Today our topic of discussion is ” Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System “. The nervous system, a sophisticated network of nerves and cells, acts as the command center of the human body. Its intricate web not only processes sensory information but also regulates all voluntary and involuntary actions. Dive deep into the fundamental structure and functionality of this system, unraveling the mysteries of the human body’s communication hub.

Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System: The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
1. Introduction: The Nervous System as the Body’s Control Center
At its core, the nervous system dictates the orchestra of human physiology. It processes external stimuli, deciphers internal signals, and governs the body’s responses, ensuring harmony within.
2. Division of the Nervous System
Broadly, the nervous-system bifurcates into:
- Central Nervous-System (CNS): Encompassing the brain and spinal cord, the CNS is the primary control center.
- Peripheral Nervous-System (PNS): Consisting of nerve fibers outside the CNS, the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
3. Cells of the Nervous System
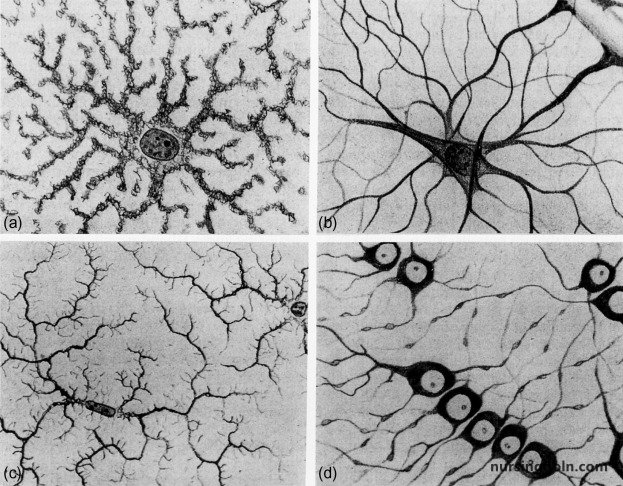
The building blocks of this system are neurons and neuroglia:
- Neurons: The primary transmitters of electrical impulses. They consist of a cell body (soma), dendrites (receiving ends), and an axon (transmitting end).
- Neuroglia (Glia): Supportive cells that protect, nourish, and insulate neurons. Common types include astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes in the CNS, and Schwann cells in the PNS.
4. Functional Classification of Neurons
Neurons are classified based on their function:
- Sensory (Afferent) Neurons: Transmit signals from sensory receptors to the CNS.
- Motor (Efferent) Neurons: Convey signals from the CNS to muscles or glands.
- Interneurons: Situated within the CNS, they process information and facilitate communication between sensory and motor neurons.
5. The Neuron’s Electrochemical Processes
A neuron communicates via electrical potentials and neurotransmitters:
- Resting Potential: The static state of a neuron, marked by a negative internal charge.
- Action Potential: The “firing” of a neuron, a rapid shift in polarity allowing the transmission of signals.
- Synaptic Transmission: The release of neurotransmitters from one neuron to another across synapses.
6. The CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
The brain, protected by the skull, is the body’s most intricate organ, divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The spinal cord, shielded by the vertebral column, acts as a relay hub and a center for certain reflex actions.
7. The PNS: Connecting the CNS to the Body
The PNS, a vast network of nerves, bridges the CNS with the body’s extremities:
- Cranial Nerves: Twelve pairs that emerge directly from the brain.
- Spinal Nerves: Arise from the spinal cord, branching out to the body.
8. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
A subset of the PNS, the ANS governs involuntary functions:
- Sympathetic Division: Often termed the “fight or flight” system, it prepares the body for stressful situations.
- Parasympathetic Division: Also known as the “rest and digest” system, it conserves energy and oversees routine bodily functions.
9. The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
The BBB is a semipermeable border that protects the brain from harmful substances in the blood. Comprising tight junctions, it allows select molecules to pass.
10. Malfunctions and Disorders of the Nervous System
Like any intricate system, the nervous system isn’t immune to disorders:
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, result from the progressive death of nerve cells.
- Epilepsy: Recurrent seizures due to excessive neuronal activity.
- Multiple Sclerosis: An autoimmune condition targeting the myelin sheath of neurons.
11. The Future of Neuroscience
With advances in research, the understanding of the nervous system continues to grow. Breakthroughs in neuroplasticity, brain-computer interfaces, and neuromodulation promise a revolutionary perspective on neurology and treatment modalities.
Conclusion
The nervous system, in its grandeur, orchestrates the symphony of human existence. Its intricate design and profound functions are a testament to the marvel of human anatomy. Delving into its basic structure and functionality offers a glimpse into the miracles of daily existence, from the simple act of touching to the complex processes of thought and emotion.
