Concept about Body Mass Index (BMI) – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Nutrition and Dietetics” prescribed by BNMC-for all Diploma in Nursing Science and Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics. This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Concept about Body Mass Index (BMI)
The body mass index (BMI), or Quetelet index, is a measure for human body shape based on an individual’s mass and height
Measure Body Mass Index (BMI):
The body mass index (BMI) or Quetelet index is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of an individual. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is universally expressed in units of kg/m², resulting from mass in kilograms and height in meters.
Formula:
Metric BMI Formula
- BMI = weight (kg) + height² (m²)
Imperial BMI Formula
- BMI = weight (lb) + height² (in²) x 703
Example Using Formula
For an adult with height of 180 cm and weight of 75 kg. Our first step needs to be to convert the height into meters (British spelling: metres). As there are 100cm in a meter, we divide our figure by 100. This gives us 1.8m.
Let’s plug those figures into our formula:
BMI = 75 (1.8 × 1.8)
BMI=753.24
This gives us a BMI figure of 23.15.
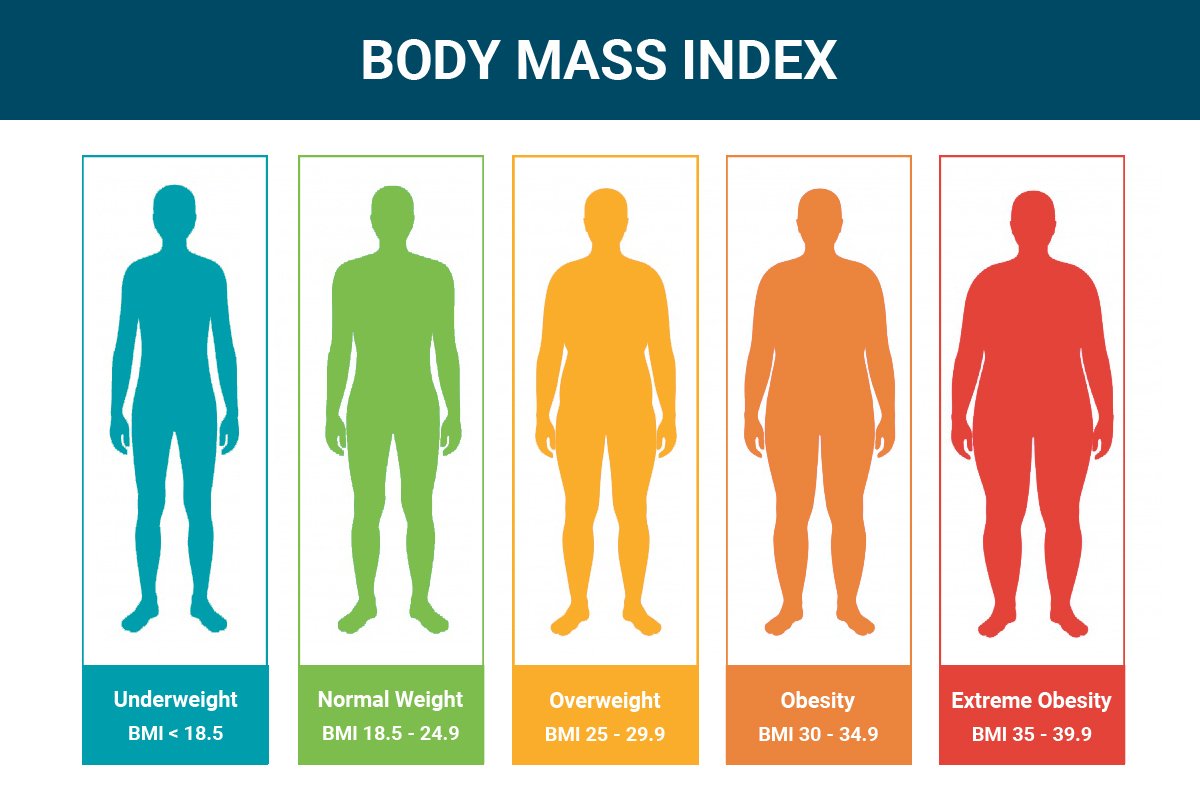
BMI Chart:
| Category | BMI range-kg/m² |
| Very severely underweight | Less than 15 |
| Severely underweight | 15.0-16.0 |
| Underweight | 16.0-18.5 |
| Normal (healthy weight) | 18.5-25 |
| Overweight | 25-30 |
| Obese class I (Moderately obese) | 30-35 |
| Obese class II (Severely obese) | 35-40 |
Obese class III (very severely obese) | Over 40 |
Nice To Know
Risks Associated with Being Overweight
Being overweight increases the risk of a number of serious diseases and health conditions. Below is a list of said risks, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
- High blood pressure
- Higher levels of LDL cholesterol, which is widely considered “bad cholesterol,” lower levels of HDL cholesterol, considered to be good cholesterol in moderation, and high levels of triglycerides
- Type II diabetes
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Osteoarthritis, a type of joint disease caused by breakdown of joint cartilage
- Sleep apnea and breathing problems
- Certain cancers (endometrial, breast, colon, kidney, gallbladder, liver)
- Low quality of life
- Mental illnesses such as clinical depression, anxiety, and others
- Body pains and difficulty with certain physical functions
- Generally, an increased risk of mortality compared to those with a healthy BMI

Risks Associated with Being Underweight
Being underweight has its own associated risks, listed below:
- Malnutrition, vitamin deficiencies, anemia (lowered ability to carry blood vessels)
- Osteoporosis, a disease that causes bone weakness, increasing the risk of breaking a bone
- A decrease in immune function
- Growth and development issues, particularly in children and teenagers
- Possible reproductive issues for women due to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Underweight women also have a higher chance of miscarriage in the first trimester
- Potential complications as a result of surgery
- Generally, an increased risk of mortality compared to those with a healthy BMI

