Basic Human Needs & Human Rights – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Basic Human Needs & Human Rights
Q. What do you understand by basic need?
Q. Define basic human needs. (DU-18, 09/ SUST-12)
Answer:
Definition of Basic Human Need:
“Basic human needs” refers to those fundamental requirements that serve as the foundation for survival. Access to the basic needs of life, including shelter, food, and clothing is necessary to the development of a strong community and a necessary precursor to individual self-sufficiency.
or
According to Abraham Maslow “Basic human needs as a hierarchy, a progression from simple physical needs to more complex emotional needs”
or
A basic human need is want of something of requirement for biological psychological, social or spiritual functioning experienced by a person without which a person cannot survive.
or
Basic human need is something that is essential to the emotional and physiological health and for survival of human.
Q. Describe the five categories of Maslow’s hierarchy needs. (DU-19, 17, 16, 14).
Q. Mention the basic human needs.
Q. What are the basic human needs? (BNMC-2023, 22, 21)
Q. Write the categories of Maslow’s Hierarchy needs. (BNMC-2019, 2020,)
Q. What are the human basic needs? Describe the Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs pyramid. (BNMC-20121)
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Basic Human Needs:
Abraham Maslow developed the Hierarchy of Needs model in 1940-50s USA, and the Hierarchy of Needs theory remains valid today for understanding human motivation, management training, and personal development According to Maslow, five categories of human needs are identified and arranged in order of importance from those essential for physical survival to those necessary to develop a person’s fullest potential.
The five categories of human needs are:
1. Physiological needs: Needs for air, nutrition, water, elimination, thermoregulation and sex.
2. Safety and security needs: Need for shelter and freedom from harm and danger.
3. Love and belonging needs (social affiliation): Need for affection feelings of belongingness and meaningful relations with others.
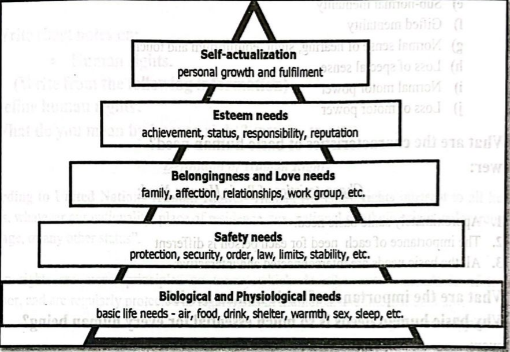
Figure: Maslow’s hierarchy needs.
4. Self-esteem needs: Need to be well thought of by oneself and others.
5. Self-actualization needs: Need to be self-fulfilled, learn, create, understand and experience one’s potential.
Q. Write down the factors which may affect basic human needs.
Q. What are the responsible factors which may affect basic human need?
Answer:
Factors That Affect Basic Needs:
A. Age: New born, child youth, adult, middle aged, aged and dying.
B. Temperament, emotional state, passing mood:
a) Normal or
b) Euphoric and hyperactive
c) Anxious fearful, agitated or hysterical or
d) Depressed and hypoactive
C. Social or cultural status: A member of a family unit with friend and status, or a person relatively along and maladjusted and hypoactive.
D. Physical and intellectual capacity.
a) Normal weight
b) Underweight
c) Overweight
d) Normal mentality
e) Sub-normal mentality
f) Gifted mentality
g) Normal sense of hearing, sight, equilibrium and touch
h) Loss of special sense
i) Normal motor power
j) Loss of motor power
Q. What are the characteristics of basic human need?
Answer:
Characteristics of Basic Human Need:
1. Approximately same basic need.
2. The importance of each need for each person is different
3. All the basic needs are interconnected and interactive.
Q. What are the importance of basic human needs?
Q. Why basic human needs is so much essential for every human being?
Answer:
Importance/Significance of Basic Human Needs to Nursing:
1. To identify clients, unmet needs
2. To realize and understand clients words and behaviors.
3. To predict clients unspoken needs
4. To collect clients data comprehensively in case of missing
5. To put clients nursing problems in adequate order.
Q. Mention the pathologic factor which modifies basic needs.
Q. Name some pathologic or disease condition which may affect basic needs.
Answer:
Pathological State Which Modifies Basic Needs:
1. Marked disturbances of fluid and electrolytic balance including starvation state, pernicious vomiting and diarrhea
2. Shock
3. Disturbance of consciousness fainting coma, delirium.
4. Exposure to cold and heat causing markedly abnormal body temperature.
5. Acute febrile states
6. A local injury, wound and infection
7. A communicable disease condition
8. Pre-operative state
9. Post-operative state
10. Immunization from disease or prescribed as treatment
11. Persistent or intractable pain.
Q. Write short notes on:
• Human rights. (Write from the following information)
Q. Define human rights?
Q. What do you mean by human right? (DU- Jan 17, 14)
Answer:
Definition of Human Right:
According to United Nations Human Rights “Human rights are rights inherent to all human beings, whatever our nationality, place of residence, sex, national or ethnic origin, color, religion, language, or any other status”.
or
Human rights are moral principles or norms, which describe certain standards of human behavior, and are regularly protected as legal rights in municipal and international law.
or
Human rights is the basic rights and freedoms to which all humans are considered to be entitled, often held to include the rights to life, liberty, equality, and a fair trial, freedom from slavery and torture, and freedom of thought and expression.

