Vitamin C Or Ascorbic Acid – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Nutrition and Dietetics” prescribed by BNMC-for all Diploma in Nursing Science and Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics. This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.

Vitamin C Or Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid is a water-soluble vitamin. It is the most sensitive of all vitamins. It is easily destroyed by heat, alkalis, drying, storage, cooking in iron vessel, by washing vegetables in water. Vitamin C is absorbed from the intestine. Ascorbic acid is a white crystalline substance”
Functions of vitamin C:
1. One of the principal functions of ascorbic acid is the formation of collagen an abundant protein that forms that intercellular substance in cartilage, bone matrices, dextrin and the muscular epithelium.
2. Vitamin C is important for wound healing and increases the ability to withstand the stress of injury and infection.
3. Ascorbic acid also plays an important role in other hydroxylation reactions.
4. Conversation of Tryptophan to serotonin, an important neurotransmitter and vasoconstrictor, and formation of norepinephrine from tyrosine involves hydroxylation reactions which require ascorbic acid.
5. Conversation of cholesterol to bile acids is another hydroxylation reaction that requires vitamin C.
6. Ascorbic acid is an important antioxidant and thus has a role in the protection of vitamin A and E and the polyunsaturated fatty acids from excessive oxidation.
7. Ascorbic acid enhances iron absorption by reducing ferric iron to ferrous iron across the intestinal mucosa.
8. It may also bind with iron to form a complex which facilitates transfer of iron across the intestinal mucosa.
9. In the circulation ascorbic acid aids in there release of iron from transferring so that it can be incorporated into tissue ferretin.
(Ref: Molly Sam’s A text book of Nutrition for Nurses/2/39-40)
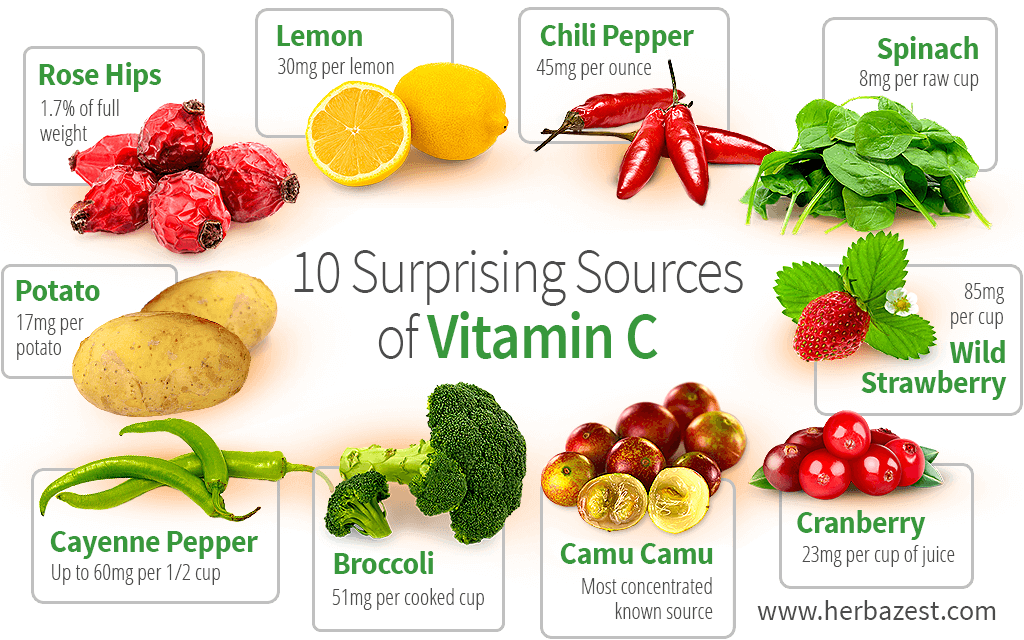
Sources of vitamin C:
1. Plant sources: All fresh fruits contain vitamin C. Citrus fruits, amloki, Lemon, tomato, guavas, grape fruits, blackberry, straw berry etc.
2. Fresh vegetable: Vegetables especially green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin C. e.g, cauliflower, cabbage, spinach, cereals etc. Roots and tubers are poor sources of vitamin C
3. Animal sources: Meat and milk contain very small amounts of vitamin C.
(Ref: Molly Sam’s A text book of Nutrition for Nurses/24/40)
Effects of deficiency of vitamin C:
1. Scurvy.
2. Listlessness.
3. Fatigue.
4. Bleeding gums.
5. Fleeting joint pain.
6. Muscle pains”
7. Person has difficulty in breathing.
8. Internal bleeding.
9. Person becomes susceptible to infection.
10. Delayed wound healing occurs.
11. Malformation of bone.
12. Degenerations of muscles.
Daily requirement of vitamin C:
| Age group | Requirement |
| Infants | 25 mg/day |
| Children | 40 mg/day |
| Normal adult | 40 mg/day |
| Pregnancy | 40 mg/day |
| Lactation | 60 mg/day |
