Concept about Phagocytosis-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
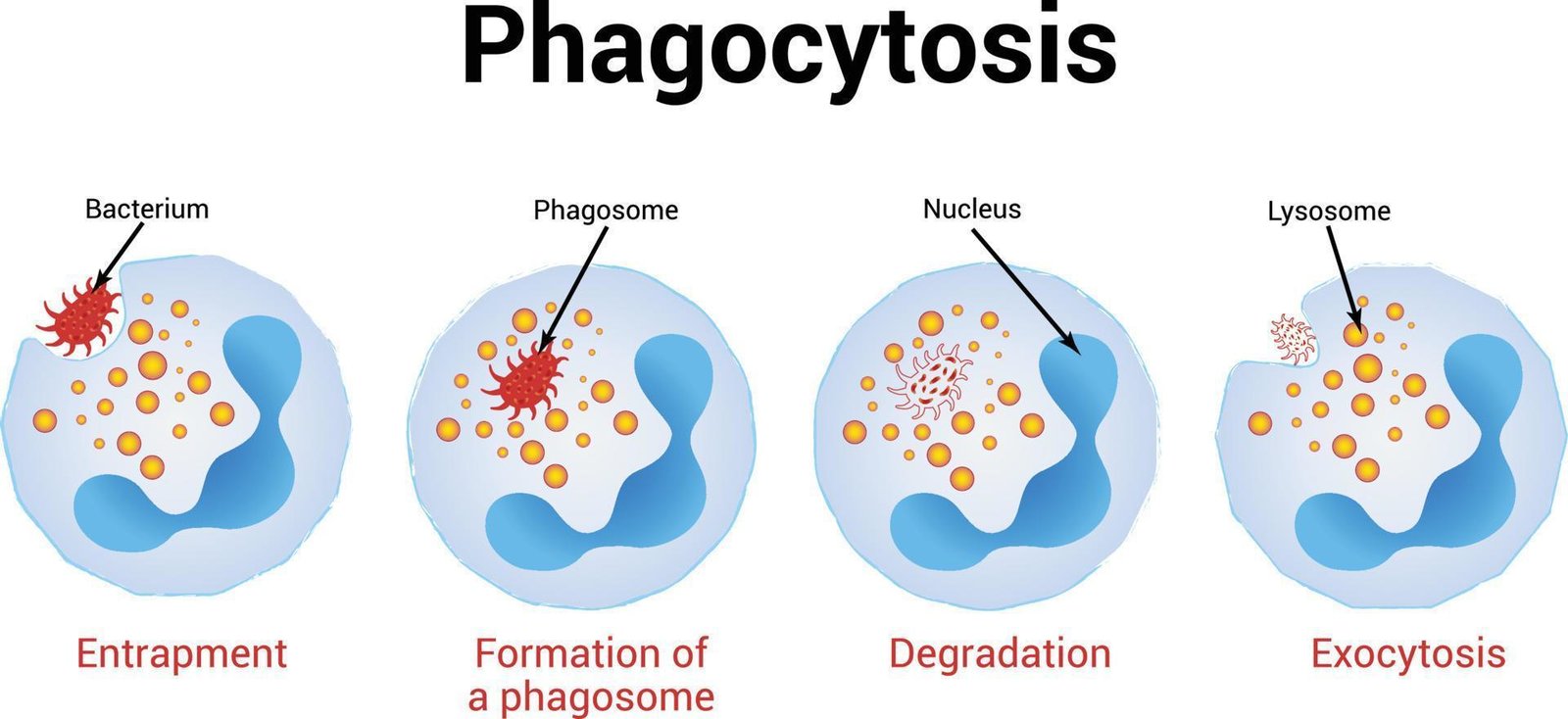
Concept about Phagocytosis
Phagocytes are specialized cells that perform phagocytosis, the ingestion of microbes or other particles such as cellular debris.
or,
Phagocytosis means, “cell eating”. The most important function of the neutrophils and macrophages is phagocytosis, which means cellular ingestion of the offending agents.
or,
Phagocytosis is a vital defense mechanism that helps protect the body from disease. Phagocytosis occurs only in phagocytes, cells that are specialized to engulf and destroy bacteria and other foreign substances.
Phagocytes include certain types of white blood cells and macrophages, which are present in most body tissues. The process of phagocytosis is a vital defense mechanism that helps protect the body from disease.
(Ref:- J. Tortora The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8 edition-P-52)
Events of Phagocytosis:
- Recognition & attachment.
- Engulfment
- Killing or degradation.
Phagocytic cells:
There are three major groups of phagocytic cells:
- Neutrophils,
- The cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system, including monocytes in the blood and macrophages (derived from monocytes) in the connective tissues; and
- Organ-specific phagocytes in the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, lungs, and brain.
