Concept about Epidermis-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept about Epidermis
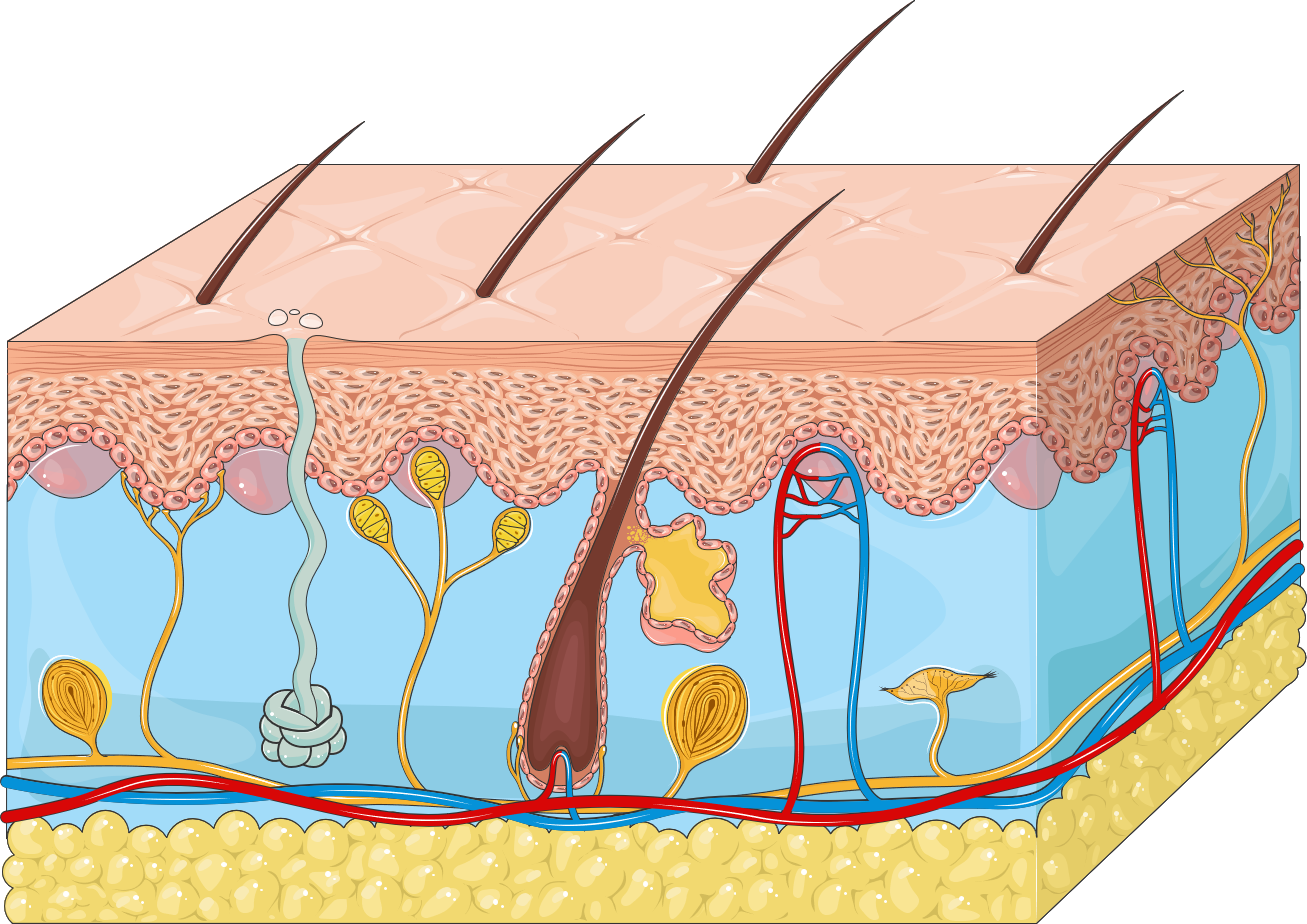
Epidermis:
The epidermis (epi = above) is the superficial, thinner portion, which is composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue.
