Caput succedaneum and Cephalohematoma- This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Caput succedaneum and Cephalohematoma
Caput succedaneum
Caput succedaneum is a serosanguineous, subcutaneous, extraperiosteal fluid collection with poorly defined margins.
Or
Caput succedaneum is a neonatal condition involving a serosanguinous, subcutaneous, extraperiosteal fluid collection with poorly defined margins caused by the pressure of the presenting part of the scalp against the dilating cervix (tourniquet effect of the cervix) during delivery.
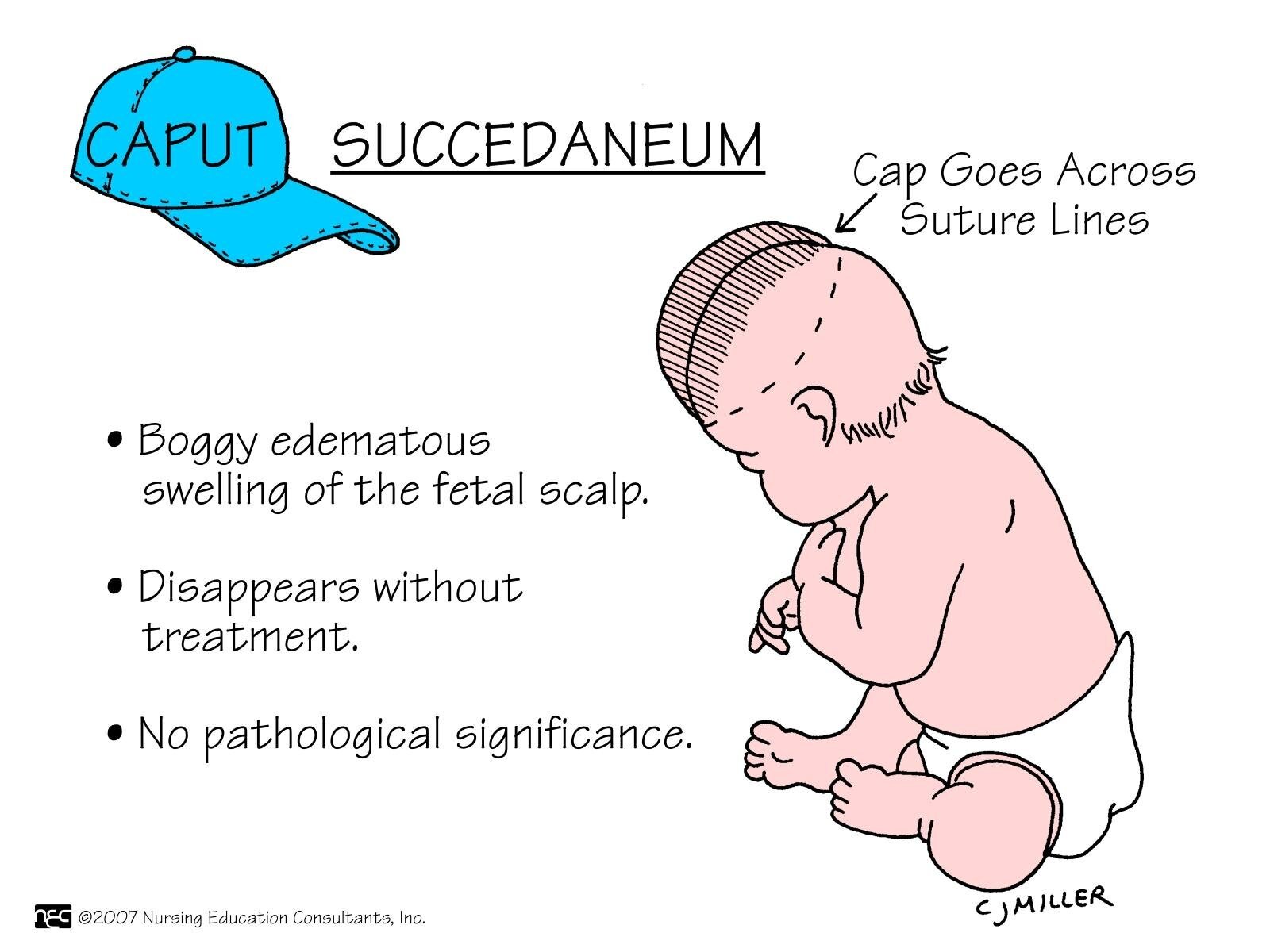
Fig: Caput succedenum
Cephalohematoma
Cephalohematoma is a subperiosteal collection of blood secondary to rupture of subperiosteal veins between the skull and the periosteum.
