Concept about Clavicle – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.
The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept about Clavicle
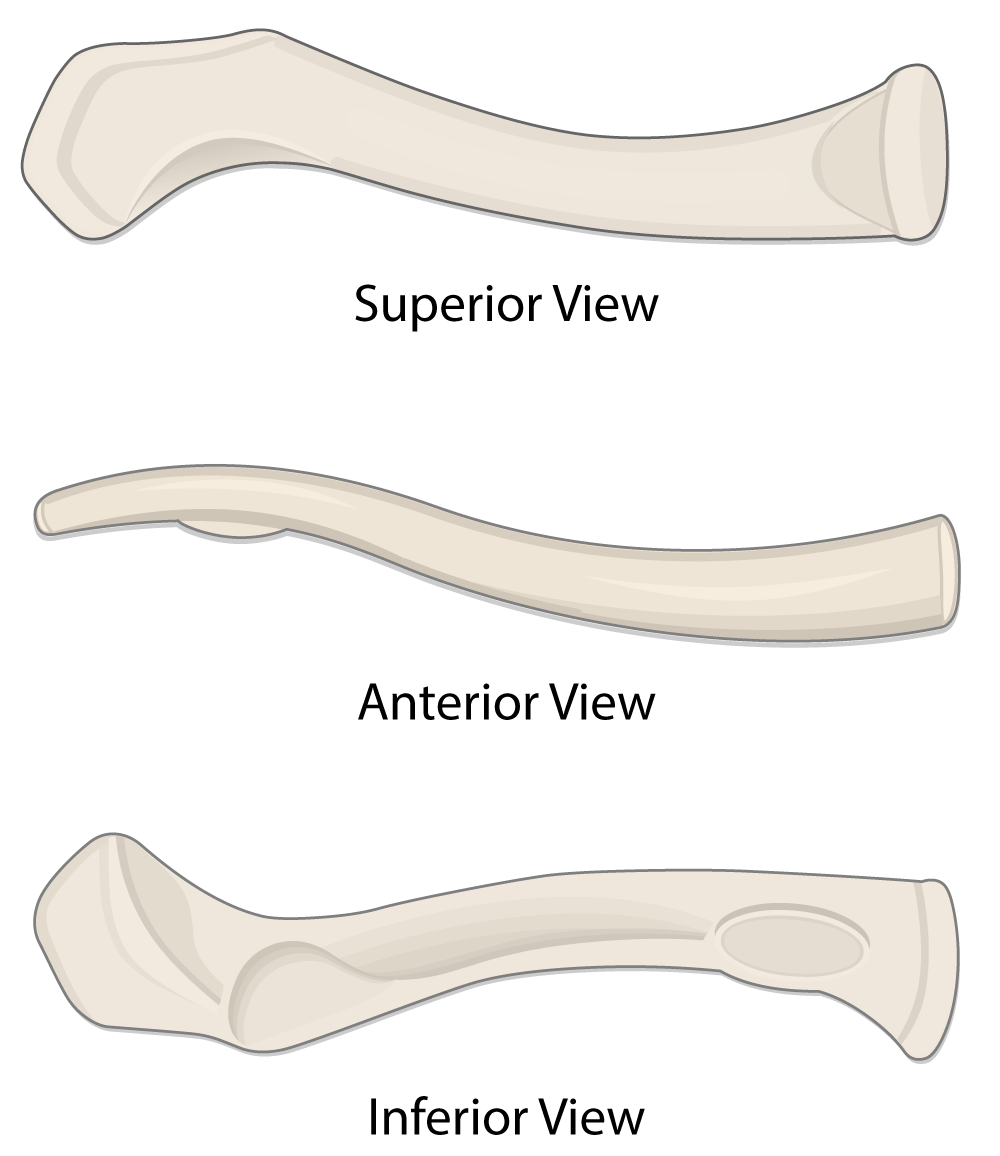
CLAVICLE
The clavicle, or collarbone, is the only bony attachment between the upper limb and the axial skeleton. It is superficial along its entire length and shaped like an “S.” The clavicle provides an attachment for muscles that connect the clavicle to the trunk and the upper limb. on the clavicle:
The following landmarks are found
Acromial end. Articulates laterally with the acromion of the scapula and forms the acromioclavicular joint.
Sternal end. Articulates medially with the manubrium and forms thesternoclavicular joint.
Conoid tubercle. Located on the inferior surface of the lateral clavicle and serves as an attachment for the coracoclavicularligament.