It contains four principal types of cells:
- Keratinocytes,
- Melanocytes,
- Langerhans cells, and
- Merkel cells
1. keratinocytes: About 90% of epidermal cells are keratinocytes (keratino = hornlike; cytes = cells), which are arranged in four or five layers and produce the protein keratin keratin is a tough, fibrous protein that helps protect the skin and underlying tissues from abrasions, heat, microbes, and chemicals.
2. Melanocytes: About 8% of the epidermal cells are melanocytes (melano = black), which produce the pigment melanin. Their long, slim projections extend between the keratinocytes and transfer melanin granules to them. Melanin is a yellow-red or brown- black pigment that contributes to skin color and absorbs damaging ultraviolet (UV) light.
3. Langerhans cells: Its participate in immune responses mounted against microbes that invade the skin. Langerhans cells help other cells of the immune system recognize an antigen (foreign microbe or substance) so that it can be destroyed. Langerhans cells are easily damaged by UV light.
4. Merkel cells: contact the flattened process of a sensory neuron (nerve cell), a structure called a tactile (Merkel) disc. Merkel cells and tactile discs detect touch sensations.
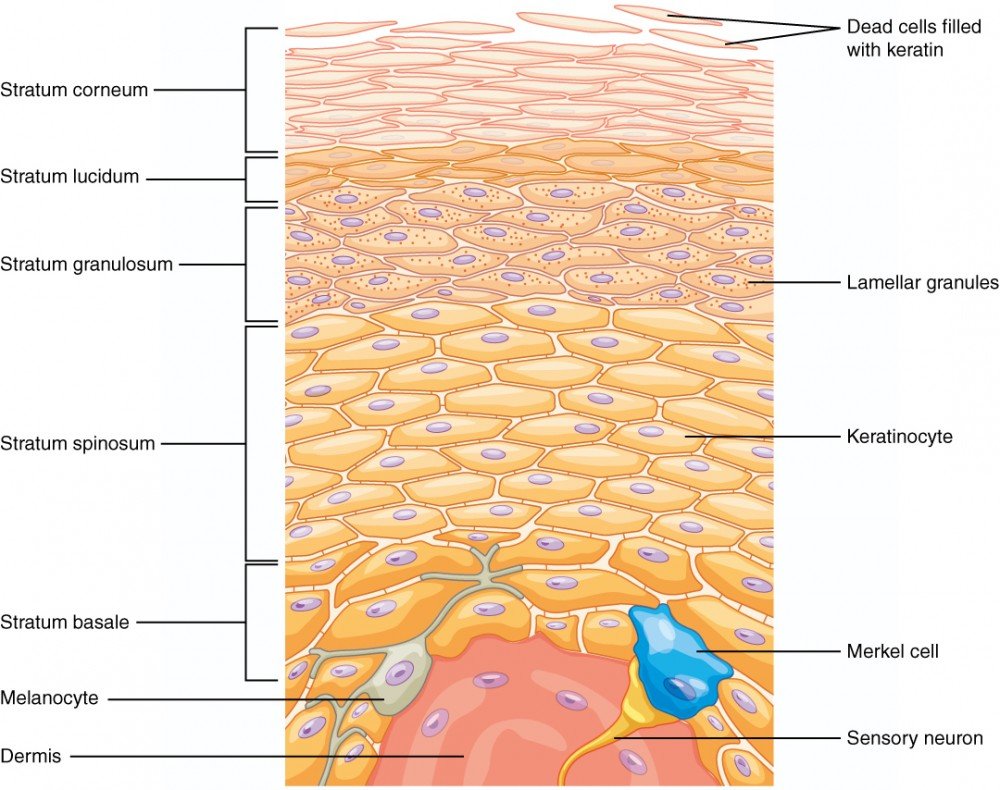
In most regions of the body the epidermis has four strata or layers-
- Stratum basale,
- Stratum spinosum,
- Stratum granulosum, and
- A thin stratum corneum. (This is called thin skin.)
Where exposure to friction is greatest, such as in the fingertips, palms, and soles, the epidermis has five layers-
- Stratum basale,
- Stratum spinosum,
- Stratum granulosum,
- Stratum lucidum, and
- A thick stratum corneum
