Bacterial Cell Wall – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Bacterial Cell Wall
Cell wall is an important structure of a bacterium. It gives shape, rigidity and support to the cell.
or
The layers of the cell envelope of bacteria lying outside the cytoplasmic membrane and inside the bacterial capsule (in capsulated bacteria) are collectively called ‘cell wall’.
Functions of Cell Wall:
- Give rigid support
- Protects against osmotic pressure
- It is the site of action of penicillins, cephalosporins and is degraded by lysozyme.
- In Gram negative bacteria, lipopolysaccharide of outer membrane acts as endotoxin.
Types of Bacterial Cell Wall:
On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group e.g. Gram -Positive and gram negative.
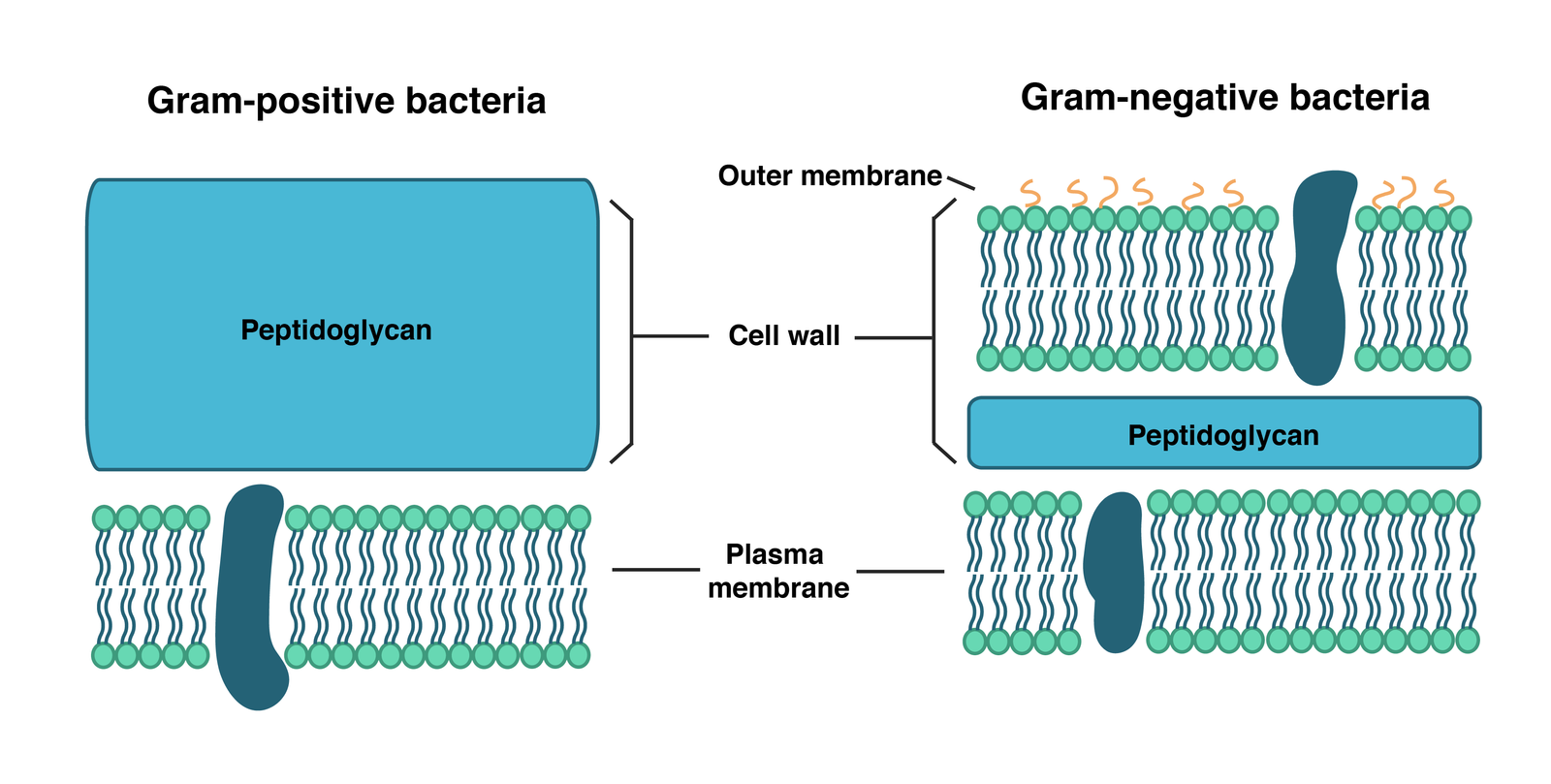
Gram positive cell wall – Cell wall composition of gram positive bacteria.
- Peptidoglycan
- Lipid
- Teichoic acid
Gram negative cell wall – Cell wall composition of gram negative bacteria
- Peptidoglycan
- Outer membrane
✓ Lipid
✓ Protein
✓ Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
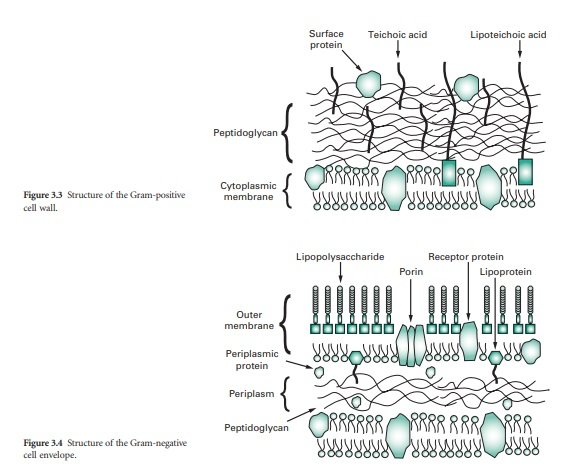
Structure/Composition of Cell Wall of Gram Positive Bacteria:
- Peptidoglycan layer (Murein)
- Teichoic acid
- Teichorunic acid
Structure/Composition of Cell Wall of Gram Negative Bacteria:
- Peptidoglycan (Murein).
- Lipoprotein.
- Phospholipid bilayer with proteins of different functions.
- Periplasmic space.
- Lipopolysaccharide of outer membrane
✓ Lipid-A
✓ Polysaccharide (antigen O)
Difference between Gram positive & Cram negative cell wall:
| Traits | Cell wall of Gram positive bacteria | Cell wall of Gram negative bacteria |
| Peptidoglycan | Thicker; many layers (30-40 layers) | Thinner, single layer |
| Teichoic acids & teichorunic acid | Present | Absent. |
| Outer membrane (lipopolysaccharide) | Absent. | Present |
| Periplasmic space | Absent. | Present |
| Gram staining | Violet | Red |
| Sensitivity to cell wall inhibiting antibiotics | More sensitive | Less sensitive |
