Communicable diseases – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Communicable diseases
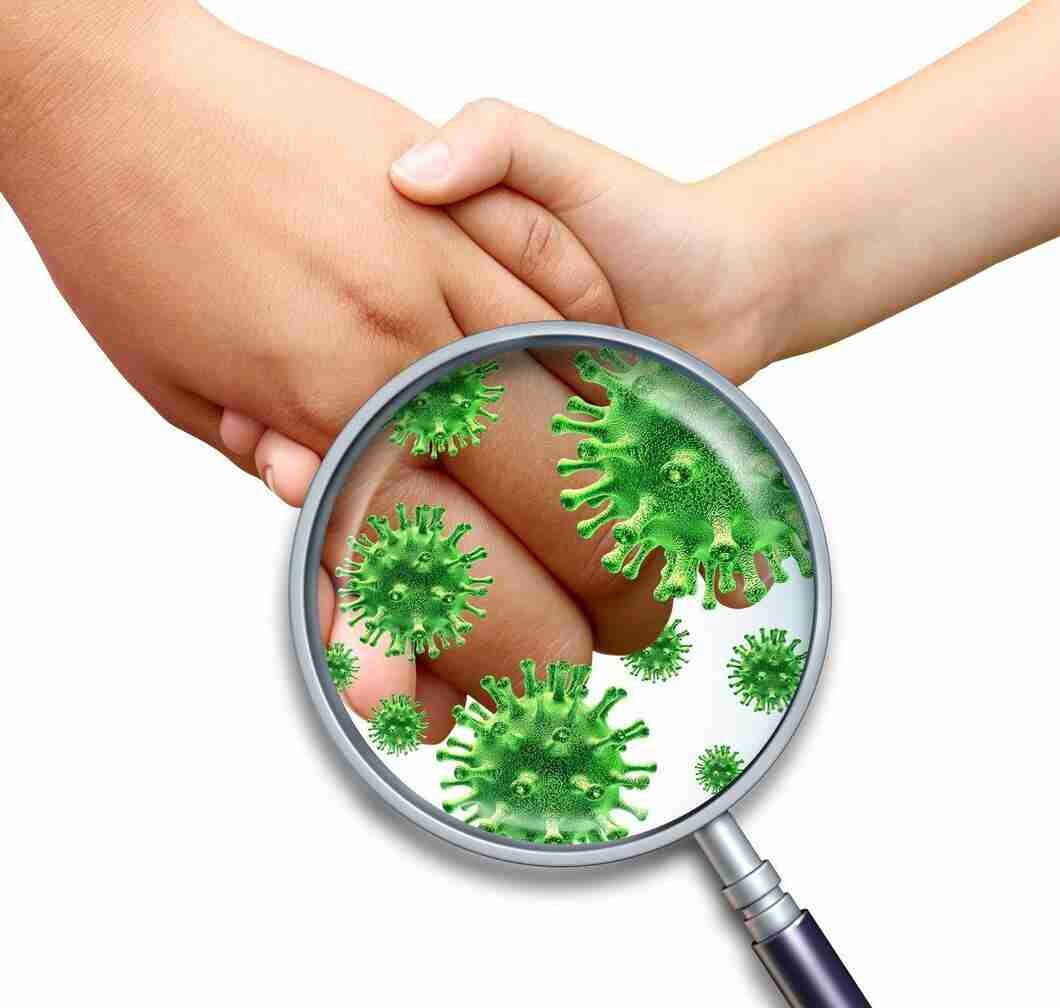

