Concept About Positioning – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Concept About Positioning
Definition of positioning:
Position defines that the attitude or posture of a patient as a particular posture used for some therapeutic procedure, which is used in hospital.
Positioning of the patient in bed:
Placing the patient in good body alignment as needed therapeutically is called positioning of the patient in bed.
[Reference: The Art of Nursing Practice, Annamma Jacob, Ed-1″, P-140]
Purposes of positioning:
1. To promote comfort to the patient.
2. To prevents complications caused by immobility. E.g.- pressure sore or bed sore.
3. To stimulate circulation.
4. To promote normal physiological functions.
5. To aid the physician in making or confirming a diagnosis. 6. To aid the physician in determining the type of treatment necessary.
7. To make the patient in comfortable and relaxation. 8. To provide for his/her privacy and safety.
[Reference: The Art of Nursing Practice, Annamma Jacob, Ed-1″, P-140+ Lecture]

General principles of positioning:
1. Maintain body mechanics.
2. Obtain assistance as required.
3. Ensure that mattress is firm and level of bed is at working height.
4. Ensure that sheets are clean and dirty.
5. Avoid placing a body part directly over another to prevent pressure. 6. Plan a regular position change schedule for the patient for 24 hours.
7. Ensure patient comfort.
8. Wash hands before and after procedure.
[Reference: The Art of Nursing Practice, Annamma Jacob, Ed-I”, P-140]

Name of the positioning of the patient in bed:
1. Fowler’s position:
- Fowler’s position: 40°-90° angle.
- Semi fowler’s position: 15°-45° angle.
- High fowler’s position: 90″ angle.
2. Orthopneic position.
3.Supine position / Dorsal recumbent position/Back lying.
