Common disorders and common terminology of integumentary system -The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.

Common disorders and common terminology of integumentary system
Abrasion (ab away, raison scraped): A portion of the epidermis that has been scraped away.
Acne: is an inflammation of sebaceous glands that usually begins at puberty, when the sebaceous glands grow in size and increase their production of sebum.
Athlete’s foot: A superficial fungus infection of the skin of the foot.
Blister: A collection of serous fluid within the epidermis or between the epidermis and dermis, due to short-term but severe friction.
Cold sore: A lesion, usually in the oral mucous membrane, caused by type 1 herpes simplex virus (HSV) transmitted by oral or respiratory routes. The virus remains dormant until triggered by factors such as ultraviolet light, hormonal changes, and emotional stress. Also called a fever blister.
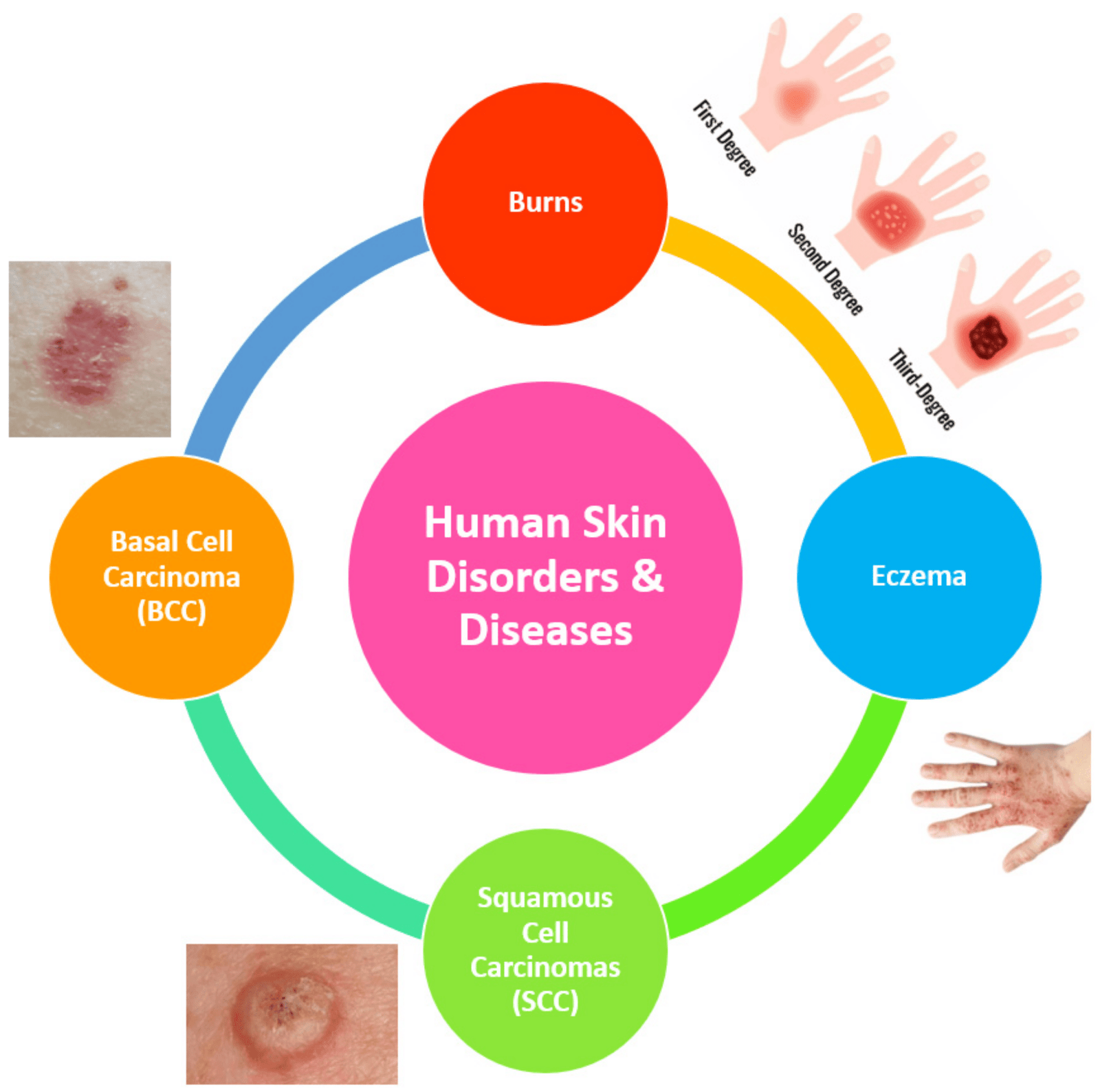
Contact dermatitis (dermat = skin; -itis = inflammation) Inflammation of the skin characterized by redness, itching, and swelling and caused by exposure of the skin to chemicals that bring about an allergic reaction, such as poison ivy toxin.
Corn: A painful thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis found principally over toe joints and between the toes, often caused by friction or pressure. Corns may be hard or soft, depending on their location. Hard corns are usually found over toe joints, and soft corns are usually found between the fourth and fifth toes.
Frostbite: Local destruction of skin and subcutaneous tissue on exposed surfaces as a result of extreme cold. In mild cases, the skin is blue and swollen and there is slight pain. In severe cases there is considerable swelling, some bleeding, no pain, and blistering. If untreated, gangrene may develop. Frostbite is treated by rapid rewarming.
Hemangioma (hem blood; angi = blood vessel; oma tumor): Localized tumor of the skin and subcutaneous layer that results from an abnormal increase in blood vessels.
Hives: Skin condition marked by reddened elevated patches that are often itchy, Most commonly caused by infections, physical trauma, medications, emotional stress, food additives, and certain food allergies.
Impetigo: Superficial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, most common in children.
Intradermal: (intra within) Within the skin. Also called intracutaneous.
Keloid: (kelis = tumor) An elevated, irregular darkened area of excess scar tissue caused by collagen formation during healing
Keratosis: Formation of a hardened growth of epidermal tissue, such as a solar keratosis, a premalignant lesion of the sun-exposed skin of the face and hands.
Laceration: An irregular tear of the skin.
Psoriasis (psora = itch): A common, chronic skin disorder in which keratinocytes divide and move more quickly than normal from the stratum basale to the stratum corneum and form flaky scales, most often on the knees, elbows, and scalp.
Pressure ulcers: also known as decubitus ulcers or bedsores, are caused by a constant deficiency of blood flow to tissues. Typically the affected tissue overlies a bony projection that has been subjected to prolonged pressure against an object such as a bed, cast, or splint.
Pruritus (pruri = to itch): Itching, one of the most common dermatological disorders. It may be caused by skin disorders (infections), systemic disorders (cancer, kidney failure), psychogenic factors (emotional stress), or allergic reactions.
Topical: Refers to a medication applied to the skin surface rather than ingested or injected.
Wart: Mass produced by uncontrolled growth of epithelial skin cells, caused by a papilloma virus. Most warts are noncancerous.
