Concept about Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Concept about Electrocardiogram (ECG)
It is a diagnostic procedure that graphically records the condition, magnitude and duration of the electrical current generated by the heart.
- Electrocardiograph: It is an instrument use to record the surface electrogram (ECG)
ECG
Definition:
The recording of the electrical changes of the heart from the surface of the body by the placement of electrode on the selected areas of the body is called electrocardiogram (ECG).
or
It is the graphical representation of the electrical potential of the heart produced when there is a potential fluctuation during the cardiac cycle.
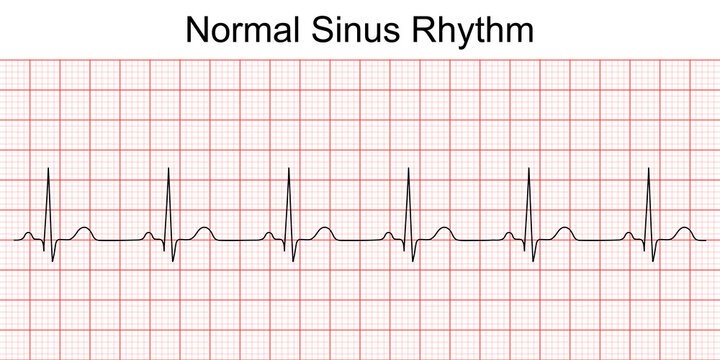
Fig: A Normal ECG
Nice to know
E.C.G leads:
A lead is a graphic illustration of the electrical potential difference between two points on the skin surface that being transmitted by the heart during the cardiac cycle.
Standard E.C.G consists of 12 different lead to provide a complete picture of the heart’s electrical activity.
These 12 leads consist of the following:
The frontal plane leads: They are orientated in the frontal or coronal plan of the body.
This are-
➤ Standard or Bipolar Limb leads.
- Lead-I
- Lead-II
- Lead-III
➤ Augmented Unipolar Limb leads.
- Lead aVR
- Lead aVL
- Lead aVF
The horizontal plane leads: These are orientated in the horizontal plane of the body. These
are-
Unipolar chest leads: Lead Vi to lead V6
Site for chest leads:
➤ V_{1} 4 ^ (th) intercostals space, right sternal border.
➤ v_{2} :4^ dagger h intercostals space over the left sternal border.
➤ V_{3} : In between V_{2} and V_{4}
➤ V_{4} : 5 ^ (th) intercostal space in the midclavicular line.
➤ V_{5} : Same horizontal plane as V_{4} over anterior axillary line.
➤ V_{6} : Same horizontal plane as V_{4} over mid axillary line.
Indications of ECG are –
A) Physiological:
- Normal heart rate is counted.
- Condition of the heart can be detected.
B) Clinical: To detect the pathological conditions like –
- Myocardial infarction.
- Atrial hypertrophy.
- Ventricular hypertrophy.
- Pericarditis.
- Arrythmia, Fibrillation, Flutter etc.
- Effects of drugs: Digitalis, Quinine etc.
Clinical importance of ECG:
ECG gives the valuable information (diagnostic and/or prognostic) about-
- Cardiac arrhythmia and conduction defects.
- Ischemia or information of the myocardium.
- Chamber enlargement and pericarditis.
- Electrolytic imbalance especially potassium..
- Determination of the effect of cardiac drugs, especially digitalis and certain anti- arrhythmic drugs.
The waves of ECG are produced due to electrical changes of the heart during cardiac cycle:
➤ During atrial depolarization -> ‘P’ wave is produced.
➤ During left to right septal depolarization -> “Q” wave is produced,
➤ During septal & left ventricular depolarization -> “R” wave is produced.
➤ During posterior basal left ventricular depolarization -> ‘S’ wave is produced.
➤ During ventricular repolarization -> ‘T’ wave is produced.
Waves and intervals of an ECG:
A. Waves are:
- P Wave = Represent atrial depolarization.
- Q Wave = Represent Left to right septal depolarization.
- R Wave = Represent Septal & left ventricular depolarization.
- S Wave = Represent Posterior basal left ventricular depolarization.
- T Wave = Represent Ventricular repolarization.
[N.B:-Q, R & S waves are collectively called ‘QRS’ complex]
B. Intervals are:
- P-R interval (about 0.18 sec)
- Q-T interval (about 0.35 sec)
- S-T interval (about 0.32 sec)
- ‘QRS’ duration (about 0.08sec)