Concept about Lumber puncture-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
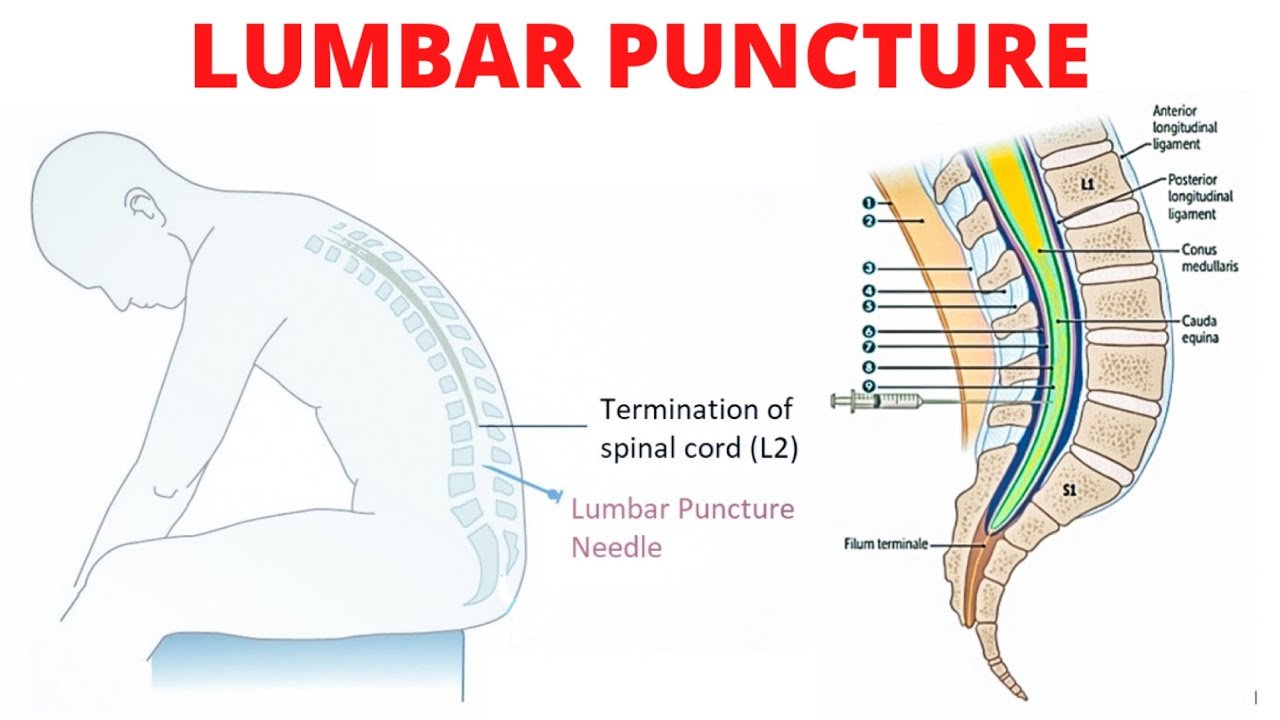
Concept about Lumber puncture
Lumbar puncture:
When indication of spinal anaesthesia or a specimen of CSF is required, it is taken from a point below the end of the cord; i.e below the 2nd lumbar vertebra. This procedure is called lumbar puncture.
Indications of Lumber or Spinal puncture:
A) Diagnostic purpose:
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Guillain Barre syndrome.
- Neurosyphilis
- Subarachonoid hemorrhage..
- Polio myelitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
B) Therapeutic purpose:
- Intrathecal administration of Methotrexate in case of acute leukemia.
- Spinal anaesthesia
Contraindication of lumber or spinal puncture:
- Very high CSF pressure (evidenced by papillaedema).
- Suspected Intracranial space occupying lesion or ICSOL eg. tumor, abscess, hematoma etc.
- Platelet count below 4 lac/cmm.
- Local infection at the puncture site.
- Meningomyelocele.
- Unconscious patient.
Complications of lumber puncture:
- Local pain
- Post-lumber puncture headache
- Hemorrhage
- Introduction of infection, e.g meningitis
- Herniation of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum.
(Ref:Ross & Wilson 9 ed, P-155)
Upper motor and lower motor neuron
Upper motor neuron:
The pyramidal cells of the motor cortex & its axons both corticospinal & corticonuclear tracts are called upper motor neuron.
They end in the motor nucler of the cranial nerves or anterior hom cells of the spinal cord.
Lower motor neuron:
The anterior horn cells of spinal cord & motor nucles of cranial nerves & their axon is called lower motor neuron.
Pain
Pain is the protective mechanism of the body, it occurs whenever any tissues are being damaged So pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage.
Pain receptor: Free nerve ending (Present in the superficial layer of skin)
Types of pain:
1. Fast pain
2. Slow pain
1. Fast pain:
Fast pain is also called-sharp pain, pricking pain, acute pain and electric pain. It occurs within 0.1 sec.
This type of pain is felt when
a) a needle is stuck into the skin
b) the skin is cut with a knife
c) the skin is acutely burned
d) the skin is exposed to electric shock etc
2. Slow pain:
Slow pain is also called slow burning pain, aching pain, throbbing pain and chronic pain. This type of pain usually associated with tissue destruction. It can lead to prolonged, unbearable suffering. It can occur in skin, deep tissue or organ.
(Ref: Guyton and Hall. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12 ed. P-598)