Or
Cephalohematoma is a traumatic subperiostealhaematoma that occurs underneath the skin, in the periosteum of the infant’s skull bone.
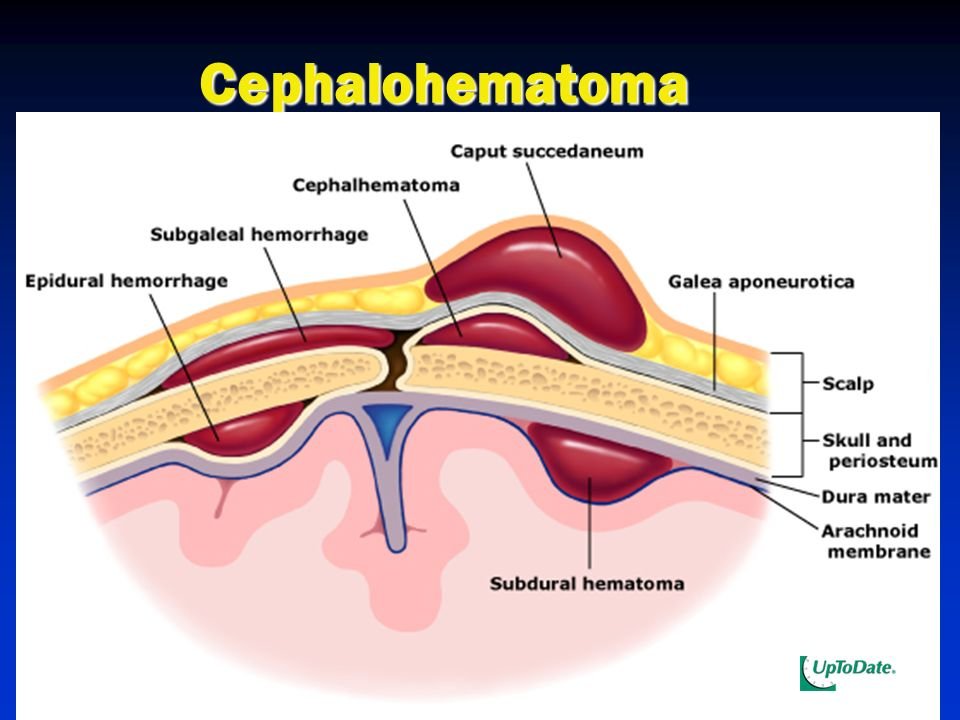
Figure: Cephalohematoma
Difference between caput succedaneum and cephalhematoma
| Points | Caput succedenum | Cephalhematoma |
| 1. Time of appearance | Present at birth | Appear within few hours after birth. |
| 2. Site of collection | Collection of edema fluid between pericranium& scalp tissue. | Collection of blood between skull bone & overlying pericranium- due to rupture of small emissary vein from the skull in normal forceps delivery. |
| 3. Margin | No well defined margin. | Well defined by sutures. |
| 4. Extention | Extends over different bones & may cross suture line. | Limited over single bone & never cross suture line |
| 5. Structure | Soft & pits on pressure. | Non-pitting but soft & elastic. |
| 6. Skin change | Skin echymotic. | No skin change. |
| 7. Related to fracture | No underlying skull bone fracture. | May be skull bone fracture skiagram of skull is necessary. |
| 8. Time of resolve | Completely absorbed within 24 hours. | Absorbed after several weeks or calcified. |
