Concept about Bladder Irrigation – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Concept about Bladder Irrigation
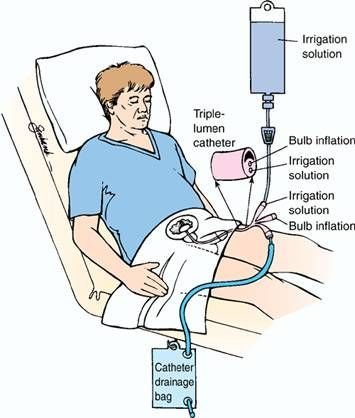
Bladder irrigation can be defined as a process of flushing out or washing out the urinary bladder with specified solution.
or
When a Foley’s catheter has been in place for a period of time. It will be necessary to flush the catheter and bladder in an aseptic manner upon the order of the physician and this process is known as bladder irrigation.
Purpose of Bladder Irrigation:
- To flush clots and debris out of bladder
- To instill medication to bladder lining
- To restore patency of the catheter.
- To clean the bladder from blood and mucus.
- To remove the catheter sedimentation.
- To relieve pain.
- Prior or introducing any medicine to bladder.
- Before prostate operation
Procedure of Bladder Irrigation:
A. Equipment’s needed
- Disposable gloves
- Disposable, water resistant,
- Sterile towel/mackintosh
- Three way retention catheter in-situ
- Sterile drainage tubing and bag in place
- Sterile antiseptic swab
- Sterile receptacle
- Sterile irrigating solution =Normal saline or Distilled water or Solution as prescribed by physician
- Infusion tubing
- IV pole
- Kidney basin
B. Procedure: Performing Bladder Irrigation
a) Assessment
1. Determine the client’s current urinary drainage system. Review the client record for intake and output and difficulties the client has been experiencing with the system. Review the result of previous irrigations.
2. Assess the client for any discomfort, bladder spasm, or distended bladder.
b) Performance
1. Explain the client what you are going to do,why it is necessary, and how she or hel can cooperate. The irrigation should not be painful or uncomfortable
2. Wash hands and observe appropriate infection control measures.
3. Provide for client privacy.
4. Apply clean gloves.
5. Empty, measure, and record the amount and appearance of urine present in the drainage bag. Discard urine and gloves. Emptying the drainage bag allows more accurate measurement of urinary output after the irrigation.
6. Prepare the equipment
- Wash hands
- Connect the irrigation infusion tubing to the irrigating solution and flush the tube with solution, keep the tip sterile. Flushing the tubing removes air and prevents it from being instilled in to the bladder.
- Apply clean gloves and cleanse the port with antiseptic swabs.
- Connect the irrigation tubing to the input port of the three way catheter.
- Connect the bag and tubing to the urinary drainage port if not already in place.
- Remove your gloves and wash your hands.
7. Irrigate the bladder.
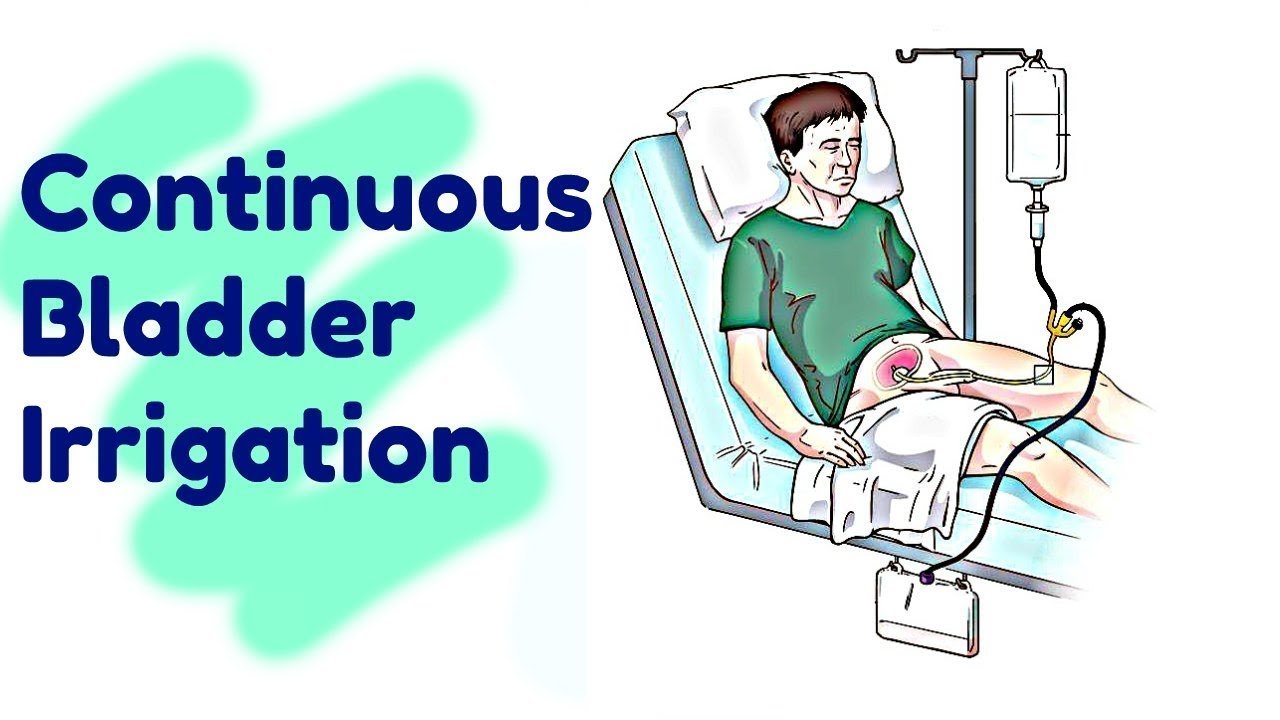
c) For continuous irrigation
1. Open the flow clamp on the urinary drainage tubing. This allows the irrigating solution to flow out of the blaauer continuously.
2. Open the regulating clamp on the irrigating tubing and adjust the flow rate as prescribed by the primary care provider or 40-60 drops per minute if not specified.
3. Assess the drainage for amount, color and clarity. The amount of drainage should equal the amount of irritant entering the bladder plus expected urine out put.
d) For intermittent irrigation
1. Determine whether the solution is to remain in the bladder for a specified time.
2. If the solution is to remain in the bladder, apply flow clamp to the urinary drainage tubing. Closing the flow clamp allows the solution to be retained in the bladder and in contact with bladder walls.
3. If the solution is being instilled to irrigate the catheter, open the flow clamp, on the urinary drainage tubing. Irrigating solution will flow through the urinary drainage port and tubing, removing mucous shreds or clots.
4. Open the flow clamp on the irrigating tubing, allowing the specified amount of solution to infuse. Clamp the tubing.
5. After specified period the solution is to retained, open the drainage tubing flow clamp and allow the bladder to empty.
6. Assess the drainage for amount, color, and clarity. The amount of drainage should equal the amount of irritant entering plus expected urine output.
7. Assess the client and the urinary output.- assess the client’s comfort
8. Empty the drainage bag and measure the contents. Subtract the amount of irritant instilled from the total volume of drainage to obtain the volume of urine output.
9. Document the procedure and results in the client’s records. Use forms or checklists supplemented by narrative notes when appropriate.
10. Note any abnormal constituents such as blood clots, pus, or mucous shreds.