Q. State the types of human rights? (CU-17, 12, 11)
Q. What are the rights of human?
Q. List the types of human rights.
Answer:
Types of Human Rights:
The idea of personal right is related to concern and respect for the individual member of society. There are three types of human rights.
1. Welfare rights (Legal right): Welfare rights are rights based on a legal entitlement to some good or benefit. These rights are guaranteed by law
2. Ethical rights (moral rights): Ethical rights are rights that are based on a moral or ethical principle.
3. Option rights: Option rights are based on the belief in the dignity and freedom of human SC Beings. Gadi vidual rights are associated with a number of concerns. Human rights become an issue or problem when the situation may arise in which an individual is in conflict with the rights of society.
Some examples of human rights include:
- The right to life.
- The right to liberty and freedom.
- The right to the pursuit of happiness.
- The right to live your life free of discrimination.
- The right to control what happens to your own body and to make medical decisions for yourself
Q. How will you collect data from a new patient followed by Gordon’s functional health pattern?
Q. Describe the ways or techniques of data collection through using Gordon’s functional health pattern
Answer:
Ways to Collect Data from a New Patient Followed by Gordon’s Functional Health Pattern
1. Health perception and health management pattern:
- How does the person describe her/his current?
- What does the person do to improve or maintain her/his health?
- What does the person know about links between lifestyle choices and health?
- How big a problem is financing health for this person?
- Can this person report the names of current medications she/he is taking and their purpose?
- If this person has allergies, what does she/he do to prevent problems?
- What does this person know about medical problems in family?
- Have there been any important illnesses or injuries in this person’s life?
2. Nutritional metabolic pattern:
- Is the person well nourished?
- How do there person’s food choices complete with recommended food intake?
- Does the person have any disease that affects nutritional – metabolic function?
3. Elimination Pattern:
- Are the person’s excretory function’s within the normal range?
- Does the person have any diseases of the digestive system, urinary system or skin?
4. Activity & Exercise Pattern:
- How does the person describe her/his weekly patter of activity and leisure, exercise and recreation?
- Does the person have any disease that affects her/his cardio-respiratory system or musculoskeletal system?
5. Cognitive cor perceptual pattern:
- Does the person have any sensory deficits? Are they corrected?
- Can this person express his/herself clearly and logically?
- How educated is this person?
- Does the person have any disease that affects mental or sensory functions?
- If this has pain, describe it and its causes.
6. Sleep & Rest Pattern:
- Describe this person’s sleep wake cycle.
- Does this person appear physically rested and relaxed?
7. Self-Perception & Self Concept Pattern:
- Is there anything unusual about this person’s appearance?
- Does this person seem comfortable with her/his appearance?
- Describe this person’s feeling state.
8. Role Relationship Pattern
- How does this person describe his/her verities roles in life?
- Has, or does this person now have positive role models for these roles?
- Which relationships are important to this person at present?
9. Sexual Reproductive Pattern:
- Is this person satisfied with her/his situation related to sexually?
- How have the person’s plans and experience matched his/her goals regarding having children?
- Does this have any disease /dysfunction of reproductive -system?
10. Pattern of Coping & Stress Tolerance
- How does this person usually cope with problems?
- Does this action help or make things worse?
- Has this person had any treatment for emotional distress?
11. Pattern of Values & Beliefs :
- What principles did this person learn as a child that is still important to her/him?
- Does this person identify with any cultural, ethnic, religious or other groups?
- What support system does this currently have?
Q. What are the human response to health and illness?
Q. State the Gordon’s 11 functional health pattern of human responses. (RU-13, 12)
Q. Write down the factors/ human responses that may affect health and illness.
Answer:
Gordon’s 11 Functional Health Pattern Of Human Responses:
Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns is a method develops By Marjorie Gordon in 1987 proposed functional health patterns as a guide for establishing a comprehensive nursing data base. By using these categories it’s possible to create a systematic and standardized approach to data collection, and enable the nurse to determine the following aspects of health and human function:
Gordon’s 11 Functional Health Patterns are-
1. Health Perception Health Management Pattern
2. Nutritional Metabolic Pattern
3. Elimination Pattern
4. Activity Exercise Pattern
5. Sleep Rest Pattern
6. Cognitive-Perceptual Pattern
7. Self-Perception-Self-Concept Pattern
8. Role-Relationship Pattern
9. Sexuality-Reproductive pattern
10. Coping-Stress Tolerance Pattern
11. Value-Belief Pattern
Q. List the basic concepts relevant to nursing. (DU-Jan 19)
Answer:
Basic Concepts Relevant to Nursing:
1. Person,
2. Environment,
3. Health, and
4. Nursing
