Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
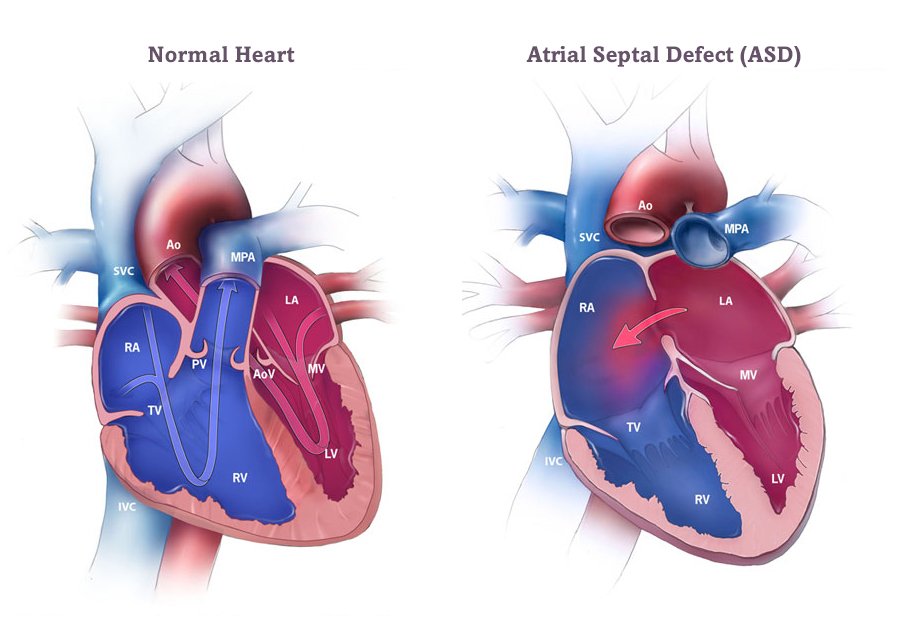
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
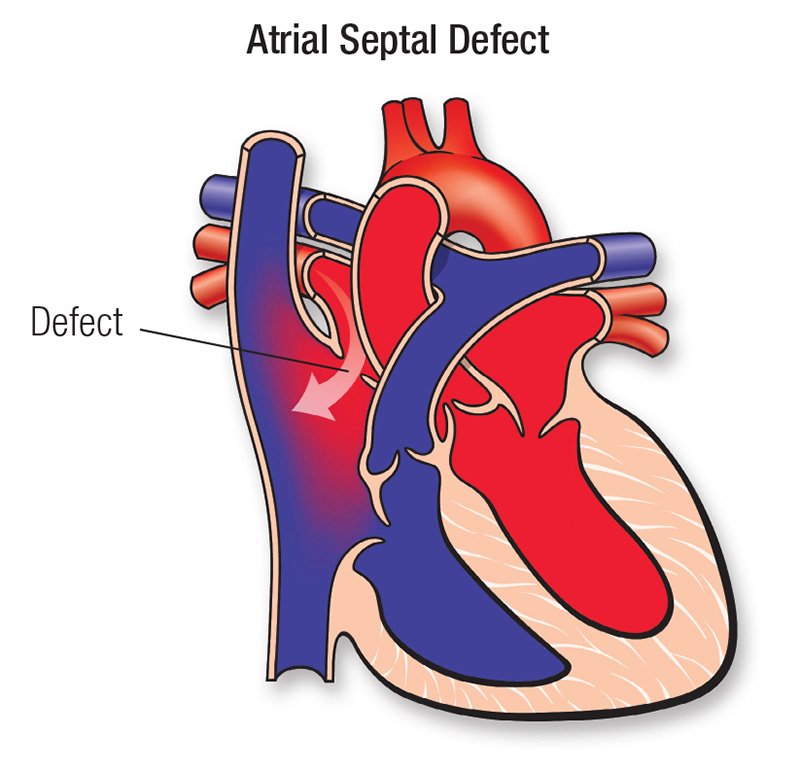
Definition of ASD
It is one of the most common congenital heart defects & occurs twice as frequently in female.
Types
Ostium secundum defects
- Most common.
- It involves the fossa ovalis which in utero was the foramen ovale.
Ostium primum defects
- Result from a defect in the atrioventricular septum and are associated with a’cleft mitral valve’ (split anterior leaflet).
Clinical Features
Symptoms
- Usually asymptomatic until third or fourth decades.
- Exertional dyspnoea.
- Fatigue.
- Palpitations.
- If pulmonary hypertension – Cyanosis, clubbing and features of heart failure.
Sign’s
- Prominent right ventricular impulse – Left parasternal heave.
- Wide fixed splitting of second heart sound (S2).
- Systolic flow murmur in pulmonary area.
- Diastolic flow murmur in tricuspid area.
Investigations
ECG
- Incomplete RBBB.
- Left axis deviation in osteum primum defect.
Chest X-ray P/A view
- Increased pulmonary vascular markings
- Prominence of right atrium, righ ventricle and main pulmonary artery.
Echocardiography
- RA, RV and pulmonary artery enlargement
- Doppler echo demonstrates abnormal turbulent flow through it.
Treatment
- Surgical closure or transcatheter device closure.
- Closure is contraindicated with significant pulmonary hypertension.
- Medical management includes antiarrhythmic therapy for associated atrial fibrillation or supraventricular tachycardia, and treatment of heart failure if developed.
(Ref by-M.R. Khan-290/4h+Davidson’s -633/22)