage destruction.
2. When the carpal bones are markedly subluxed.
3. Non union or malunion of scaphoid.
4. Severely comminuted fracture of the distal end of radious.
5. Volkman ischaemia paralysis (Less common).
6. Poliomyelitis in wrist
7. Spastic cerebral palsy of wrist.
[Ref-Adult Orthpaedic nursing, Lippincott, P-388]
Ankle arthrodesis:
An ankle arthrodesis is an operation to induce bony ankylosis in the ankle joint.
Preoperative management of arthrodesis patients:
A) Psychological or mental preparation:
Operative case should be psychological or mentally prepared.
1) The nurse should talking and reassuring him or her and giving him or her confidence that nurse and doctor will do best.
2) The relative should be informed as to the type of operation.
3) The patients and relatives permission for operation must be obtained.
B) Physical Preparation:
i.Routine care:
The ward nurses are responsible for carrying out and reporting on th
1. Laboratory work Blood, urine and stool etc.
2. Temperature, pulse and respiration (TPR) of the patient should be taken and recorded 4 hourly. Any fever and rapid or irregular pulse or low and high blood pressure to be reported.
3. Symptoms of a cold or chronic cough should be reported.
4. Preparation of the site of operation. Shave the area (according to the shaving, procedure).
5.Record height and weight. If patient is anaemic it should be reported.
ii) Preoperative care:
When the patient is really for surgery, the surgeon writes orders for preoperative preparation.
1. Check the patient’s admission ticket.
2. Consent for operation and anesthesia from patient or relatives to be obtained.
3. Shave and clean the operation area.
4. All jewellary or valuable things should be removed and gives to the relatives or place in the safe.
5. If any false teeth, limbs or eye they must be removed.
6. The patient should be given a through bath.
7. Nothing should be given to drink after midnight and should be instructed not to eat or drink after midnight and light diet is given in the evening.
8. Enema simplex should be given according to ordered, if necessary.
9. Nasogastric tube should be inserted and stomach contains should be aspirate, if ordered.
10. Patient should be a fear clean hospital clothes.
11. The bladder should be emptied and the patient will be sent to the O.T (Operation Theater) with all necessary records and articles.
iii) GIT preparations:
1. Nothing per oral must be maintained day before operations from night.
2. If the operation is evening give light diet on the morning.
3. If patints feel thurst give seeps of water.
4. avoid any kind of food to prevent vomiting.
C) Preoperative teaching:
1. Deep breathing
2. Active or passive exercise of the joints of the body.
3. Proper hygienic practice after operation
4. Correct medication regularly.
[Ref-Lippincott, Adult orthopedic nursing+ Luckmann and Sorensenn, Medical and surgical nursing]
Nursing management of patients with an arthrodesis:
1) Assessment:
a) Check vital signs.
b) Observing the patients general color and warmth.
c) Determine the patients level of consciousness and orientation.
d) Assess the level of pain type, severity, location of pain
e) Check heart sound, lung sounds for any abnormality.
f) Neurovascular assessment of the legs.
g) Note the type of intravenous solution and rate per minutes.
h) Check urinary output every hourly.
2) Nursing diagnosis:
a) pain and discomfort related to bone and soft tissue trauma from surgery.
b) Impaired physical mobility related to lack of joint mobility.
c) Impaired skin integrity related to the immobilization device.
d) Increased anxiety related to knowledge deficit about surgical procedure and progress of diseases.
3) Nursing intervention:
a) Alleviation of pain:
b) Note the type, severity and location of pain to help determine the cause of pain.
e) Keep the area in comfortable position.
d) Immobilize the part of arthrodesis to reduce pain.
e) Elevate the limb to reduce pain and swelling.
f) Give analgesics according to doctor’s order.
g) Increase physical mobility:
i) Lying on supine position after coming from post anesthesia room.
ii) Exercise body parts regularly in right way.
iii) Exercise on arm to develop arm strength for crutch walking.
iv) Assist the patients in daily activities. v) Avoid weight bearing activity up to 8-12 weeks.
h) Maintaining skin integrity:
i) Observe the bony prominence of back.
ii) Change the position 2 hourly.
iii) Assess signs and symptoms of bed sores.
iv) Give back message to improve circulations.
v) Give cotton pad under the bonny prominence to reduce chance of pressure sores,
vi) Keep linen dry free of wrinkles,
vii) Keep the bony prominent soft by applying lubricate or powder.
viii) Keep the patients well hydrated and maintain well balance diet.
i) Reducing anxiety:
i) Assess the cause of anxiety.
ii) Assurance of the patients that he will cure readily.
iii) Tell him that nurses and doctors will do the best.
iv) Encourage the patients and family to verbalize questions.
v) Encourage to use relaxation technique, such as exercise, deep breathing,listening song, watching movie.