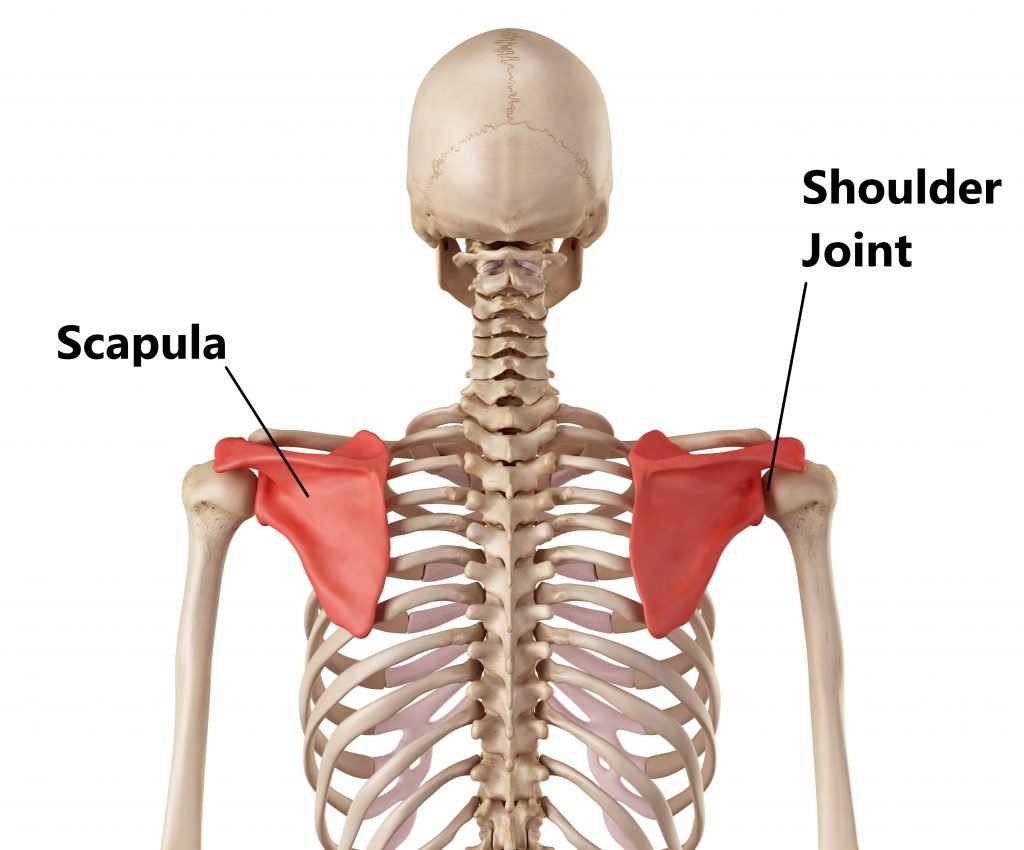
Concept about of SCAPULA
The scapula, or shoulder blade, is a large, flat triangular bonewith three angles (lateral, superior, and inferior), three borders(superior, lateral, and medial), two surfaces (costal and posterior), and three processes (acromion, spine, and coracoid). The following landmarks are found onthe scapula:
Subscapular fossa. Located anteriorly and characterized bya shallow, concave fossa. Because the subscapular fossa glidesupon the ribs, it is also known as the costal surface.
Acromion. A relatively large projection of the anterolateralsurface of the spine, the acromion arches over the glenohumeraljoint and articulates with the clavicle.
Spine. Very prominent and palpable; the spine subdividesthe posterior surface of the scapula into a small supraspinousfossa and a larger infraspinous fossa.
Supraspinous fossa. Located on the posterior surface of thescapula and superior to the spine of the scapula.
Infraspinous fossa. Located on the posterior surface of thescapula and inferior to the spine of the scapula.
Suprascapular notch. A small notch medial to the root of thecoracoid process where the suprascapular nerve, artery, andvein course.
Glenoid cavity (fossa). A shallow cavity that articulateswith the head of the humerus to form the glenohumeraljoint.
Supraglenoid tubercle. Located superior to the glenoid cavity and serves as the attachment for the long head of thebiceps brachii muscle.
Infraglenoid tubercle. Located inferior to the glenoid cavityand serves as the attachment for the long head of the tricepsbrachii muscle.
Coracoid process. A prominent and palpable hook-likestructure inferior to the clavicle. The coracoid process servesas an attachment for the pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis,and short head of the biceps brachii muscles.