Organ-specific phagocytes, such as the microglia of the brain, are embryologically and functionally related to macrophages and may be considered part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. The Kupffer cells in the liver, as well as phagocytic cells in the spleen and lymph nodes, are fixed phagocytes.
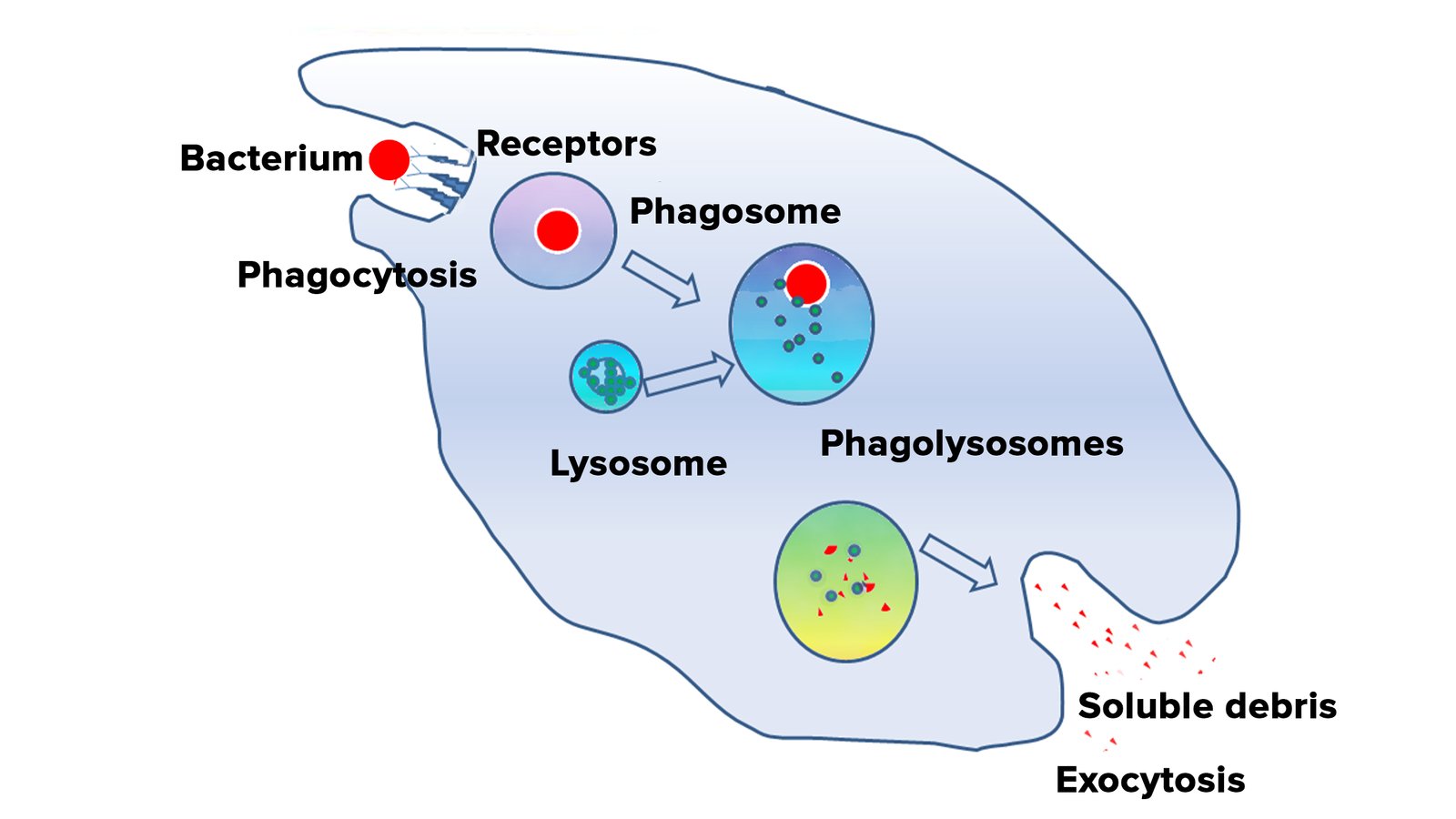
Importance of phagocytosis:
In this process, phagocytic cells engulf the foreign particles (bacteria, dead cells, tissue debris etc).
(Ref: Guyton and Hall, 12th ed, P-425 + Stuart Ira Fox, 12th edition, P-488)
Phagocytic Cells and Their Location
| Phagocyte | Location |
| Neutrophils | Blood and all tissues. |
| Monocytes | Blood |
| Tissue macrophages (histiocytes) | All tissues (including spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow |
| Kupffer cells | Liver |
| Alveolar macrophages | Lungs |
| Microglia | Central nervous system |
