Cervical And Perineal Tear – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Cervical And Perineal Tear
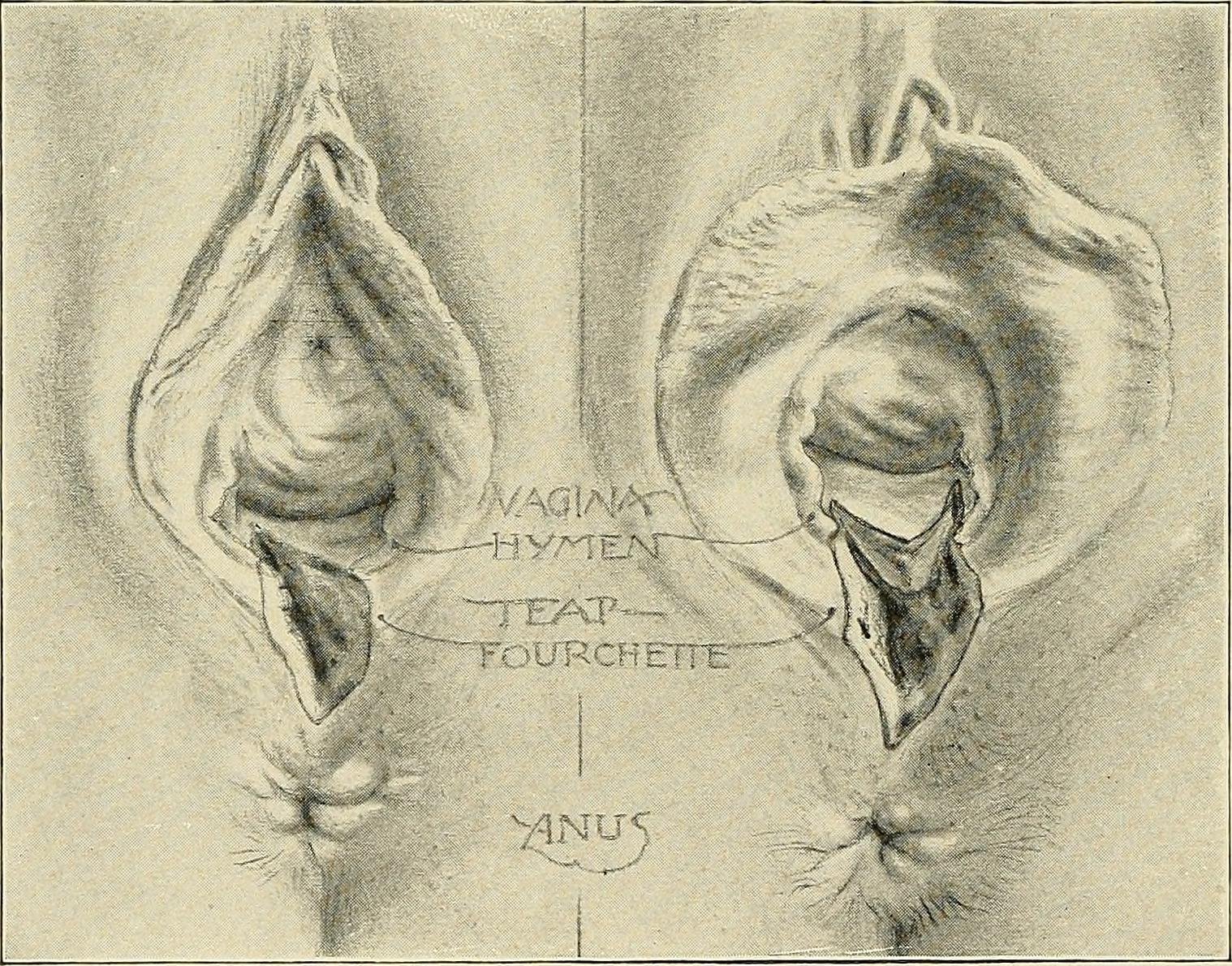
Types of perineal tear
First degree:
Involves lacerations of the remnants of the hymen, the fourchette, lower part of the vagina and the perineal skin but the perineal body’remains intact.
Second degree:
Involves lacerations of the posterior vaginal wall and varying degrees of tear of the perineal body excluding the anal sphincter.
Third degree:
Injury to the perineum involving posterior vaginal wall and tear of the perineal body including the anal sphincter complex (both external and internal anal sphincters) without involvement of the anal canal or even the rectum.
Fourth degree (complete):
Injury to the perineum involving the anal sphincter complex with anal and rectal mucosa.
Causes of perineal tear
A. Over stretching of the perineum: Due to –
a. Large baby.
b. Face-to pubis or face delivery.
c. Outlet contraction with narrow pubic arch.
d. Shoulder delivery (posterior one).
e. Forceps delivery (to accommodate additional space).
B. Rapid stretching of the perineum: Due to –
Rapid delivery of the head during uterine contraction.
- Precipitate labour.
- Delivery of the after coming head in breech.
C. Inelastic perineum:
- Rigid perineum (elderly primigravidae).
- Scar in the perineum, following previous operations (episiotomy or perineorrhaphy and vulval oedema).
Management of 2°/3° perineal tear
Steps of prepair of complete perineal tear:
Recent tear should be repaired immediately following the delivery of the placenta. – If delayed beyond 24 hours, the complete tear should be repaired after 3 months.
Step-1:
- Patient is put in lithotomy position.
- Antiseptic cleaning of the local area is done.
- Repair may be done with local infiltration of 1% lignocaine hydrochloride (10-15ml) or with pudendal block or preferably under general anesthesia.
Step-2:
- The rectal and anal muscles are first sutured from above downwards.
- The rectal muscles including the para rectal fascia are then sutured.
- “The torn ends of the sphincter ani-externus are then reconstructed with a figure of eight stitch.
- End to end sphincter approximation (not overlapping) is done.
Step-3:
- Repair of perianal muscle is done by interrupted sutures.
Step-4:
- The vaginal wall and the perineal skin are opposed by interrupted sutures.

After care:
- A low residual diet consisting of milk, bread egg, biscuits, fish, sweets etc, onwards.
- Lactulose 8 ml 2 times daily beginning on the 2 day and increasing the dose to 15 nd on the 3 day
- Any one of the broad spectrum antibiotics
- Metronidazole 400 mg thrice daily is to be continued for 5-7 days