4. Horizontal recumbent position.
5. Prone position.
6. Lateral position/Side lying position.
7. Sim’s position.
8. Dorsal lithotomy position.
9. Trendlenburg position.
10. Knee-chest/Genupectoral position.
[Reference: The Art of Nursing Practice, Annamma Jacob, Ed-1, P-(140-145) + Lecture]
| Name of the bed positioning of patient | Example |
| Fowler’s position: a. Fowler’s position: 40°-90° angle. b. Semi fowler’s position: 15°-45° angle. c. High fowler’s position: 90° angle. | 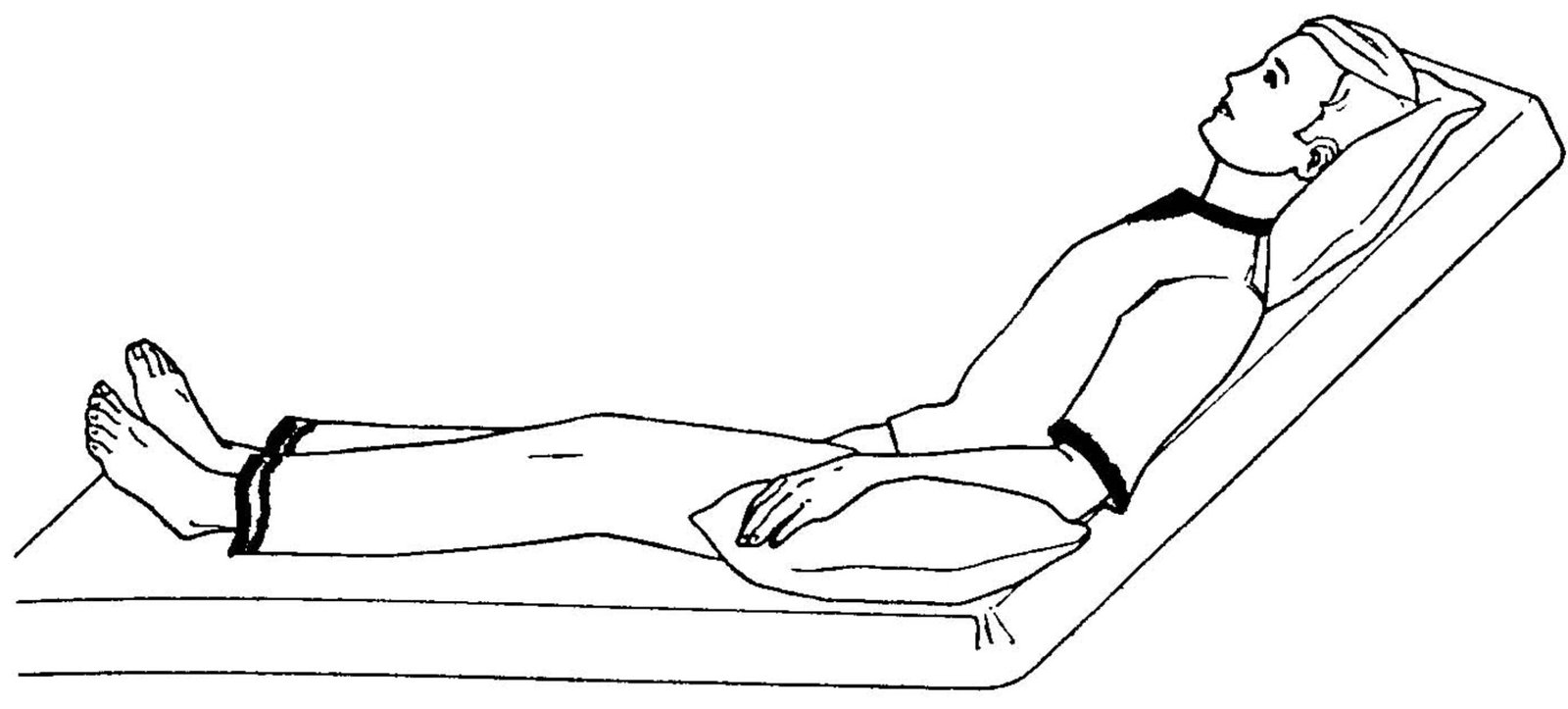 |
| Supine position / Dorsal recumbent position /Back lying |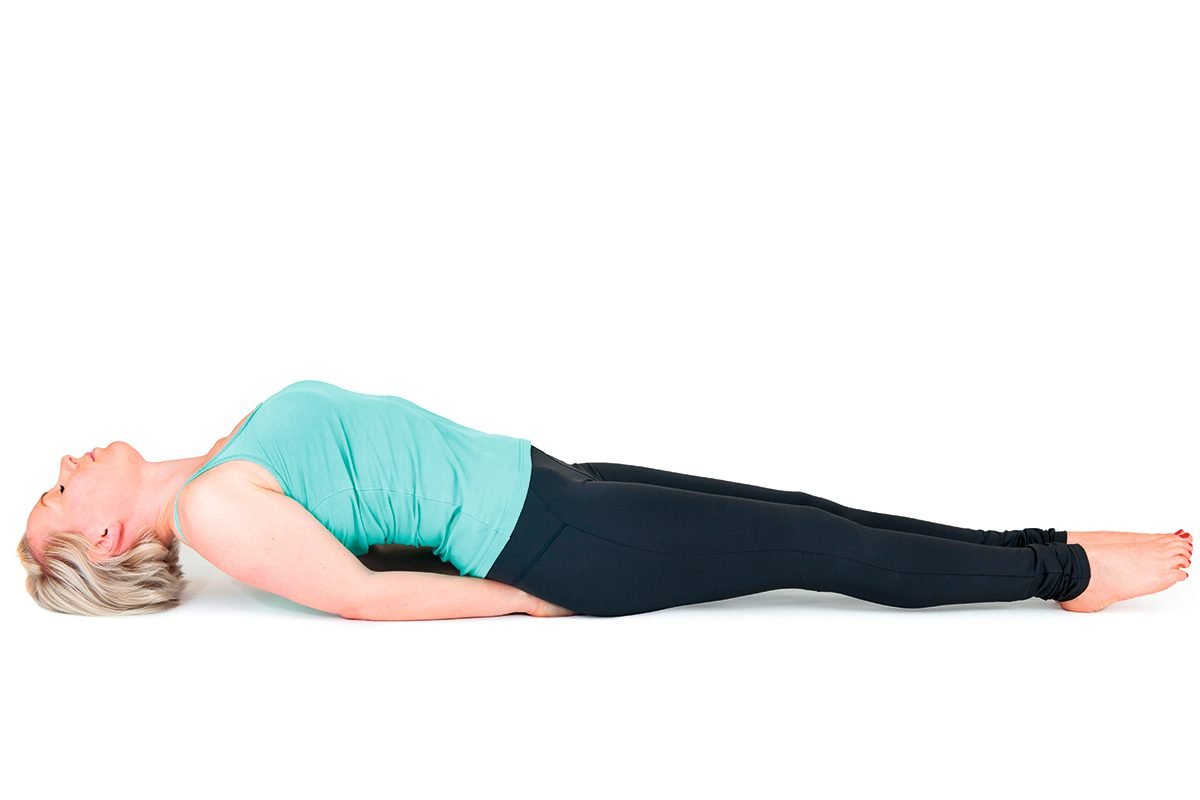  |
| Horizontal recumbent position |  |
| Prone position | 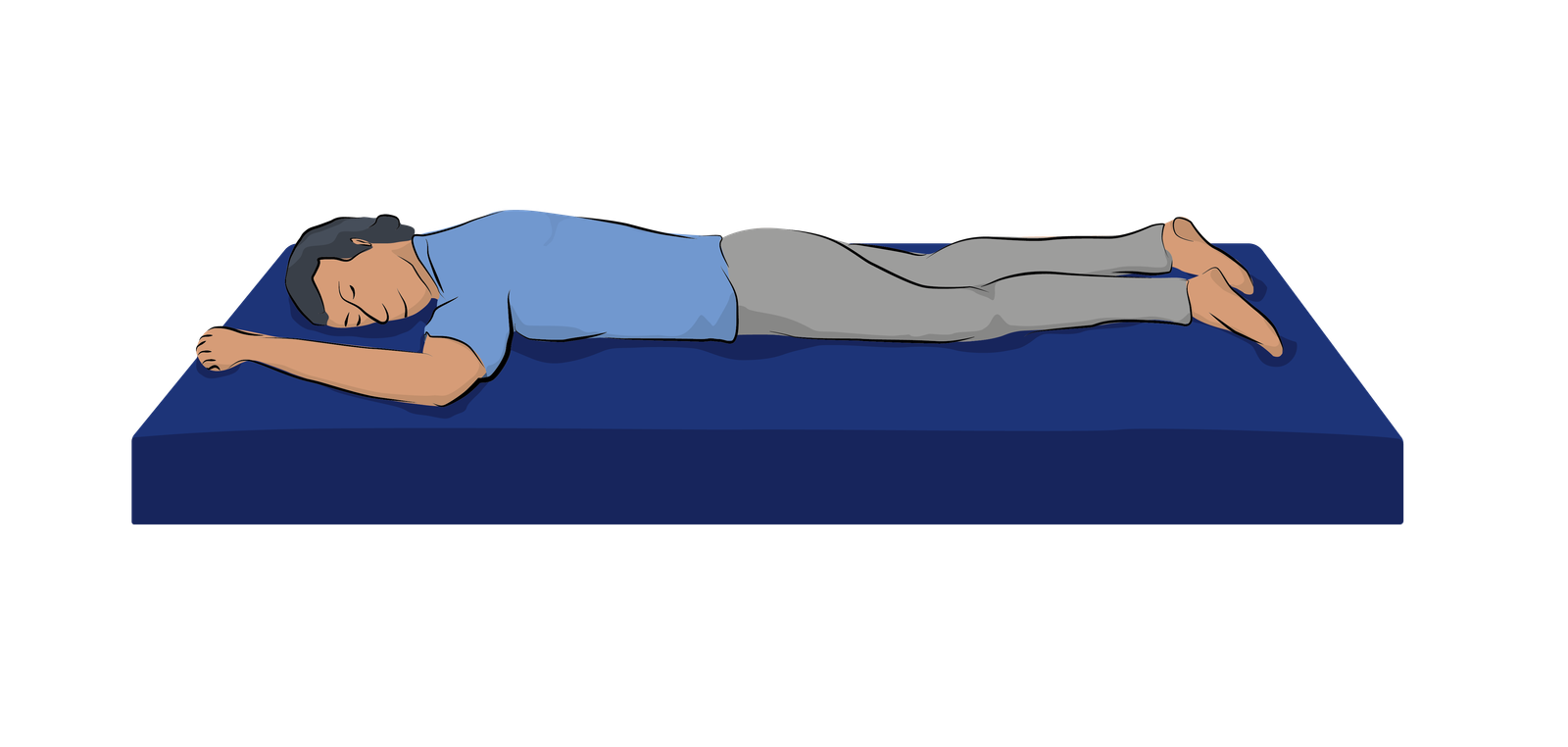 |
| Lateral position/Side lying position | 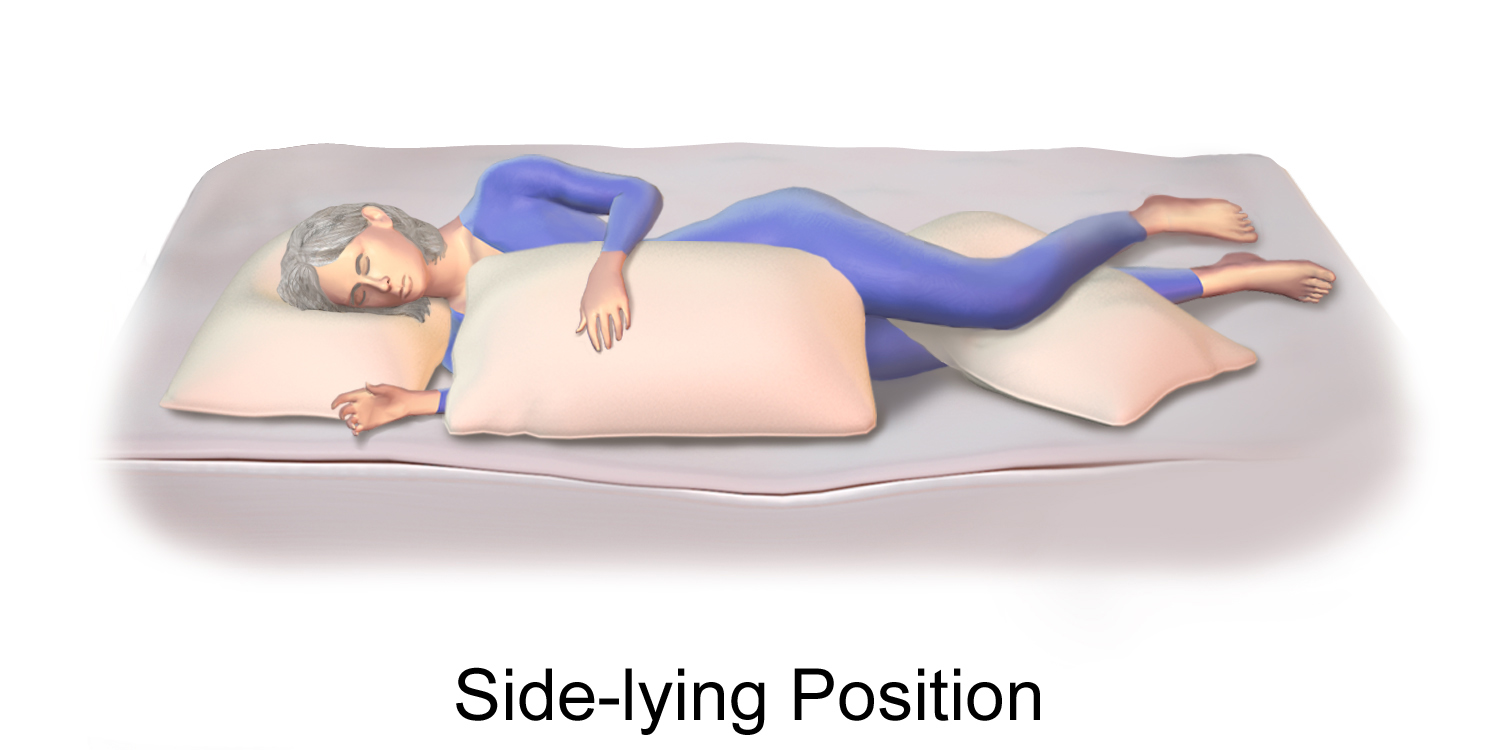 |
| Sim’s position / semi prone position | 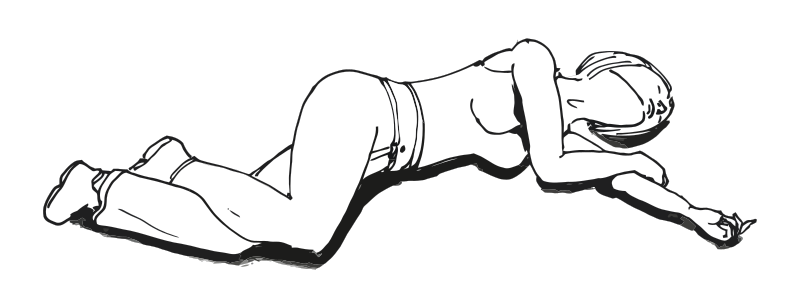 |