Mode of Transmission of Disease:
A. Direct transmission or contact:
- Direct contact: Touching an infected person by any means, including Sexual contact. eg. Leprosy, many skin and eye infections, STD (sexual transmitted disease) and AIDS
- Droplet infection:- Disease transmission by saliva and nasopharyngeal secretions through coughing or sneezing, speaking and spitting into the atmosphere. eg. Tuberculosis (TB), Diphtheria, Pertussis, and many other respiratory infections.
- Contact with soil. eg. Hookworm larvae, Tetanus, mycosis,
- Trans-placental:- AIDS, Hepatitis B, Syphilis, etc.
- Skin or mucous membrane: – eg, Rabies viruses by dog bite, HBV.
B. Indirect transmission or contact:
It occurs by touching any object or surface. It encompasses the 5 “F”s these are flies, finger, fomites, food and fluid.
- Vehicle borne:- Water, food, ice, blood, serum, plasma and other biological product, eg
- Vector borne: – Biological, Mechanical. Dilexmoo
- Airborne transmission: – If the microorganism remain in the air for long periods as droplet nuclei and dusto
- Fomite borne: – Soiled clothes, towels, linen, handkerchiefs, cups, spoons, pencils, books, toys, door, handles, drinding glasses, tap, syringes, instruments and surgical dressings.
Unclean hands and fingers.
(Ref by-Park/24h/101,104)
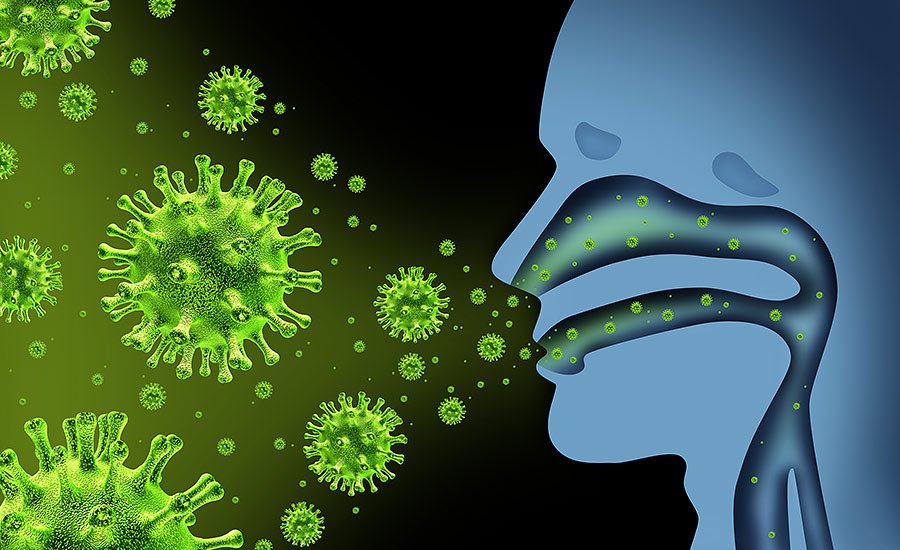
Definition of Communicable Disease:
An illness due to a specific infectious agent or its toxic product capable of being directly or indirectly transmitted from man to man, man to animal, animal to man, animal to animal or from environment (through air, dust, soil, water, food etc) to man or animal.
Classification of Communicable Disease:
| 1. Bacterial diseases: | Diphtheria, enteric fever, whooping cough,plague, anthrax |
| 2. Viral diseases: | Poliomyelitis, viral hepatitis, influenza, bird flu etc |
| 3. Protozoal diseases: | Amoebiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, malaria ete.lafiq/3 |
| 4. Helminthic diseases: | Ascariasis, ancylostomiasis, filariasis, taeniasis etc. |
| 5. Sexual transmitted diseases: | Syphilis, gonorrhea, AIDS etc. |
| 6. Zoonotic diseases | Rabies, brucellosis, hydatid disease etc. |
| 7. Arthropod borne diseases: | Dengue, malaria, kala-azar etc. |
| 8. Others | ARI, SARS, Food poisoning |
(Ref by-Park/24th/98)
Or
| Respiratory infection | Small pox, chickenpox, Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Influenza, Diphtheria, Whooping cough, Meningococcal meningitis, ARI, SARS, TB. |
| Intestinal infection | Poliomyelitis, viral hepatitis, cholera, Acute diarrheal diseases, typhoid fever, Food poisoning, Ameobeasis, Ascariasis, Hookworm infection, |
| Arthropod borne disease | The dengue syndrome malaria, lympathic filariasis |
| Zoonosis | Rabies, Yellow fever, Brucellosis, plague, Human salmenolosis, Ricketsial diseas, Taeniasis, Hydatid disease, Leismeniasis, |
| Surface infection | Trachoma, tetanus, Leprosy, STD, Endemic treponomatosis, AIDS |
common communicable & Non-communicable disease in children
| Communicable Disease in Children | Non-Communicable Disease in Children |
|
|
Principle Control of Communicable Disease:

1. Controlling the reservoir:
- Early diagnosis
- Notification
- Epidemiological investigation
- Isolation
- Treatments
- Quarantine
2. Interrupt transmission:
- Water treatment: Simple chlorination to complex treatment
- Proper sanitation
- Clear practices: Hand washing, adequate cooking.
- Control of vectors
3. Protection of susceptible host:
- Active immunization
- Passive immunization
- Combined passive and active immunization
- Chemoprophylaxis

Preventive Measure of Communicable Disease:
1. Handle & Prepare Food Safely:
- Food can carry germs. Wash hands, utensils, and surfaces often when preparing any food, especially raw meat.
Always wash fruits and vegetables.
2. Wash Hands Often:
- Learn how, when, and why to wash your hands.
3. Clean & Disinfect Commonly Used Surfaces:
- Germs can live on surfaces. Cleaning with soap and water is usually enough.
4. Cough & Sneeze into Your Sleeve:
- Learn how and when to cover your cough and sneeze.
5. Don’t Share Personal Items:
- Avoid sharing personal items that can’t be disinfected, like toothbrushes and razors, or sharing towels between washes. Needles should never be shared, should only be used once, and then thrown away properly.
6. Get Vaccinated:
- Vaccines can prevent many infectious diseases. Maintain EPI Schedule.
7. Avoid Touching Wild Animals:
- You and your pets should avoid touching wild animals which can carry germs that cause infectious diseases.
8. Stay Home When Sick

Diseases Transmitted Through Feco Oral Route:
1. Viral disease:
- Poliomyelitis
- Viral hepatitis A, E
- Acute diarrhea
2. Bacterial diseases:
- Cholera
- Bacillary dysentery
- Typhoid fever
- Food poisoning
3. Protozoal diseases:
- Amoebiasis
- Giardiasis
4. Helminthic diseases:
- Ascariasis
- Taeniasis
- Pin worm infestation
- Tape worm infestation
Read more:
