Autoimmune diseases-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Autoimmune diseases
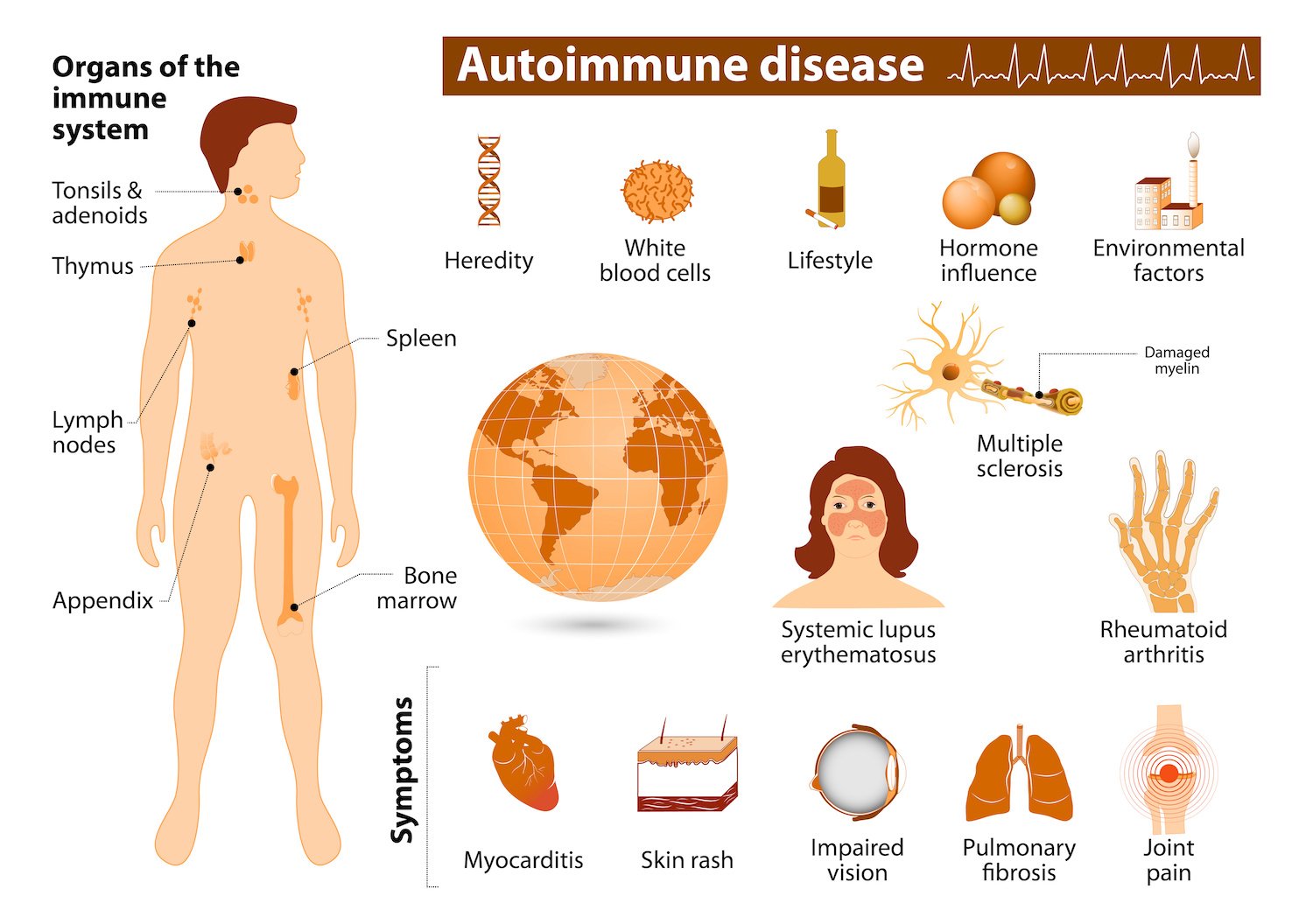
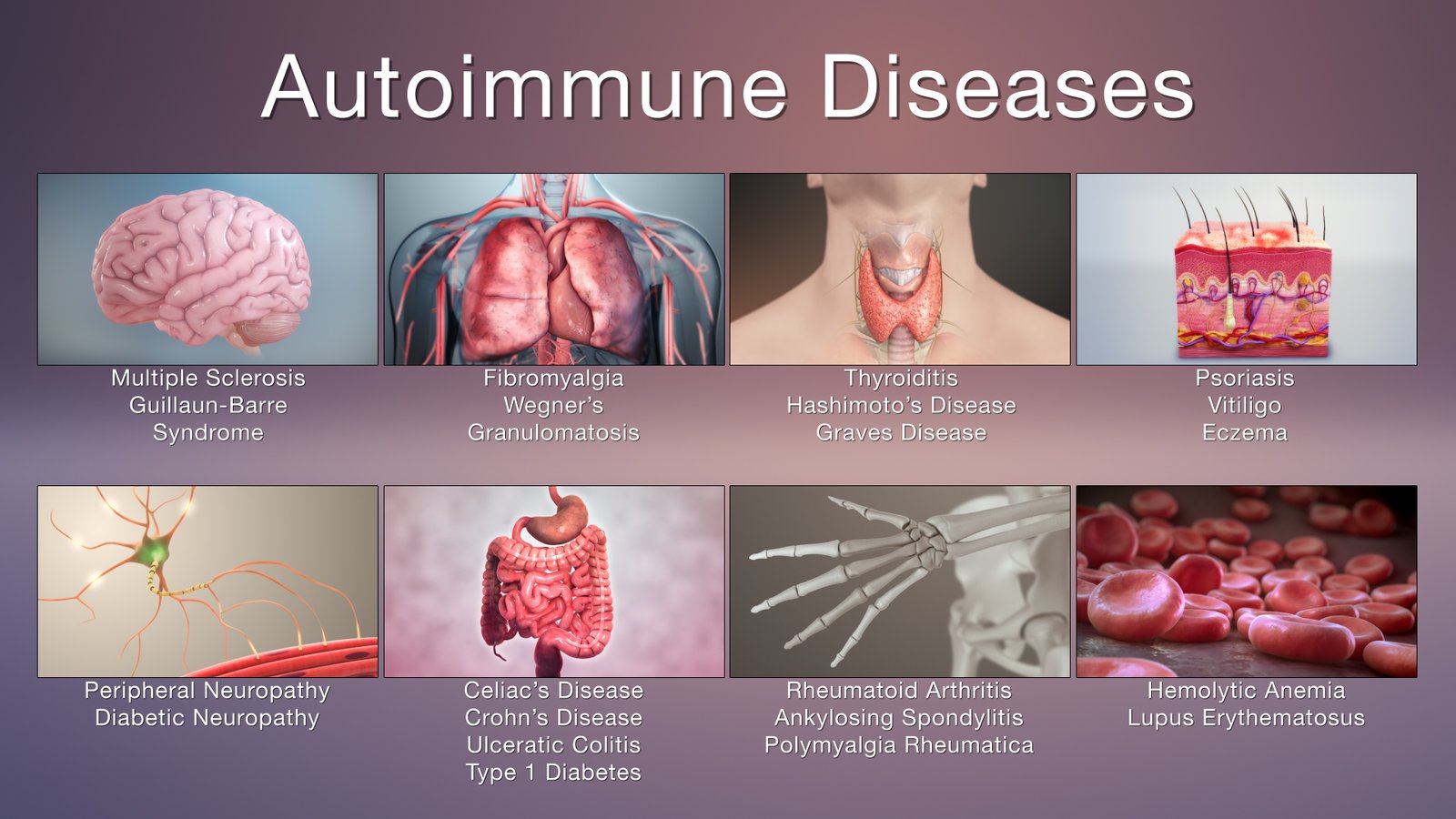
Autoimmune diseases are those produced by failure of the immune system to recognize and tolerate self-antigens. This failure results in the activation of autoreactive T cells and the production of autoantibodies by B cells, causing inflammation and organ damage
There are over 40 known or suspected autoimmune diseases that affect 5% to 7% of the population. Two-thirds of those affected are women.
The most common autoimmune diseases are:-
- Rheumatoid arthritis,
- Type I diabetes mellitus,
- Multiple sclerosis,
- Graves’ disease,
- Glomerulonephritis,
- Thyroiditis,
- Pernicious anemia,
- Psoriasis, and
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Some common disorders and common termrminology of Lymphatic system & Immunity
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): is a condition in which a person experiences a telltale assortment of infections due to the progressive destruction of immune system cells by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AIDS represents the end stage of infection by HIV. A person who is infected with HIV may be symptom-free for many years, even while the virus is actively attacking the immune system.
