Concept about Lactation – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept about Lactation
Lactation (lact = milk) is the production and ejection of milk from the mammary glands. A principal hormone in promoting milk production is prolactin (PRL), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. Even though prolactin levels increase as the pregnancy progresses, no milk production occurs because progesterone inhibits the effects of prolactin.
After delivery, the levels of progesterone and estrogens in the mother’s blood decrease, and the inhibition is removed. The principal stimulus in maintaining prolactin production during lactation is the sucking action of the infant. Suckling initiates nerve impulses from stretch receptors in the nipples to the hypothalamus, and more prolactin is released by the anterior pituitary.
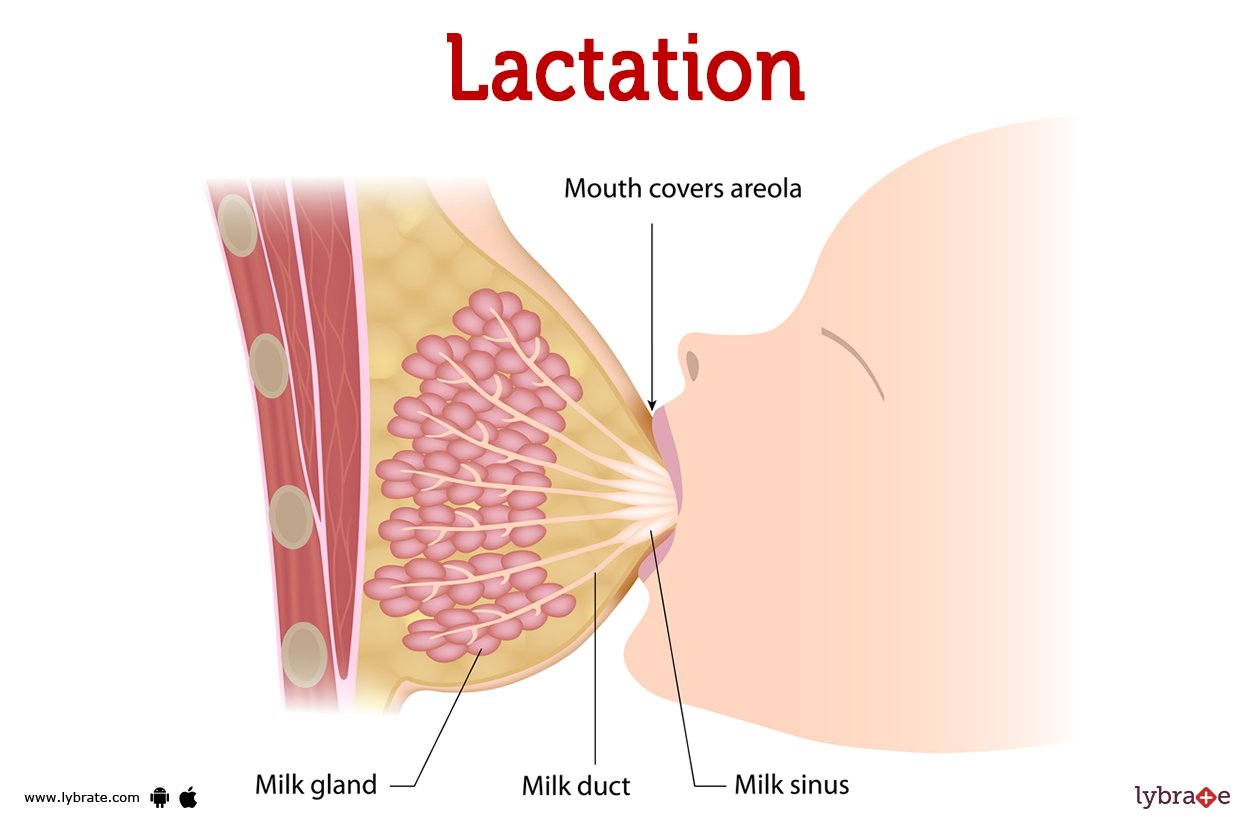
Oxytocin causes the release of milk into the mammary ducts. Milk formed by the glandular cells of the breasts is stored until the baby begins active suckling. Stimulation of touch receptors in the nipple initiates sensory nerve impulses that are relayed to the hypothalamus. In response, secretion of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary increases.
Oxytocin stimulates contraction of smooth-muscle-like cells surrounding the glandular cells and ducts. The resulting compression moves the milk from the alveoli of the mammary glands into the mammary ducts, where it can be suckled. During late pregnancy and the first few days after birth, the mammary glands secrete a cloudy fluid called colostrum.

Milk production and the milk-ejection reflex.
Lactation occurs in two stages: milk production (stimulated by prolactin) and milk ejection (stimulated by oxytocin). The stimulus of sucking triggers a neuroendocrine reflex that results in increased secretion of oxytocin and prolactin.
(Ref: DC Dutta’s Obst, 7th ed)