| Dorsal lithotomy position | 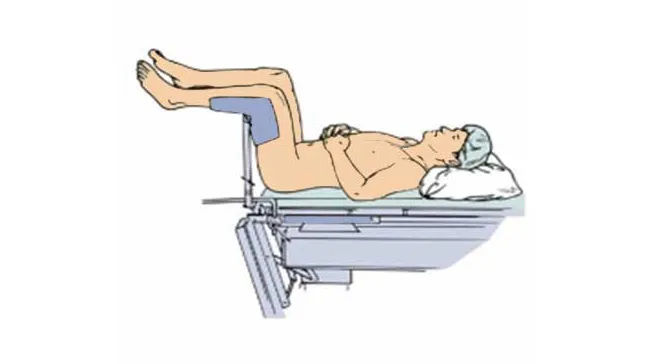 |
| Trendlenburg position | 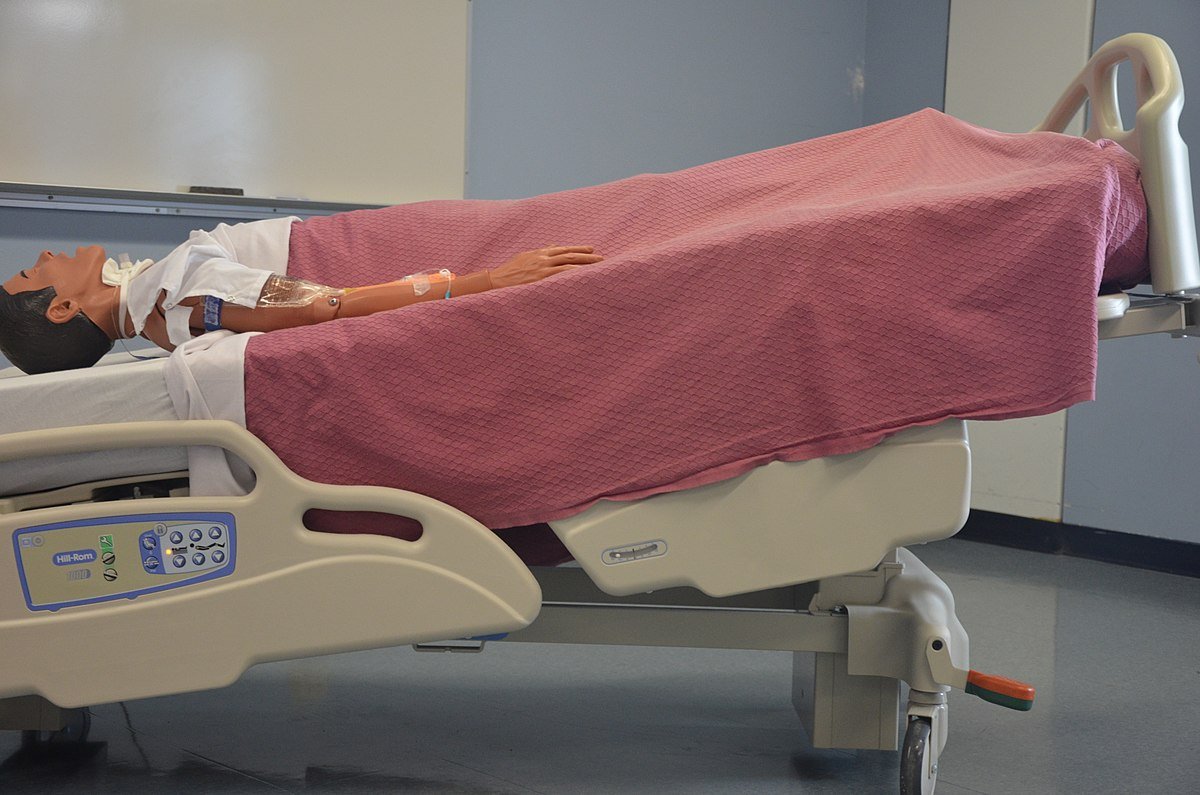 |
| Knee-chest/Genupectoral position |  |
| Right lateral recumbent position | 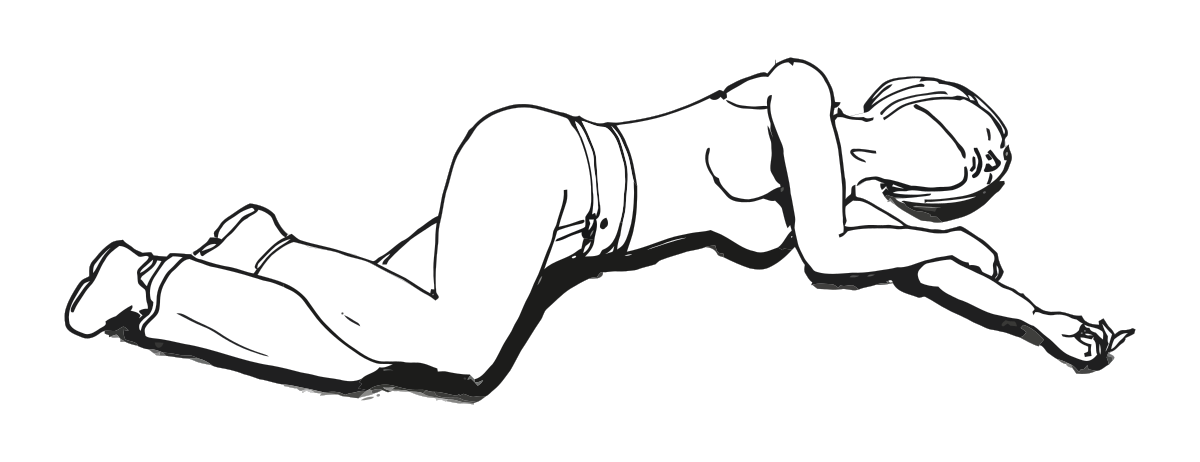 |
| Left lateral recumbent position |  |
| Orthopneic position | 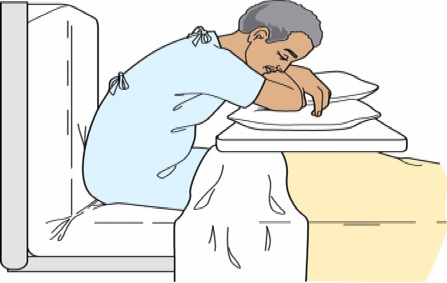 |
| Knee chest |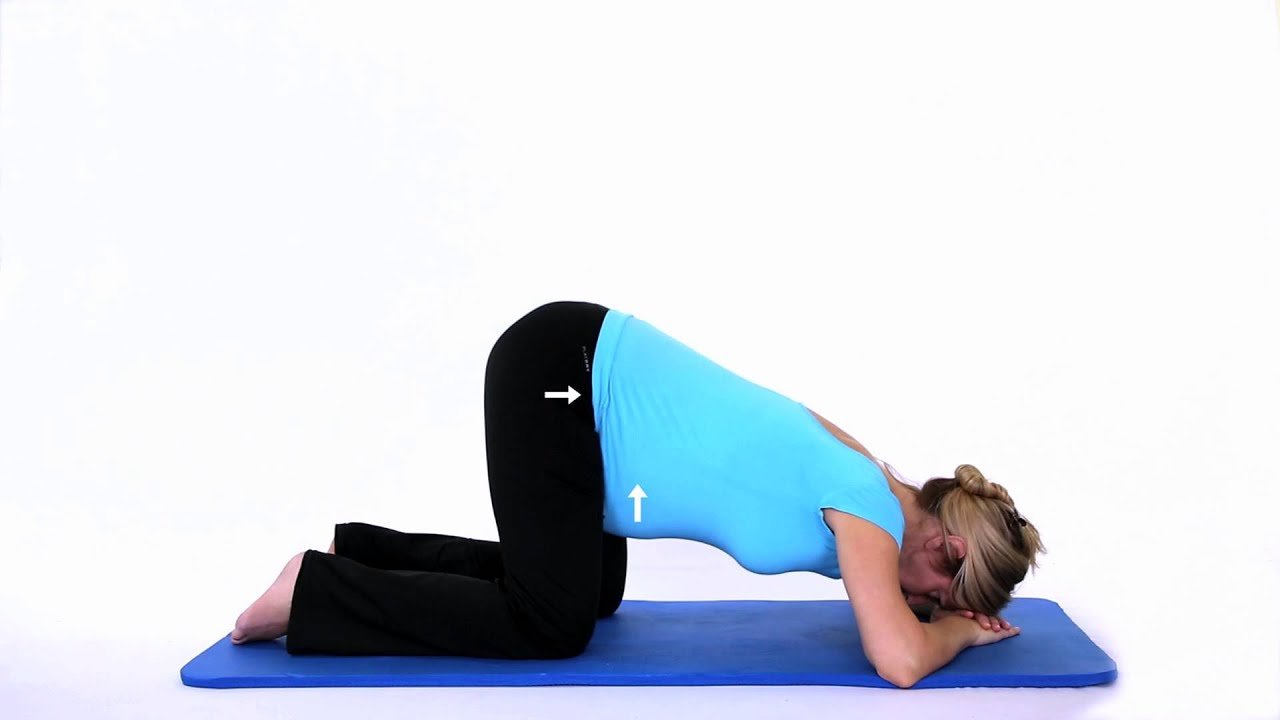  |
