Assisting with passive range of motion and exercises – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Assisting with passive range of motion and exercises
Definition of Exercise:
Exercise is an activity requiring exertion, done to improve health or to correct deformity
or
Physical exercise means purposeful physical activity that is beneficial to all age groups and the health risks of a sedentary life are well documented.
or
Physical exercise is any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness
Benefit of Physical Exercise:
1. It helps maintain muscle tone
2. It helps to maintain mobility of joints.
3. It prevents and corrects deformities
4. It stimulates circulation of blood and prevents venous stasis.
5. It helps in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
6. It prevents varicose vein, reduce oedema and workload on heart.
7. It helps to prevent venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
8. It prevents obesity and regulate body temperature.
9. It improves appetite and digestion and prevents constipation.
10. Reduction of elevated blood sugar.
11. Decreased low-density blood lipids.
12. Improved physical appearance.
13. Increased bone density.
14. Promotion of sleep.
15. It prevents bedsore and adds to the beauty of person.
Types of Exercise:
Exercise is performed to promote fitness or to achieve therapeutic outcome. The two major types of exercise are:
A. Fitness exercise: It develops and maintains cardio respiratory function, muscular strength and endurance. There are two types of fitness exercise:
a) Isotonic exercise: Isotonic exercise is one method of muscular exercise. In contrast, isometric exercise is when muscular contractions occur without movement of the involved parts of the body
b) Isometric exercise: Isometric exercise or isometrics are a type of strength training in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction.
B. Therapeutic exercise: Therapeutic exercise (activity performed by people with health risks or those being treated for an existing health problem) are performed to prevent health-related complications or to restore lost functions.
a) Active exercise/Active range of motion: Active exercise is the exercise performed by the patient himself independently without assistance.
b) Passive exercise/Passive range of motion: Passive exercises are also known as passive range of motion (ROM) exercises; and the range of motion includes how far the patient can move his/her joints in different directions. These exercises are considered passive because he doesn’t exert any effort. Instead, someone (nurse/physiotherapist) helps him move his muscles and joints through their full range of motion for him.
Active Exercise:
Active exercise is the exercise performed by the patient himself independently without assistance.
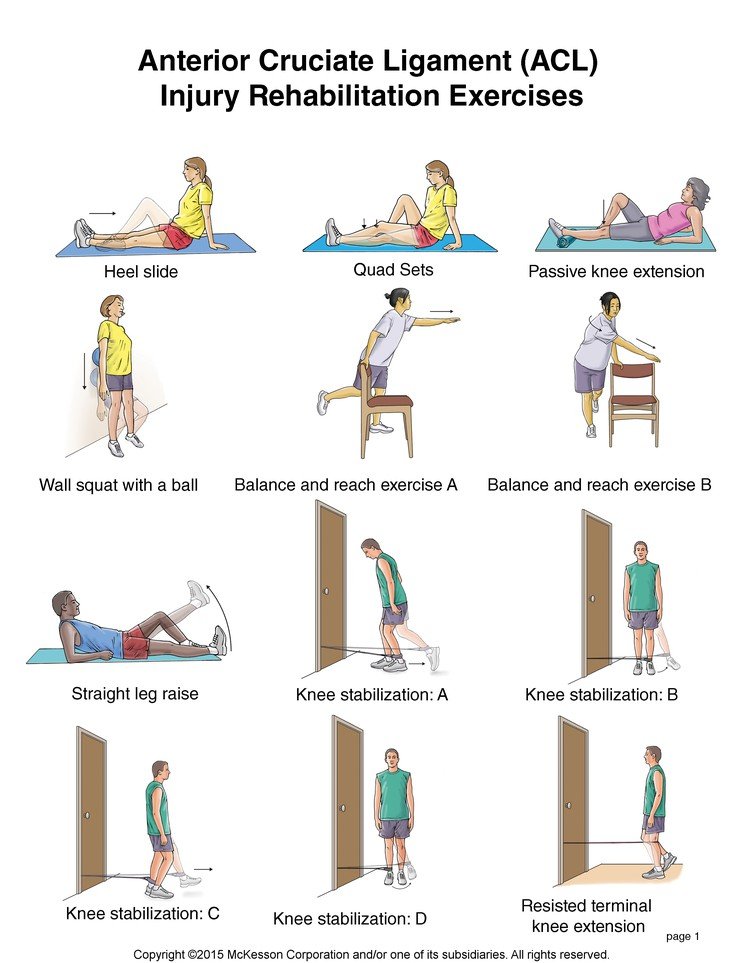
Figure: Performing active exercise by a patient with ligament injury.
Active exercises can include active range of motion, like self-stretching, or general exercises where you get your muscles moving, like leg exercises.
