Cold chain – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Cold chain
The cold chain is a system of storage & transport of vaccine at optimum temperature from the manufacturer to the actual vaccination site.
The system is as follows:
Procurement of vaccine by the air
↓
Airport Expanded Program on Immunization
↓
By vehicle
↓
EPI headquarter cold room
↓
By vehicle (in cold boxes)
↓
District ILR & deep freeze
↓
By vehicle (in cold box)
↓
Thana & ILR refrigerator (1 month)
↓
Vaccine-carrier
↓
Field level (8 hours storage)
↓
Ice vaccine pack
↓
Use of vaccine.
Cold Chain Equipment
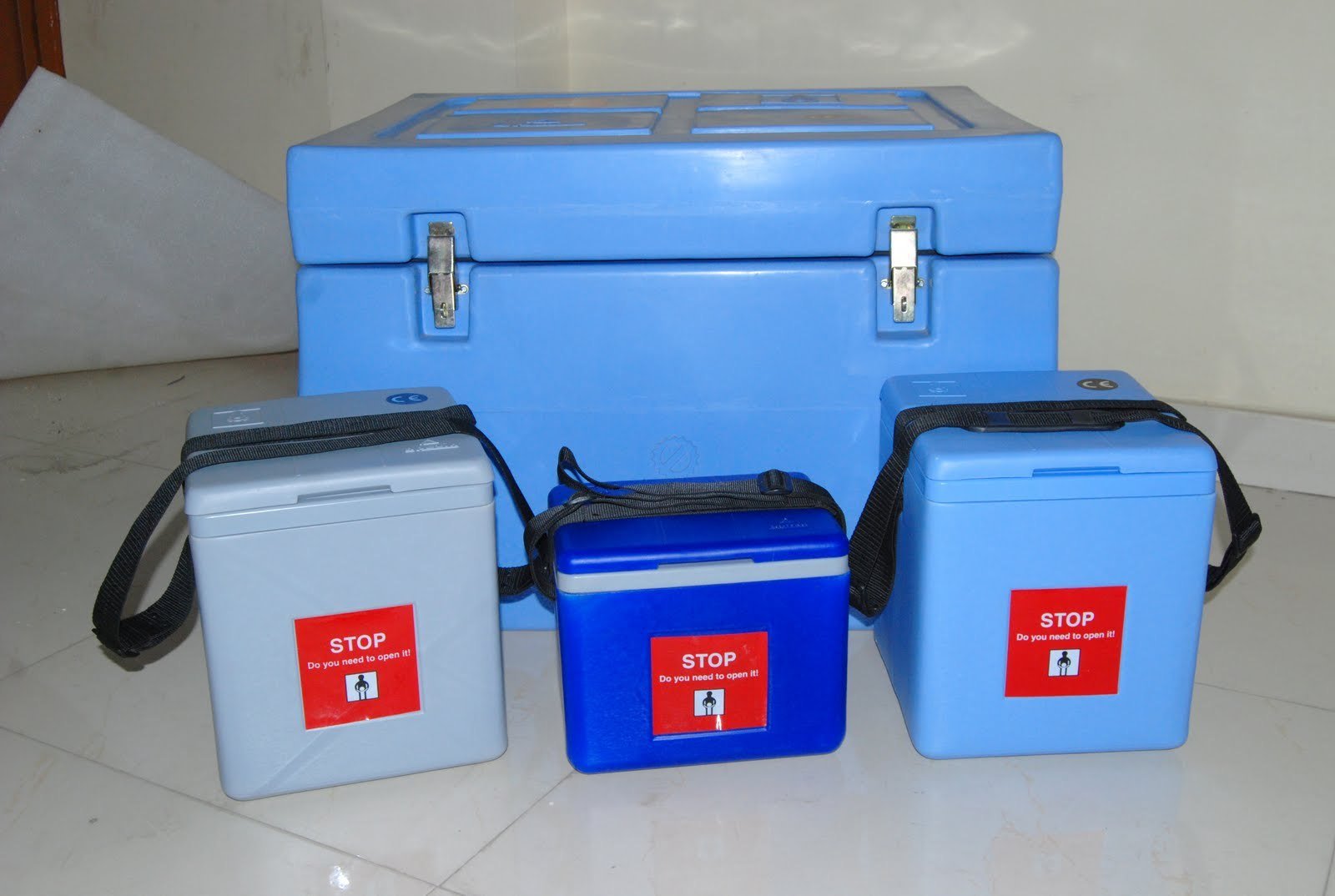

A. Walk in cold chain room (WIC)
- Located at regional level.
- Store vaccine up to 3 months.
- Serve 4-5 districts.
B. Deep freezers & ice lined refrigerators (ILR’S)
- To make ice parks
- To store OPV and measles vaccine
- District & WIC location
C. Small deep freezers & ILR
- PHCS
- Urban FPC
- Post-partumcenter
D. Cold boxes: Keep vaccine cold up to 1 week
E. Vaccine-carriers: Keep vaccine safe up to 3 days
F. Day carriers safe few hours.
G. Ice packs
Importance of cold chain
- To maintain potency of vaccine.
