Today our topic of discussion is ” Autonomic Reflexes and Homeostasis “. In the bustling theatre of the human body, with every organ playing its part, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) stands out as the conductor, ensuring harmony and balance. The magic wand of the ANS, ensuring this equilibrium, is its capacity to govern autonomic reflexes and maintain homeostasis. Dive with us into this intricate symphony to understand how the ANS seamlessly achieves this.
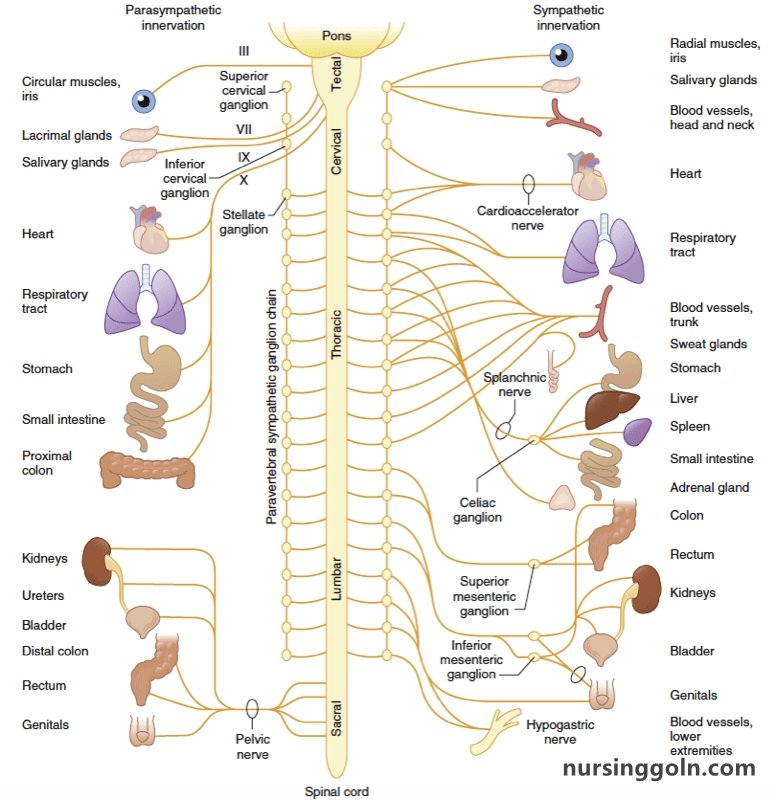
Autonomic Reflexes and Homeostasis: The Autonomic Nervous System
1. Unveiling Homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to keep its internal environment relatively stable, irrespective of external changes. From temperature to blood pressure, countless variables need regulation, and it’s the ANS that oversees this monumental task.
2. Autonomic Reflexes: The ANS Responds
Autonomic reflexes are immediate, involuntary responses orchestrated by the ANS to internal or external stimuli. These reflex arcs often involve sensory input, central processing in the brain or spinal cord, and an effector response. These reflexes are pivotal for homeostatic regulation.
3. The Baroreceptor Reflex: A Case Study
A classic example of an autonomic reflex is the baroreceptor reflex, which maintains blood pressure:
- Sensory Input: Baroreceptors, specialized nerve endings located in major arteries, sense changes in blood pressure.
- Central Processing: The brainstem receives this sensory input and integrates the information.
- Effector Response: The ANS modulates heart rate and blood vessel diameter to adjust blood pressure accordingly.
4. Thermoregulation: Balancing Body Temperature
The ANS plays a critical role in ensuring our body temperature remains stable:
- Cooling Mechanisms: In hot environments, the ANS activates sweat glands and dilates skin blood vessels to dissipate heat.
- Warming Mechanisms: In cold conditions, the ANS constricts skin blood vessels and induces shivering to generate heat.

5. The Chemical Balance: pH and Gas Regulation
To ensure metabolic processes run optimally, the ANS, in partnership with the respiratory and renal systems, maintains pH balance and regulates oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Chemoreceptors detect changes in these parameters and elicit autonomic responses like altering breathing rate.
6. Digestive Reflexes
Digestion is a ballet of coordinated movements and secretions, guided by the ANS:
- Gastrocolic Reflex: After eating, this reflex initiates bowel movements to make space for incoming food.
- Enterogastric Reflex: When the duodenum detects too much acidity or distension, this reflex reduces stomach emptying to prevent overloading.
7. Autonomic Dysreflexia: When Reflexes Go Awry
In conditions like spinal cord injuries, autonomic reflexes can malfunction. Autonomic dysreflexia involves an excessive reflexive response to stimuli, resulting in dangerous blood pressure spikes. Understanding this emphasizes the importance of regulated autonomic reflexes.
8. Maintaining Fluid Balance
Via osmoreceptors, the ANS detects changes in blood osmolarity (indicative of hydration status). If dehydration is sensed, the ANS prompts the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to conserve water and triggers thirst.
9. The Enteric Division: A Special Mention
Often dubbed the “second brain,” the enteric nervous system manages gastrointestinal homeostasis. From motility to enzyme secretion, it ensures the digestive system operates in harmony with the body’s needs.

10. Future Insights: Modulating Autonomic Reflexes
Emerging research explores novel ways to harness the power of autonomic reflexes. For instance:
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Electrically stimulating the vagus nerve has shown promise in conditions like epilepsy and depression.
- Biofeedback: This technique teaches individuals to consciously control certain autonomic functions, offering therapeutic benefits.
11. Conclusion: The Unseen Maestro at Work
As we journey through daily life, facing its ups and downs, our bodies are in a constant dance of adjustment, thanks to the ANS. Autonomic reflexes and homeostasis, while perhaps clinically cold terms, embody the body’s profound commitment to balance and survival. Recognizing the grandeur of these mechanisms, we not only appreciate the unseen maestro within us but also glimpse into the frontiers of medical interventions that could redefine human well-being.
