Concept about Haemoglobin (H6) – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Concept about Haemoglobin (H6)
Haemoglobin consists of the protein ‘globin’ united with the pigment ‘heam’ and ‘Globulin’ is a polypeptide. There are two pairs of polypeptide chains in each Hb molecule.
‘Heam’ is an iron-containing porphyrin known as iron-protoporphyrin IX.
or
Haemoglobin is the red pigment of the blood and comprises of a chromoprotein consisting of a nonspecific simple protein called globin and a specific prosthetic group called haem (an iron containing pigment).
Molecular weight: 68,000.
Range of Hb:
- In adult male : 14-18 gm/dl of blood
- In adult female : 12-15.5 gm/dl of blood
- At birth : About 23 gm/dl of blood
- At one month : About 10.5 gm/dl of blood
- At one year : About 12 gm/dl of blood.
(N.B: One gram of Hb combine with 1.34 ml of oxygen)
Heam containing substances are:
- Hemoglobin
- Myoglobin
- Catalase
- Cytochrome
Functions of Hb:
➤ Gaseous exchanges: Carries oxygen from lungs to tissue & carries carbon-dioxide from the tissue to lung.
➤ Hemoglobin acts as a buffer in maintaining acid base balance.
➤ It reserves iron & protein.
Normal Range of Hemoglobin:
Sex & age | Normal level of haemoglobin (gm/dl) | |
| Average | Range | |
| Adult male | 15.5 | 14-18 |
| Adult female | 14 | 12-16 |
| At birth | 23 | |
| At 1 year | 12 | |
Hemoglobin synthesis:
Synthesis of hemoglobin begins in the proerythroblasts and continues even into the reticulocyte stage of the red blood cells. Therefore, when reticulocytes leave the bone marrow and pass into the blood stream, they continue to form minute quantities of hemoglobin for another day or so until they become mature erythrocytes.
Heme synthesis:
➤ Site: Mitochondria
➤ Raw material: Succinyl CoA, glycine and iron
➤ Steps:
- Succinyl-CoA, formed in the Krebs metabolic cycle from acetic acid
- succinyl Co-A +2 Glycine → Pyrrole.
- 4 pyrrole → Protoporphyrin IX
- Protoporphyrin-IX + Fe++ → Heme.
Globin chain synthesis:
➤ Site: Ribosome of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
➤ Raw material: Amino acids
➤ Steps:
- DNA → transcription → mRNA → translation → Polypeptide chain
Combination of Heme with Globin:
- Heme + Polypeptide chain → Hemoglobin chain (a or ẞ)
- 2a chain + 2ẞ chain → Hemoglobin Adult.
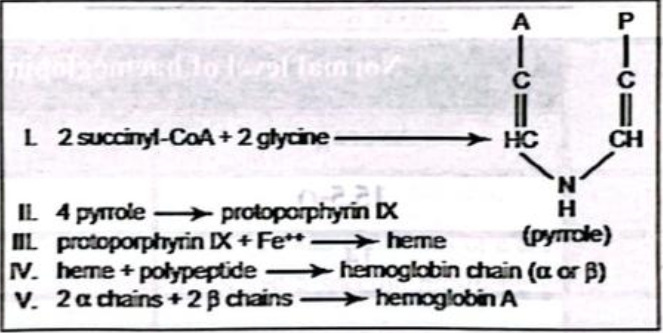
Fig: Hemoglobin synthesis
Chemical structure of haemoglobin:
➤ Haemoglobin consists of 2 a chains and 2 ẞ chains.
➤ Each chain consists of haem and polypeptide chain (globin).
➤ Haem is an iron-containing porphyrin known as iron-protoporphyrin-IX.
➤ The porphyrin nucleus consists essentially of four pyrol rings joined together by four methine (=CH-) bridges. The porphyrin are thus tetra-pyrroles. The pyrrole rings are numbered I, II, III, IV.
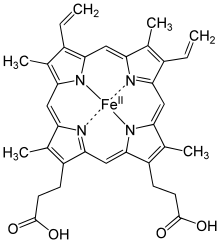
hemoglobin
➤ There are eight side chains attached to four pyrrole rings. They are numbered 1 to 8. The side chains are methyl (-CH3) at 1, 3, 5 & 8 positions, vinyl (-CH=CH2) at 2 & 4 positions and propionic acid (-CH2-CH2-COOH) at 6 & 8 position.
➤ The iron in haem is in the ferrous (Fe) form. It is attached to the N of each pyrrole ring and N of imidazole group of the associated globin.
➤ Globin is a polypeptide consisting of amino acids
Nutritional/dietary factors for Hb synthesis:
i. Protein. – main
ii. Iron. – main
iii. Cobalt.
iv. Copper.
v. Vitamin B6 and Vitamin C
Factors required for haemoglobin synthesis:
- First class protein: Necessary for the synthesis of globin portion.
- Metals: Iron, copper, manganese, cobalt.
- Vitamins: Vitamin B12, folic acid, vitamin C, riboflavin and nicotinic acid.
- Endocrines: Thyroid, adrenal cortex and pituitary gland.
- Porphyrins: They are readily synthesized in the body.
- Genetic control: Exerted by the genes located on autosomal chromosomes.
Differences between Hb-A & Hb-F:
| Adult hemoglobin (Hb-A) | Fetal hemoglobin (Hb-F) |
| 1. Hb-A contains 20 and 2ẞ chains. | 1. Hb-F contains 2a and 2y chains. |
| 2. It is normally 98% in adult | 2. It is normally absent in adult but present in fetus. |
| 3. It saturates at a relatively high oxygen tension. | 3. It saturates at low oxygen tension. |
| 4. It binds with 2-3 diphosp hoglycerate. (DPG) | 4. It binds less avidly with 2-3 diphosphoglycerate. (DPG) |
| 5. It is not resistant to the action of alkali. | 5. It is resistant to the action of alkali. |
Types of Haemoglobin:
➤ Normal haemoglobins & their structures:
| Normal haemoglobins | Types | Structure | a=141 amino acids. B = 146 amino acids. 6146 amino acids, y=146 amino acids |
| Adult | Hb A Hb A2 | a2b2 a2S2 | |
| Fetal | Hb F Hb Bart’s | a2y2 y4 | |
| Embryonic | Hb Gower 1 Hb Gower 2 Hb Portland | T2€2 a2 €2 T2Y2 |
Haemoglobinopathies:
The haemoglobinopathies are characterized by the production of structurally defective haemoglobin due to abnormalities in the formation of the globin moiety of the molecule.
Abnormal haemoglobins (haemoglobinopathies) and their structures:
| Abnormal НЬ | Structure | Main Defect |
| Hb S | α2β2 | Number-6 glutamic acid is replaced by valine. |
| Hb C | α2β2 | Number-6 glutamic acid is replaced by lysine. |
| Hb E | α2β2 | Number-26 glutamic acid is replaced by lysine |
| Hb D Punjub | α2β2 | Number-121 glutamic acid is replaced by |
[Ref-de Gruchy / 6th /123 (Table: 7.2)

