Bone Grafting – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting:
Bone can be transferred for grafting from one area of the body to another to stimulate osteogenesis through the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoprogenitor cells.
[Ref-Apleys//317)
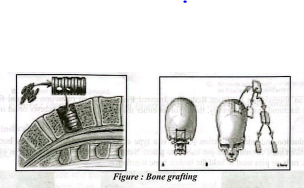
Sites bones are obtained for bone grafting:
Bone can be stored in sterile containers and frozen up to 12 months before use.
1) The ileum.
2) The greater trochanter.
3) Head of the tibia.
4) Ribs.
5) Fibula.
[Ref- Orthopaedic nursing and rehabilitation/9/170)
Riks for grafts from the iliac crest:
1. Acquired bowel herniation (this becomes a risk for larger donor sites (>4 cm)) About 20 cases have been reported in the literature from 1945 till 1989 and only a few hundred cases have been reported worldwide.
2. Meralgia paresthetica (injury to the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve also called Bernhardt-Roth’s syndrome).
3. Pelvic instability.
4. Fracture (extremely rare and usually with other factors.
5. Injury to the clunial nerves (this will cause posterior pelvic pain which is worsened by sitting).
6. Injury to the ilioinguinal nerve.
7. Infection.
8. Minor hematoma (a common occurrence).
9. Deep hematoma requiring surgical intervention.
10. Seroma.
11. Ureteral injury.
12. Pseudoaneurysm of iliac artery (rare).
13. Tumor transplantation.
14. Cosmetic defects (chiefly caused by not preserving the superior pelvic brim).
15. Chronic pain.
Basic requirements for osteogenesis for bone grafting: There are three basic requirement of osteogenesis:
1) Osteoprogenitor cells.
2) A bone matrix.
3) Growth factor.
