Chronic Renal Failure – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Chronic Renal Failure
Definition of CRF:
CRF refers to an irreversible deterioration in renal function which classically develops over a period of years.
Causes of Chronic CRF:
1. Congenital and inherited:
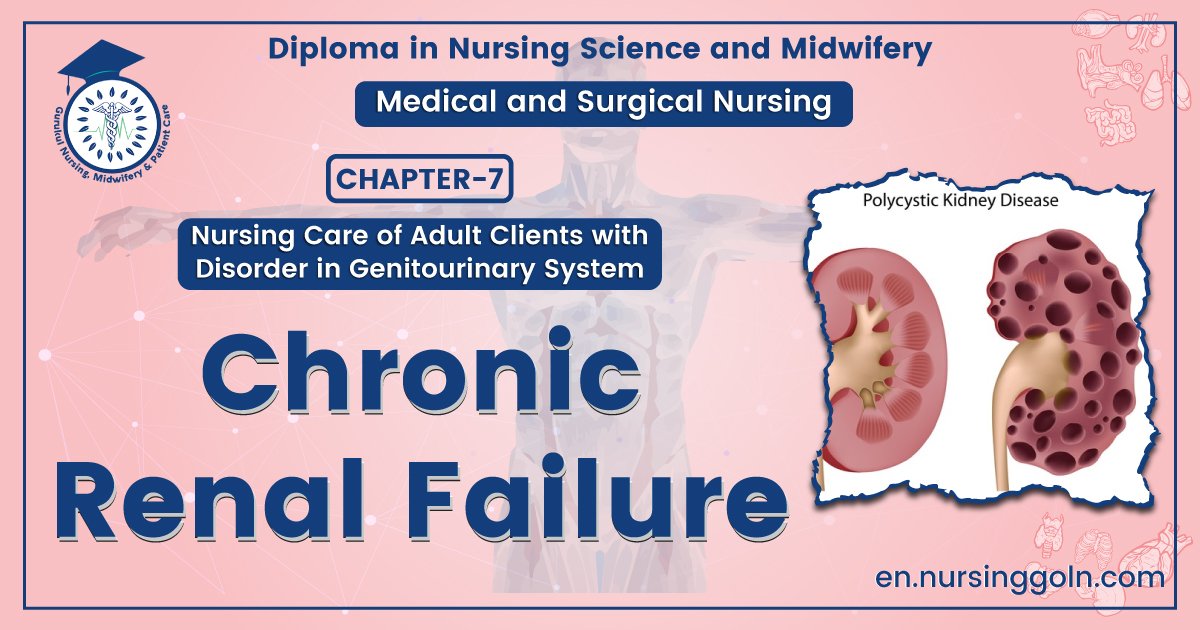
- Adult Polycystic kidney disease (APKD)
- Alport’s syndrome.
2. Vascular disease:
- Renal artery stenosis
3. HTN
4. Glomerular disease:
- IgA nephropathy-most common.
5. Interstitial disease:
- Chronic pyelonephritis
- Reflux nephropathy.
- Analgesic nephropathy.
6. Systemic inflammatory disease:
- SLE
- Vasculitis (PAN).
7. Diabetes mellitus.
8. Amyloidosis.
9. Obstructive uropathy.
10. Unknown.

Clinical Features:
Patients may remain asymptomatic until the GFR is 15 ml/min or less (until 70% nephrons are dead)
➤ Anaemia
➤ Renal osteodystrophy:
- Osteomalacia
- Osteitis fibrosa
- Osteoporosis
- Osteosclerosis
➤Generalized myopathy:
- Muscle cramps
- Restless leg syndrome setawah
➤ Neuropathy:
- Paraesthesia
- Foot drop
➤ Endocrine abnormalities:
- Hypertension
- Atherosclerosis
- Pericarditis
➤ Acidosis:
- Breathlessness
- Deep respirationdolo de
➤Infection:
Urinary tract infection is common Bleeding: Cutaneous ecchymoses and mucosal bleeds (in advanced causes)
➤ Gastrointestinal disorders:
Anorexia followed by nausea and vomiting is commonly seen (especially in the morning)
Stages of Chronic Renal Failure:
Below shows the five stages of CKD and GFR for each stage:
- Stage 1 with normal or high GFR (GFR > 90 mL/min)
- Stage 2 Mild CKD (GFR = 60-89 mL/min)
- Stage 3A Moderate CKD (GFR-45-59 mL/min)
- Stage 3B Moderate CKD (GFR = 30-44 mL/min)
- Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR <15 mL/min)
- Stage 4 Severe, CKD (GFR-15-29 mL/min)

Investigation of CRF:
- Urine for RME, C/S: Volume increase, pH decrease.
- Blood for TC, DC, Hb%, ESR: anaemia
- Total platelet count: Low
- Blood urea creatinine: Raised
- Serum electrolytes: Hyperkalaemia
- X-ray chest and KUB region
- Ultrasonography of KUB region
- CT scan (DTPA/DMSA)
- Renal biopsy (confirmatory)
Management of CRF:
Conservative (Symptomatic):
a) Diet: Restriction of dietary protein to about 40 g/day (0.58 g/kg/d in children) with adequate carbohydrate (250 g) and fat (60 g) to provide an adequate calorie (at least 1700 kcal)
b) Fluid: Fluid restriction if GFR is <5 ml/min or cardiac failure is present.
c) Electrolytes:
- No sodium restriction in absence of oedema, cardiac failure or hypertension.
- Restriction of potassium: Avoid high potassium foods (eg, banana, tomatoes, coffee chocolate)
d) Hypertension and cardiac fallure:
- Hypertension: Antihypertensive drug (eg, ACE inhibitors, Ca-antagonists)
- Cardiac failure: Digoixn
e) Renal osteodystrophy:
- Hypocalaemia: 1 a hydroxyl cholecalciferol 0.25-1 µg/d
- Hyper phosphataemia: Avoid high phosphate food (milk, cheese, eggs) and use of phosphate binding drug –
✓ Calcium carbonate 500 mg with each meal, or
✓Aluminum hydroxide capsules (Alucap) 300-600 mg before each meal..
✔ Parathyroidectomy may be needed.
- Correction of anaemia, infection if present
f) Treatment of pruritus:
- Antihistamine
- UV rays
- Proper skin care + maintenance of hygiene
- Replacement of renal function:
- a) Haemodialysis
- b) Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
- c) Renal transplantation (definitive treatment)
Difference between ARF and CRF:
| Point | ARF | CRF |
| Duration to develop | Within days to weeks | Over period of years |
| Oliguria/anuria | Usually present | Usually not present |
| BP | Hypotension | Hypertension |
| Anemia | Usually absent | Present |
| Hyperkalaemia | Severe | Moderate |
| Reversibility | Usually reversible | Irreversible |
| Size of kidney | Normal | Small |
| Renal osteodystrophy | Absent | May be present |
| Peripheral neuropathy | Absent | May be present |
| Myopathy | Absent | May be present |
Complication of (CRF)
- Hypertension
- Pericarditis
- Cardiomyopathy
- CCF
- Severe anaemia
- Bleeding, gastric ulcer
- Hepatitis
- Peripheral neuropathy