Concept about Hormone-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept about Hormone

Hormone:
“Hormone” is derived from a Greek word meaning “I excite”
A hormone is a chemical substance that is secreted into the internal body fluid by one cell or a group of cells and has a physiological control effect on the other cells of the body.
(Ref-Guyton & Hall, Text book of Medical Physiology, 12thed, P-905)
Classification of hormones:
A. According to their chemical nature:
- Peptide hormone or protein hormone, eg. Insulin, GH, FSH, LH, TSH etc.
- Steroid hormone. e.g. Aldosterone, Testosterone etc.
- Amines hormone. e.g. EP, NEP etc. (EP-Epinephine, NEP= Norepinephine)
B. According to the site of action:
- Local hormones. e.g. Histamine, gastrin, CCK etc.
- Tropic hormones. e.g. TSH, FSH etc.
(Ref: Guyton & Hall, Text book of Medical Physiology, 12th ed, P-882.)
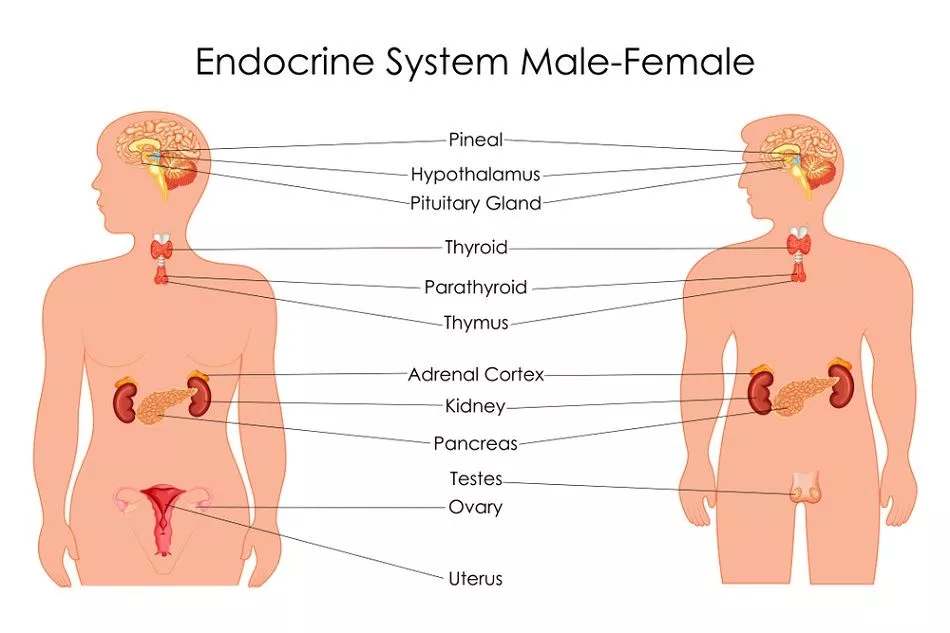
The different endocrine gland with their major hormones, target organs and important function:
| Endocrine Gland/Tissue | Major Hormones | Primary Target Organs | Primary Effects/functions |
| Hypothalamus | Releasing and inhibiting hormones:
| Anterior & posterior pituitary | Regulates secretion of pituitary hormones
|
| Anterior pituitary |
| Most tissues, Endocrine glands and other organs eg:- Ovaries, Testes, Breast, Thyroid gland etc. | Stimulates growth and development of target organs; stimulates secretion of other hormones, ovulation & Production of milk in the breast, etc |
| Posterior pituitary |
|
| Antidiuretic hormone promotes water retention and vasoconstriction, oxytocin stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary secretory units |
| Thyroid gland |
| Most organs | Thyroxine and triiodothyronine promote growth and development and stimulate basal rate of cell respiration (basal metabolic rate or BMR), calcitonin may participate in the regulation of blood Ca2+ levels |
| Parathyroid glands | PTH (Parathyroid hormone) | Bone, small intestine, and kidneys | Increases Ca2+ concentration in blood |
| Thymus | Thymopoietin | Lymph nodes | Stimulates white blood cell production |
| Islets of Langerhans (pancreas) |
| Many organs Liver and adipose tissue | Insulin promotes cellular uptake of glucose and formation of glycogen and fat; glucagon stimulates hydrolysis of glycogen and fat |
| Adrenal cortex |
| Liver and muscles Kidneys | Glucocorticoids influence glucose metabolism, aldosterone promotes Na+ retention, K+ excretion |
| Adrenal medulla | Epinephrine | Heart, bronchioles, and blood vessels | Causes adrenergic stimulation |
| Ovaries |
| Female reproductive tract and mammary glands | Maintains structure of reproductive tract and promotes secondary sex characteristics |
| Testes | Testosterone | Prostate, seminal vesicles, and other organs | Stimulates secondary sexual development. |
| Placenta | HCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin) | Ovary | Promotes growth of corpus luteum and secretion of oestrogen and progesterone by corpus luteum. |
| Pineal gland | Melatonin | Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary | Affects secretion of gonadotrophic hormones |
| Heart | Atrial natriuretic hormone | Kidneys | Promotes excretion of Na in the urine |
| Stomach | Gastrin | Stomach | Stimulates acid secretion |
| Liver | Somatomedins | Cartilage | Stimulates cell division and growth |
| Kidneys | Erythropoietin | Bone marrow | Stimulates red blood cell production |
| Small intestine | Secretin and cholecystokinin | Stomach, liver, and pancreas | Inhibits gastric motility and stimulates bile and pancreatic juice secretion |