Allergic Reactions: A person who is overly reactive to a substance that is tolerated by most other people is said to be allergic. Whenever an allergic reaction takes place, some tissue injury occurs. The antigens that induce an allergic reaction are termed allergens.
Common allergens include certain foods (milk, peanuts, shellfish, eggs), antibiotics (penicillin, tetracycline), vaccines (pertussis, typhoid), venoms (honeybee, wasp, snake), cosmetics, chemicals in plants such as poison ivy, pollens, dust, molds, iodine-containing dyes used in certain x-ray procedures, and even microbes.
Anaphylactic shock: In anaphylactic shock, which may occur in a susceptible individual who has just received a triggering drug or been stung by a wasp, wheezing and shortness of breath as airways constrict are usually accompanied by shock due to vasodilation and fluid loss from blood. Injecting epinephrine to dilate the airways and strengthen the heartbeat usually is effective in this life-threatening emergency.
Autoimmune diseases: are those produced by failure of the immune system to recognize and tolerate self-antigens. This failure results in the activation of autoreactive T cells and the production of autoantibodies by B cells, causing inflammation and organ damage.
Lymphomas: (lim-FO=mas; lymph-=clear water; -oma tumor) are cancers of the lymphatic organs, especially the lymph nodes. Most have no known cause. The two main types of lymphomas are Hodgkin disease and non- Hodgkin lymphoma.
