The body cavity-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
The body cavity

Definition:
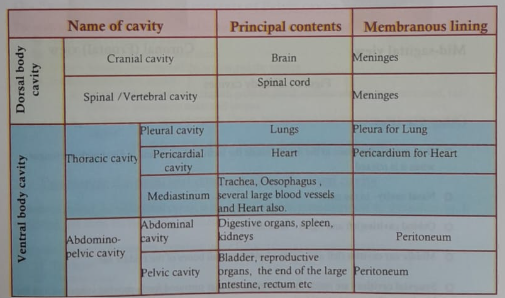
Body cavities are confined spaces in which organs are protected, separated and supported by associated membranes. (See the figure #118) or, Spaces in the body that contain internal organs are called cavities:
Types of body cavities
There are two principal cavities of the human body as the dorsal body cavity (posterior) and Ventral body cavity (anterior), which are again divided into small cavities as follows:
A. Dorsal cavity: Bones of the cranial portion of the skull and vertebral column, toward the posterior (dorsal) side of the body.
a) Cranial cavity: Contains the brain.
b) Spinal cavity: Contains the spinal cord, which is an extension of the brain.
B. Ventral cavity: Anterior portion of the torso, divided by the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity.
a) Thoracic cavity: The chest, contains the trachea, bronchi, lungs, esophagus, heart and great blood vessels, thymus gland, lymph nodes, and nerve, as well as the following smaller cavities
- Pleural cavities: Contains each lung
- Pericardial cavity: Contains the heart
- The mediastinum: The central portion of the thoracic cavity is an anatomical region called the mediastinum. It is between the lungs, extending from the sternum (breastbone) to the vertebral column (backbone), and from the first rnb to the diaphragm, and contains all thoracic organs except the lungs themselves. Among the structures in the mediastinum are the heart, esophagus, trachea, and several large blood vessels
b) Abdominopelvic cavity: An imaginary line running across the hipbones and dividing the body into the abdominal and pelvic cavities
- Abdominal cavity: Contains the stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen. mall intestines, and most of the large intestine
- Pelvic cavity: Contains the end of the large intestine, rectum, internal female reproductive organs, urinary bladder etc
Other Cavities
- Oral cavity-the space in the mouth inside the teeth and gums and is filled with the tongue when it is relaxed.
- Nasal cavity in the nose
- Orbital cavities(left and right)- hold the eyes
- Middle ear cavities (left and right)-hold the small bones of the middle ear
- Synovial cavities are inside the joint capsules that surround freely moving joints (such as the hip, knee, elbow, and shoulder)
(Ref: Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13 ed, P-16)

- The main organs and structures contained in the thoracic cavity are mentioned below-
- The trachea, two bronchi, two lungs
- The oesophagus
- The heart, aorta, superior and inferior vena cava and other blood vessels
- The lymph nodes and lymph vessels
- The nerves
The main organs and structures contained in the abdominal cavity are mentioned below-
- Abdominal part of oesophagus.
- The Stomach, small intestine and most of the large intestine
- The liver, gallbladder and bill ducts.
- The pancreas.
- Two kidneys, Two adrenal (suprarenal) glands and upper part of the ureters
- The spleen.
- Some nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes and lymph vessels
The main organs and structures contained in the Pelvic cavity are mentioned below
- Some loops of the small intestine
- Sigmoid colon, rectum and anal canal
- Urinary bladder, lower part of the ureters and the urethra
- Internal reproductive organs.
- In the male reproductive organs prostate gland, seminal vesicles, spermatic cord, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts and urethra.
- In female reproductive organs- Uterus, rwo fallopian/uterine tubes, two ovaries and vagina
(Ref: Stuart Ira Fox, Human physiology – 12th ed)
The mediastinum, or mediastinal cavity, is the central visceral compartment of the thoracic cavity. It completely separates the two pleural cavities
The main organs and structures contained in the Pelvic cavity are menhoned below
- The heart
- Thymus gland
- Portions of the esophagus
- Portions of the trachea
- Aortic arch
- Superior vena cava
- Some nerves and lymph nodes
- etc
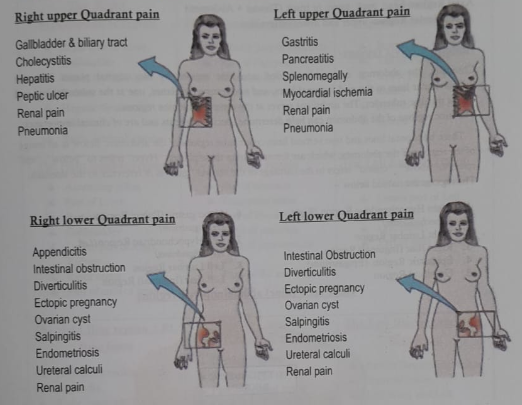
Body Quadrants
Quadrants are another way our bodies are divided into regions for both diagnostic and descriptive purposes. Mainly upperQuadrant and lowerQuadrant then are both are divided into right and left. (See the figure # 1.21)
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
- Right upper Quadrant
- Left upper Quadrant
- Right lower Quadrant
- Left lower Quadrant
List the organs of four quadrants
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
- Right lobe of liver.
- Gallbladder,
- Part of the transverse colon,
- Part of pylorus,
- Hepatic flexure,
- Right kidney, and
- Duodenum.
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
- Left lobe of liver.
- Stomach
- Small intestine,
- Transverse colon
- splemc flexure.
- pancreas
- left kidney and
- spleen.
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
- Ceacum,
- Ascending colon,
- Small intestine,
- Appendix
- Bladder if distended,
- Right ureter,
- Right spermatic duct (men),
- Right ovary and
- Right tube and uterus if enlarged (women)
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
- Small intestine,
- Left ureter
- Sigmoid flexure.
- Descending colon.
- Bladder if distended.
- Left spermatic duct (men)
- left ovary
- Left uterine tube and
- Uterus if enlarged (women)
Possible locations of quadrant pain due to some diseases or disorders