Passive Exercise:
These are movements or activities carried out by another person to exercise the patient. Nurse or physiotherapist gives the passive exercises. Passive exercises are given to the patient while sponge bath is given by nurse. It is helpful to prevent deformities
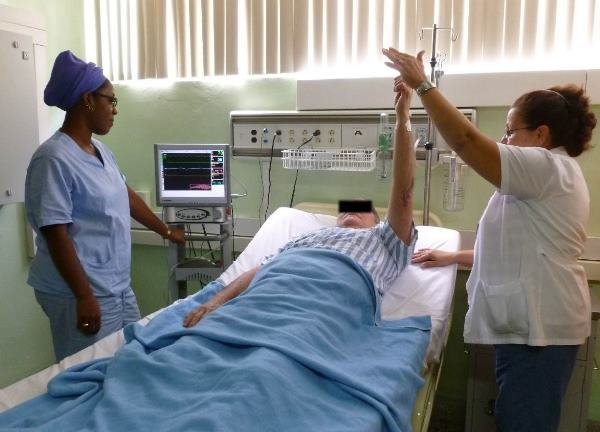
Figure: Nurse helps the patient to perform passive exercise.
Procedure of Performing Active Exercise:
Active exercise performed by a person in daily living can be
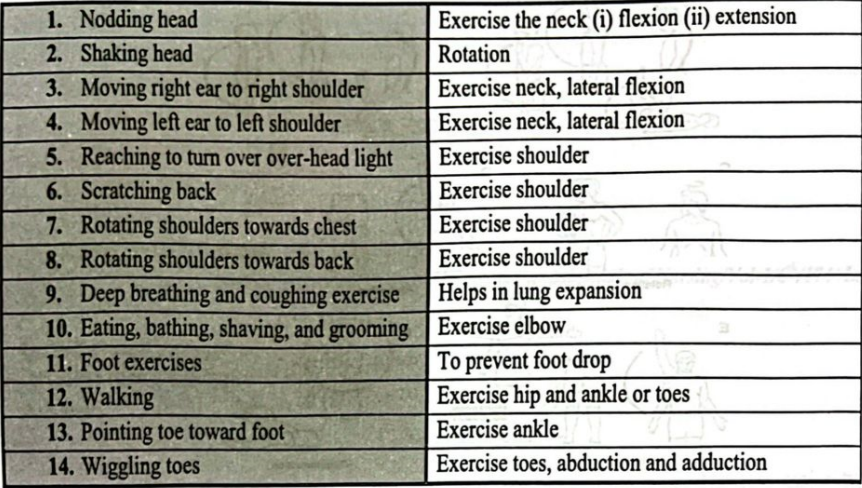
Points to Remember During Exercise
1. Patients should wear loose clothes
2. Room should be well-ventilated.
3. Exercise should be done following doctors order
4. Avoid over-fatigue
5. Avoid chills and draughts
6. Have a fixed time daily for exercises.
REST
Definition of Rest:
Rest is essential for everybody. It does not mean inactivity. People often find a change of activity as relaxing as sitting or lying down. For some, walking, swimming, skating etc, are relaxing. Talking, watching TV, etc. promote rest. Freedom from anxiety is important in rest. Rest means a feeling of peace, relief and relaxation
Sleep:
Sleep is an essential part of our lives and normally, we cieep 8 hours a day. Sleeping is necessary for refreshing body cells. It is essential for growth and repair of body tissues. Discomfort of any kind interferes with a person’s ability to rest and sleep.
Common problems of sleep:
Common problems of sleep:
1. Insomnia (inability to get sleep)
2. Hypersomnia (excessive sleep)
3. Narcolepsy (sudden irresistible sleep attacks)
4. Somnambulism (sleep walking)
5. Enuresis (bed wetting) in children
6. Night terrors are problems of children
Insomnia
It is defined as the inability to sleep.
or
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired
Causes:
1. Discomfort
2. Changes in sleep hours
3. Faulty habits of hygiene
4. Disease conditions
5. Psychological distress such as anxiety, depression, fear and worries.
Nursing Measures to Prevent Insomnia and To Promote Sleep
1. Administer analgesics or sedatives about 30 minutes before bed-time, if ordered.
2. Encourage patients to wear clean loose fitting clothes
3. Remove irritating substances like bed bugs, wrinkled sheets, drainage tube etc
4. Position the patient in a way that helps him in relaxation
5. Offer a glass of warm milk just before bed time
6. Provide enough warmth to avoid cold
7. Warm bath can be given in the evening 8. Provide a light meal in the evening
9. Protect the patient from loud noises, light, odour and dirt
10. Complete all nursing procedures before bed time
11. Keep bed linen clean and dry
12. Provide a comfortable bed
13. Relieve fear and anxieties of the patient by proper explanation
14. Remain with the patient till he sleeps
15. Help him do his daily prayers
16. Reading at bed time will induce sleep.
17. Make him pass urine before sleep
18. Keep necessary conversation at low levels during right
19. Some prefer light music to induce sleep.
