Concept about Bile-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept about Bile
Bile is a yellowish green fluid containing bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, and other compounds substances dissolved in an alkaline electrolyte solution
Site of formation:Hepatocyte of the liver
Site of storage: Gall bladder
Daily secretion:600-1200ml/day
Colour:Yellowish green (Due to bilirubin & biliverdin)
Composition of bile:
a. Bile pigments:
- Bilirubin
- Bliverdin.
b. Bile salts:
- Na K glycocholate
- Na-K’ tarurocholate
c. Lecithin & cholesterol
d.Electrolytes eg. Na, K, HCO, etc
Taste of bile:Bitter
P of bile: Liver bile:7.8-8.6
Gall bladder bile:7.0-7.4
Functions of bile:
- Neutralized the acid chyme coming from stomach
- Emulsify the fat globules.
- Reduce surface tension of the fat.
- Help in digestion & absorption of fat
- Absorption of fat soluble vitamins (Vit-A,D,E & K).
(Ref: Guyton & Hall, 12th edition, P-784)

Name the movement of GIT. What is ‘Peristalsis’.
Movements of the GIT:
A. Movement of stomach:
- Mixing movement (In full stomach).
- Propulsive movement (In full stomach).
- Hunger contraction (In empty stomach).
B. Movement of small intestine:
- Peristalsis: propulsive contraction
- Segmentation: mixing contraction
C. Movement of large intestine:
- Haustration: mixing movement
- Mass movement: propulsive movement.
Peristalsis
Peristalsis is a reflex response that initiate when the gut wall is stretched by the content of the lumen and it occurs in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Or,
The anal ward movement of the contents of the gut is known as propulsive movement or peristalsis.
Or,
The basic propulsive movement of GIT is peristalsis
Velocity: 2.25 cm/second
Purpose of peristalsis:
- Propulsion of food-chyme from oral to aboral direction.
- Helps in mixing food particles with digestive enzymes
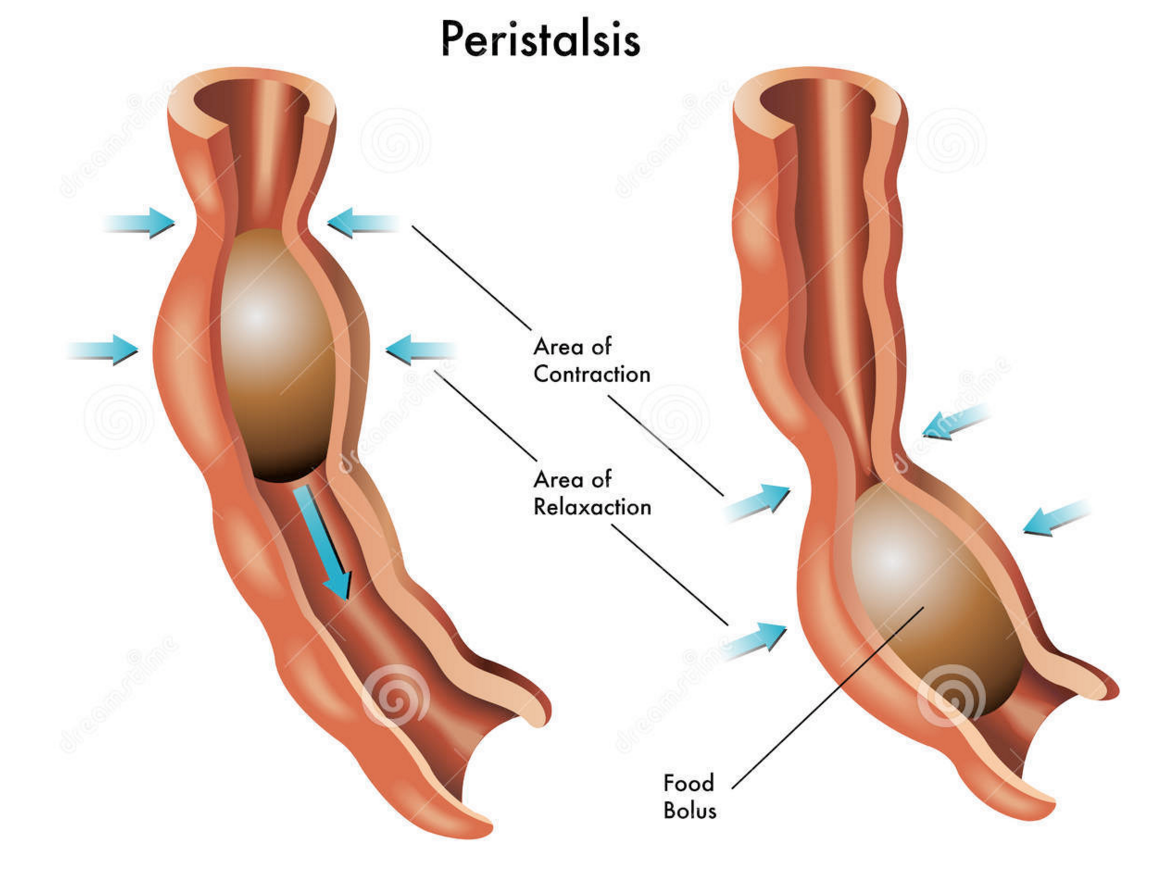
Peristalses occur in:
- GIT
- 2 Bile duct
- Ducts of the glands
- Ureters
- Other smooth muscle tubes of the body
Read more:
