Concept about Osteoblastoma – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Concept about Osteoblastoma
Definition osteoblastoma:
Osteoid osteoma is a benign osteoblastic tumor with a well-demarcated nidus of 1 than one cm surrounded by a distinct reactive bone.
[Ref-John Ebnezar’s, “Textbook of Orthopedics”, 4″ edition, P-6]
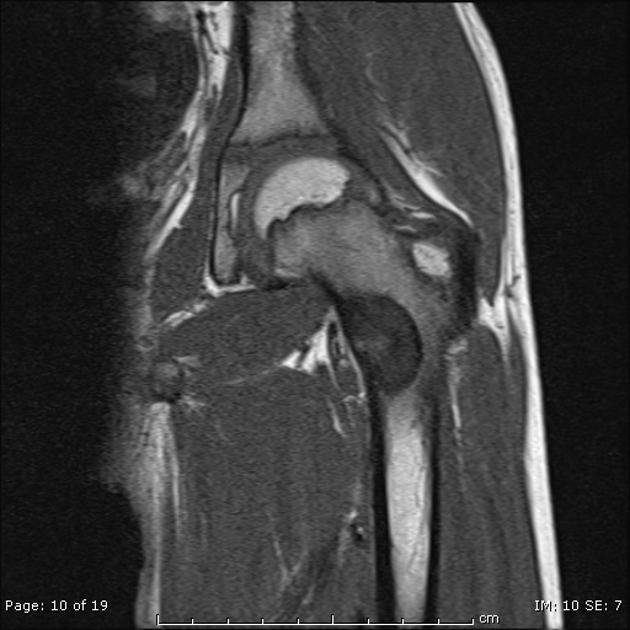
Clinical features of Giant Osteoid Osteoma:
1) Age: Commonly found in young adults between 10 and 25 years of age.
2) Sex: Male predominant (M: F-2: 1).
3) Site: It tends to occur in the spine and the flat bones.
4) Complain of vague and localized intermittent pain, which is more at night.
5) Complain of limp due to pain.
6) Mild swelling.
7) Local area may be tender.
8) Temperature is not raised.
9) Skin is not stretched, shiny or warm.
10) When the lesion occurs in the spine, the patient presents with acute backache.
11) Local muscle spasm.
[Ref- John Ebnezar’s, “Text Orthopedics”, ” edition, Page-624]
Treatment of Giant Osteoid Osteoma:
A) Conservative treatment:
1) Rest of affected part.
2) Analgesics.
B) Surgery: Excision and bone grafting
[Ref-John Ebnezar’s, “Text Orthopedics”, ” edition, Page-624]