Bone cell – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.
The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Bone cell
There are four major types of cells are present in bone tissue: osteogenic cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
1.Osteogenic cells: are unspecialized stem cells derived from mesenchyme, the tissue from which almost all connective tissues are formed. They are the only bone cells to undergo cell division, the resulting cells develop into osteoblasts. Osteogenic cells are found along the inner portion of the periosteum, in the endosteum, and in the canals within bone that contain blood vessels.
2.Osteoblasts: are bone-building cells. They synthesize and secrete collagen fibers and other organic components needed to build the extracellular matrix of bone tissue. As osteoblasts surround themselves with extracellular matrix, they become trapped in their secretions and become osteocytes. (Note: Blasts in bone or any other connective tissue secrete extracellular matrix.)
3. Osteocytes: mature bone cells, are the main cells in bone tissue and maintain its daily metabolism, such as the exchange of nutrients and wastes with the blood. Like osteoblasts, osteocytes do not undergo cell division. (Note: Cytes in bone or any other tissue maintain the tissue.)
4. Osteoclasts: are huge cells derived from the fusion of as many as 50 monocytes (a type of white blood cell) and are concentrated in the endosteum. They release powerful lysosomal enzymes and acids that digest the protein and mineral components of the bone extracellular matrix.
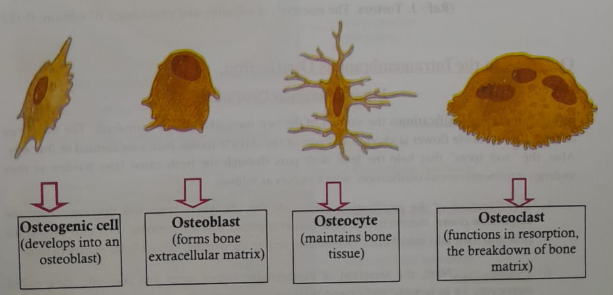
This breakdown of bone extracellular matrix, termed resorption, is part of the normal development, growth, maintenance, and repair of bone. (Note: Clasts in bone break down extracellular matrix.)
