Capsule of Bacteria – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
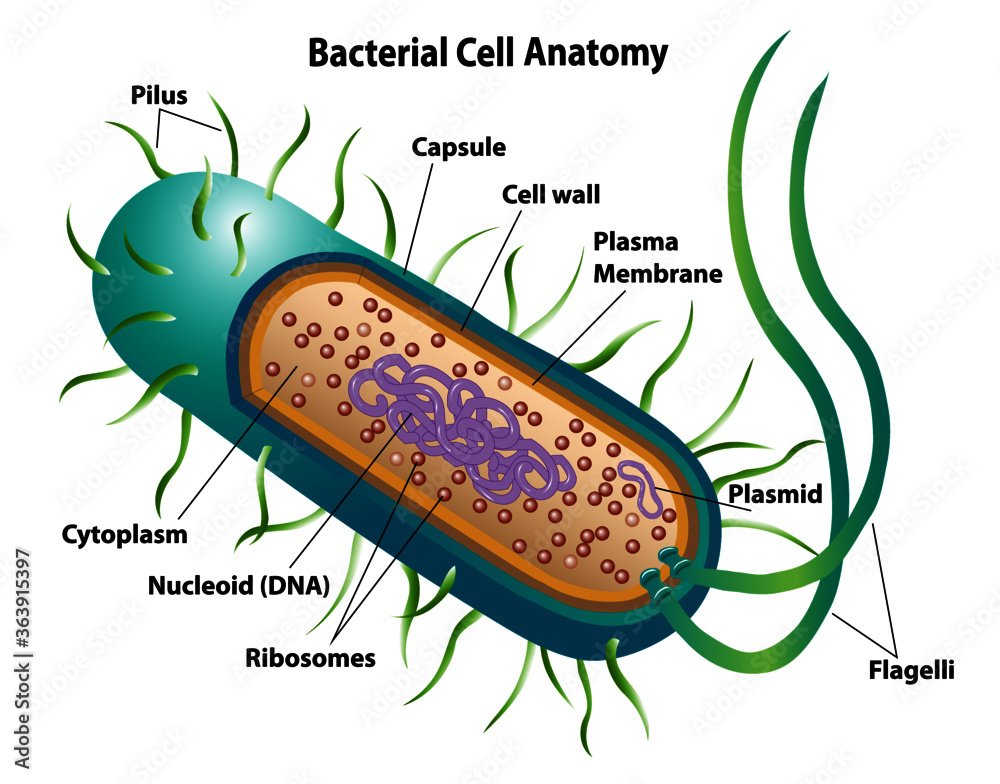
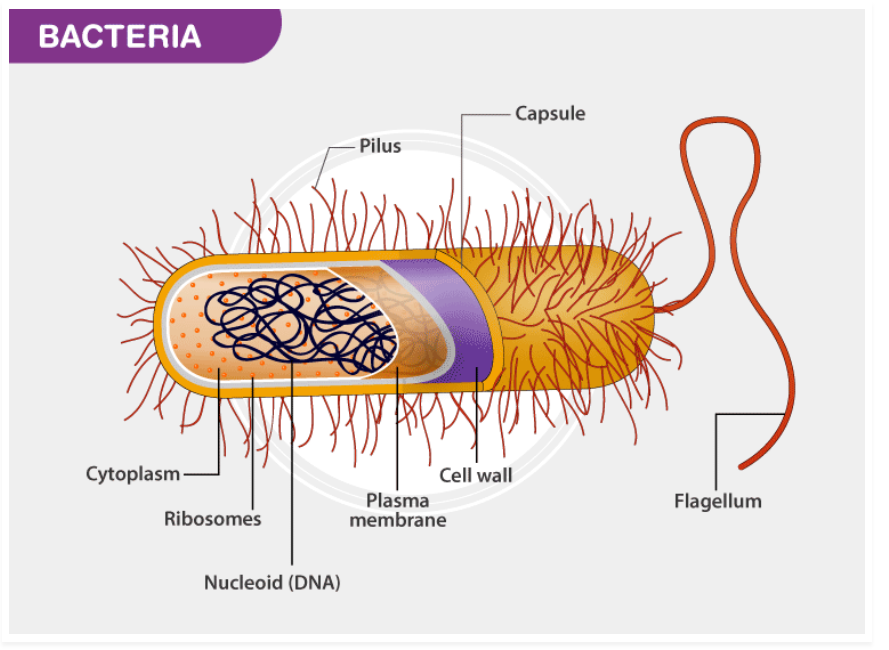
Capsule of Bacteria
The bacterial capsule is a very large structure of many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell.
or
The capsule is a gelatinous layer covering the entire bacterium, situated outer to the cell wall.
Function of Capsule / Role of Capsule in Bacterial Pathogenesis:
- It prevents phagocytosis.
- Adhesion to host cell surface
- Invasiveness.
Importance of bacterial capsule:
The capsule is important for four reasons –
- It is a determinant of virulence of many bacteria, since it limits the abuity of phagocytes to engulf the bacteria. Variants of encapsulated bacteria that have lost the ability to produce a capsule are usually nonpathogenic.
- Specific identification of an organism can be made by using antiserum against the capsular polysaccharide. In the presence of the homologous antibody, the capsule will swell greatly. This swelling phenomenon, which is used in the clinical laboratory to identify certain organisms, is called the Quellung reaction.
- Capsular polysaccharides are used as the antigens in certain vaccines, for they are capable of eliciting protective antibodies. For example, the purified capsular polysaccharides of 23 types of S. pneumoniae are present in the current vaccine.
- The capsule may play a role in the adherence of bacteria to human tissues, which is an important initial step in causing infection.
Importance of Bacterial Capsule as Virulence Factor:
- It prevents phagocytosis.
- Adhesion to host cell surface.
- Invasiveness.
Composition of Bacterial Capsule:
➤ Water: 98%
➤ Solids: only 2% and solids constituent may be complex polysaccharide, polypeptide or hyaluronic acid,
Name of Capsulated Bacteria According to Composition:
Polysaccharide capsule: (most of the capsulated bacteria)
Example:
- Neisseria meningitides
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Bordetella pertussis
- Some strains of staphylococcus.
Polypeptide capsule:
Example:
- Bacillus anthracis
Hyaluronic acid capsule:
Example:
- Streptococcus pyogens.