- For the storage of vaccine.
- For the transportation of vaccine at low temperature
Immunological Disorders
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Autoimmune diseases
- Immunologic deficiency syndromes
- Amyloidosis
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity may be defined as inappropriate or excessive immune response to an antigen stimulus in a pre-sensitized host leading to tissue damage.
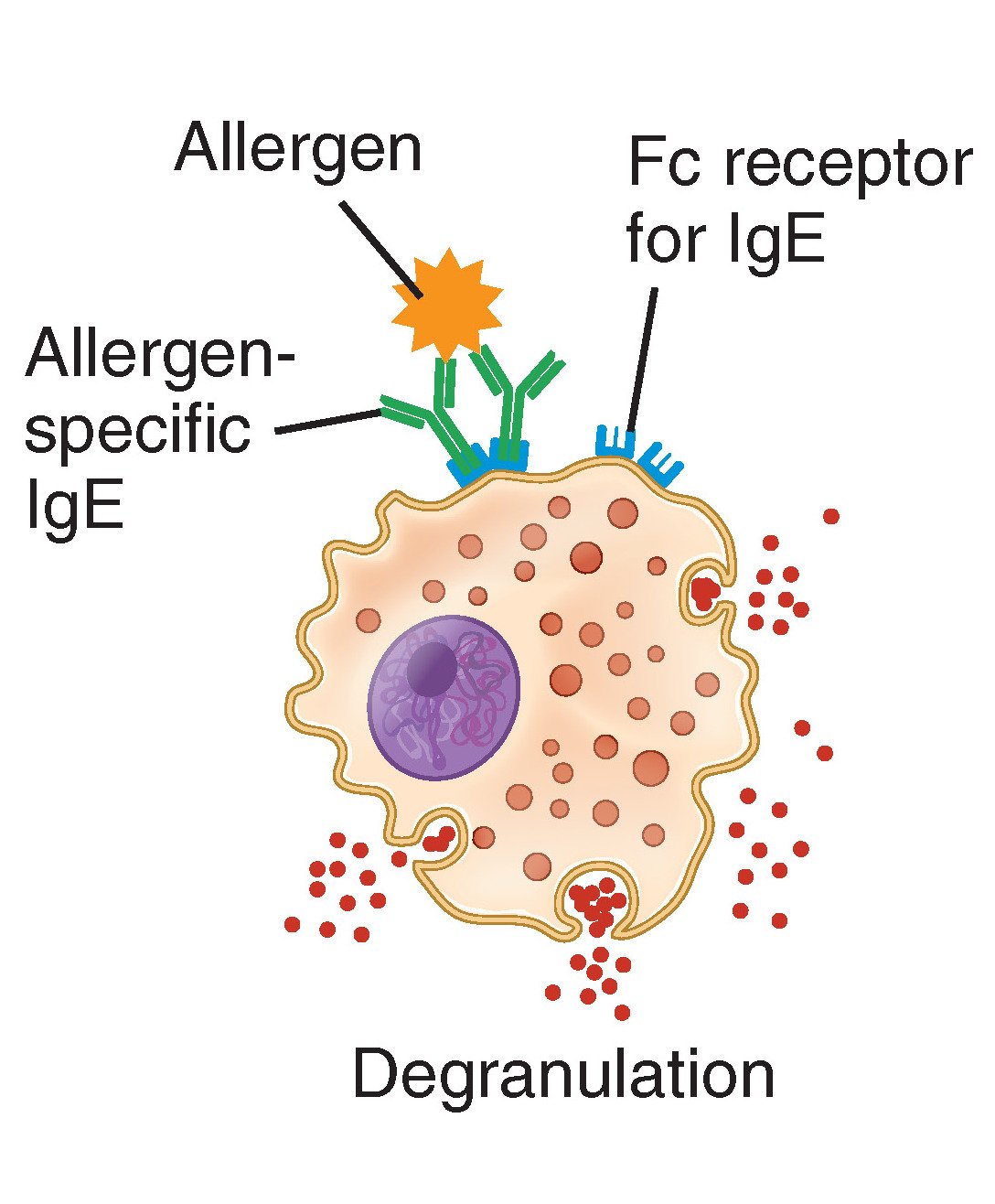
Classification of Hypersensitivity
Coombs and Gel (combined) classification:
- Type 1 or anaphylactic hypersensitivity
- Type II or cytotoxic hypersensitivity
- Type III or immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
- Type IV or delayed or cell-mediated hypersensitivity
On the basis of onset of action
- Immediate (requires minutes to hours) e.g. Types I, II, III
- Delayed (requires hours to days) e.g. Type-IV
On the basis of mechanism of action
- Antibody mediated, e.g. Types I, II, III & V.
- Cell mediated, e.g. Type-IV hypersensitivity.