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
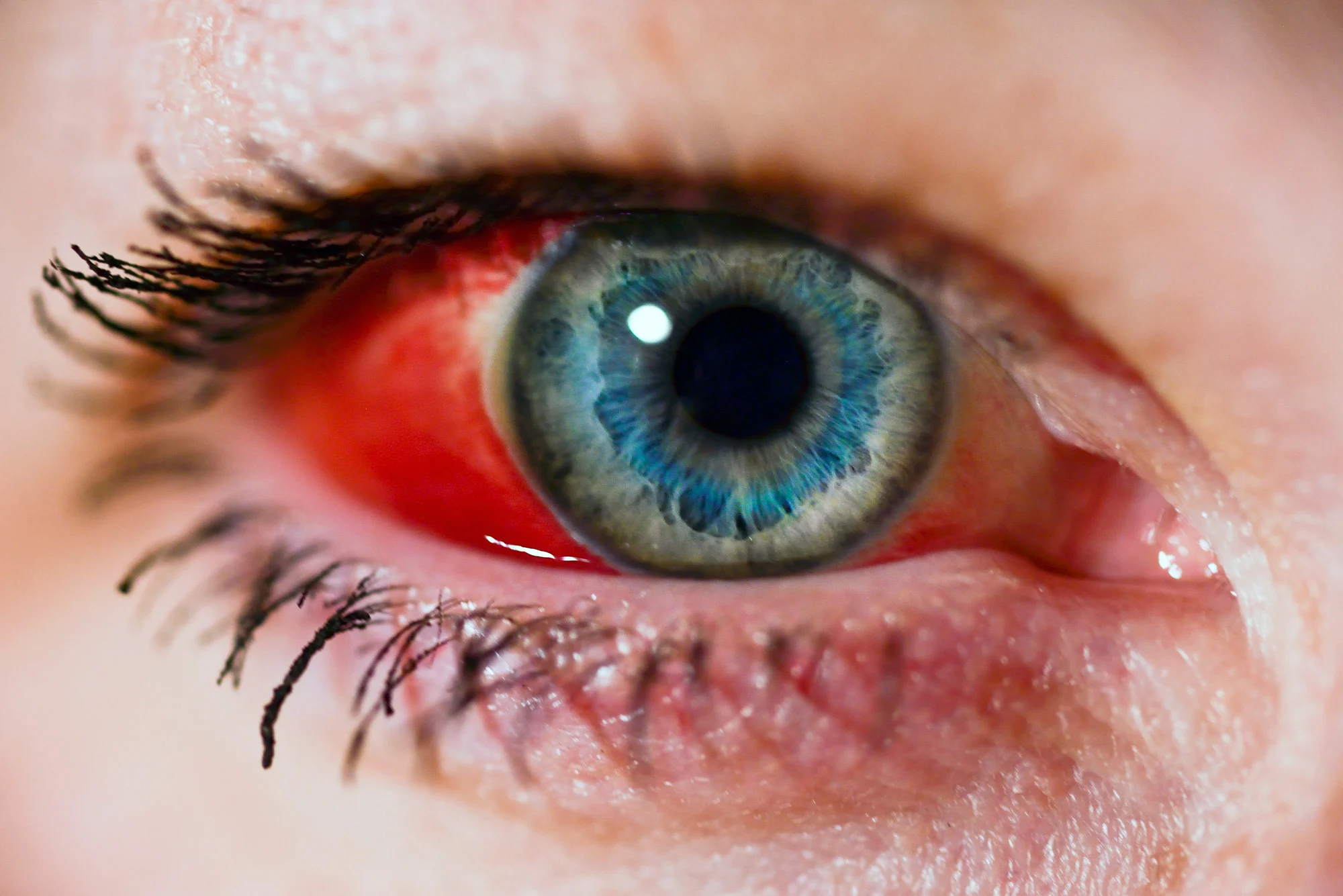
Subconjunctival hemorrhage is a bright red patch appearing in the white of the eye. This condition is one of several disorders called red eye.
Causes
The white of the eye (sclera) is covered with a thin layer of clear tissue called the bulbar conjunctiva. A subconjunctival hemorrhage occurs when a small blood vessel breaks open and bleeds within the conjunctiva. The blood is often very visible, but since it is confined within the conjunctiva, it does not move and cannot be wiped away. The problem may occur without injury. It is often first noticed when you wake up and look in a mirror. Some things that may cause a subconjunctival hemorrhage include:
- Sudden increases in pressure, such as violent sneezing or coughing
- Having high blood pressure or taking blood thinners
- Rubbing the eyes
- Viral infection
- Certain eye surgeries or injuries
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is common in newborn infants. In this case, the condition is thought to be caused by the pressure changes across the infant’s body during childbirth.