| Standing position |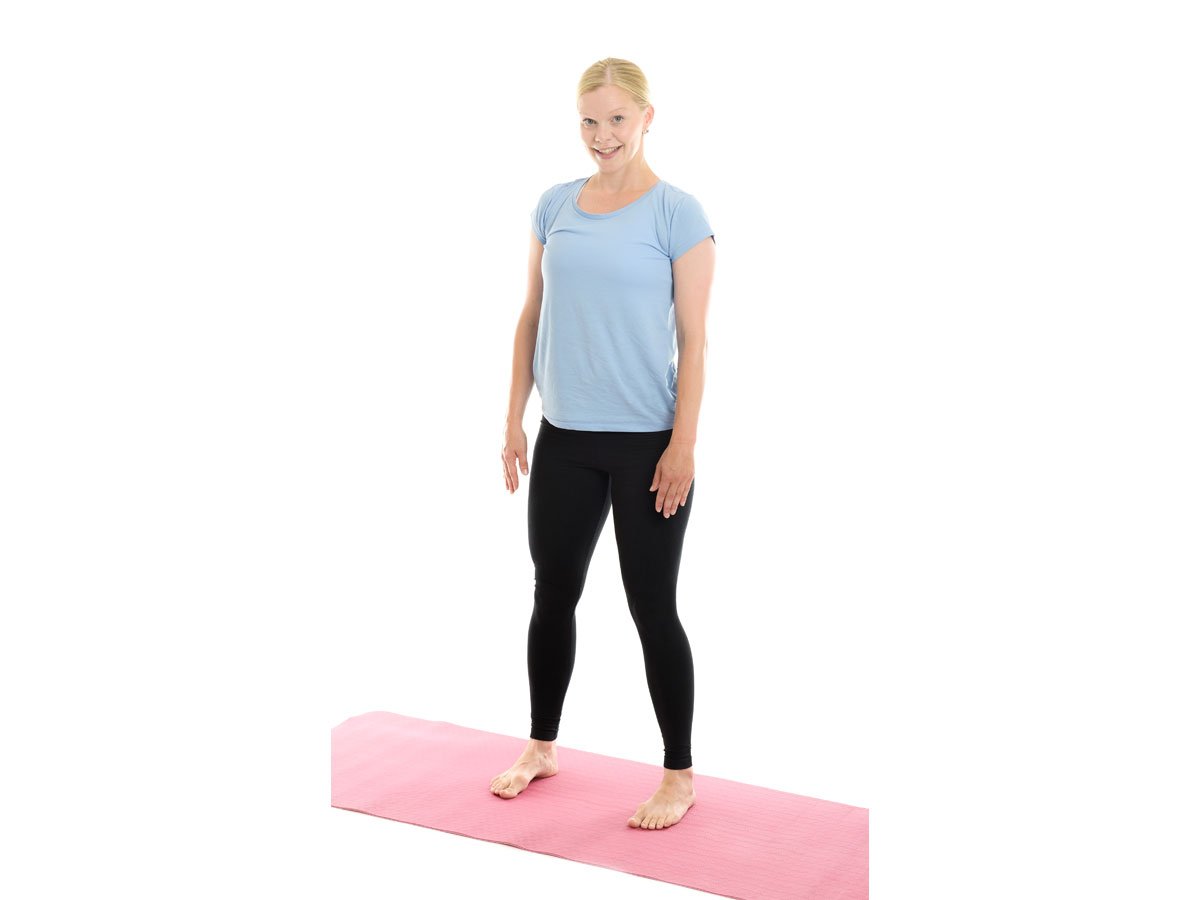  |
| Sitting position |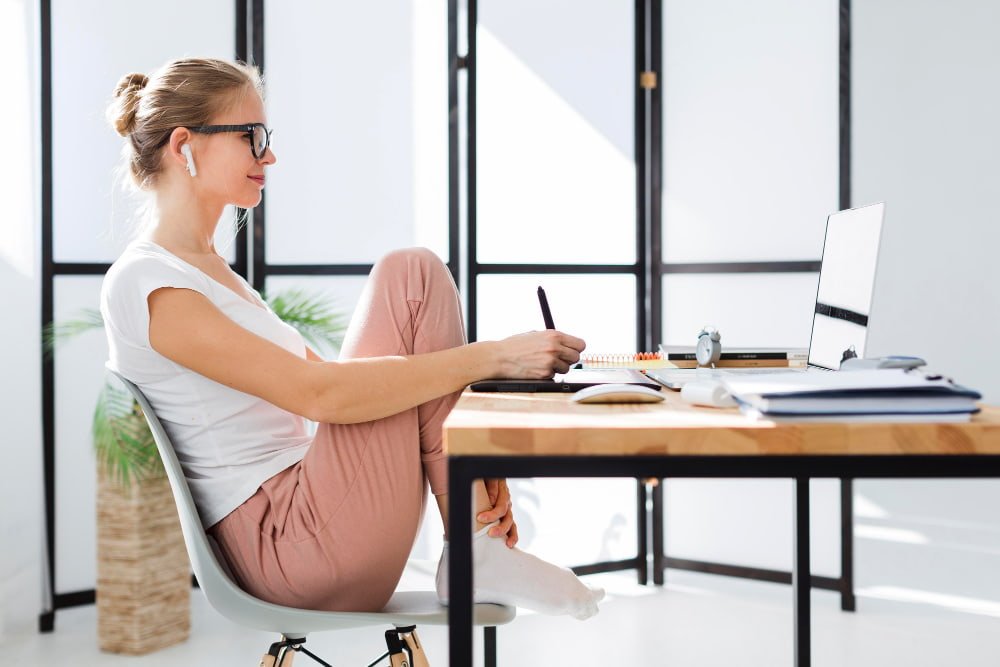  |
| Squatting position |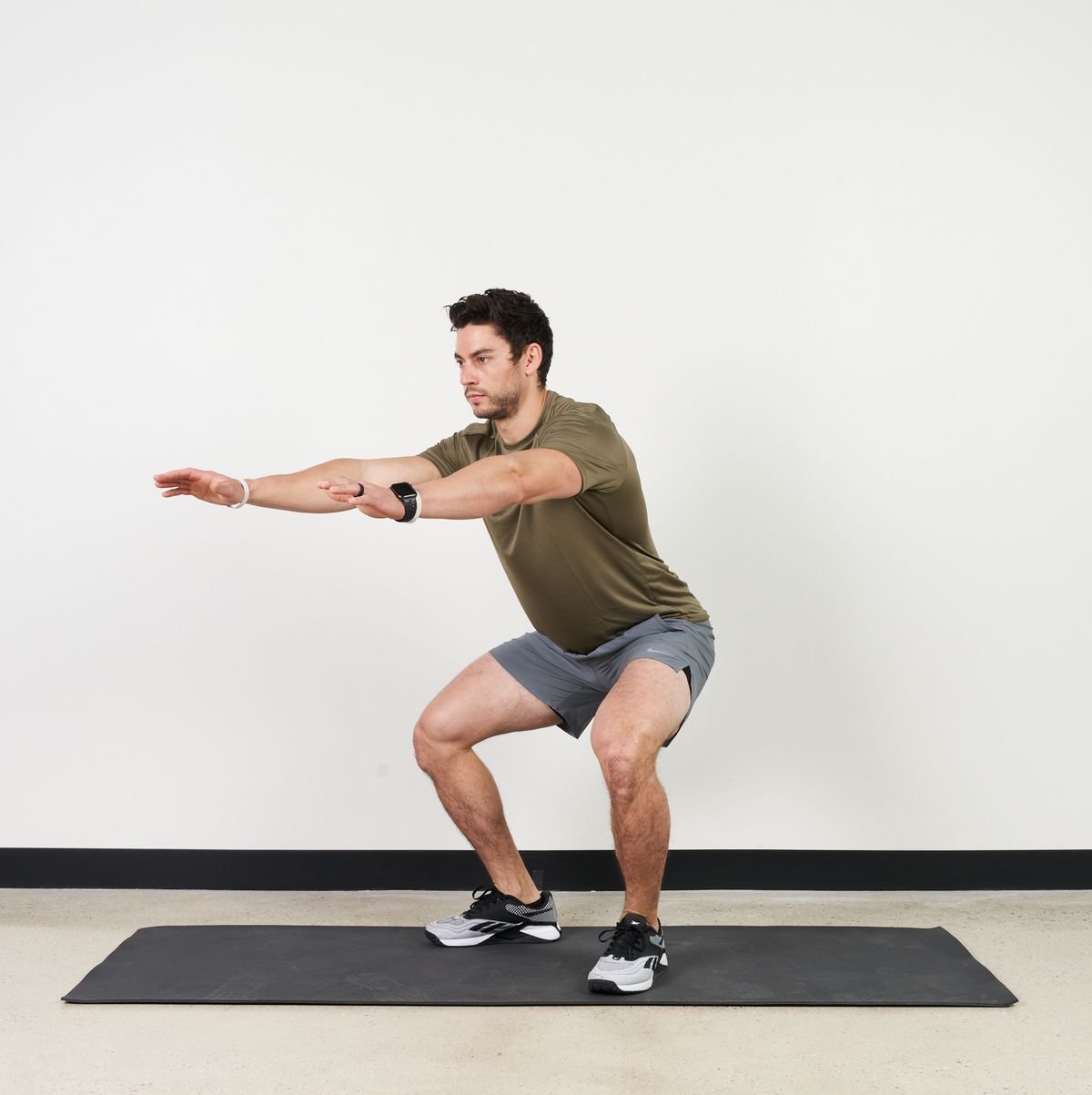  |
[Reference: The Art of Nursing Practice, Annamma Jacob Ed-I”, P-(140-145)+Lecture+ Internet]
Therapeutic exercise:
Therapeutic exercise is the motion of the body or its parts to achive symptom free movement and function

Importance or of therapeutic exercise for disable patient:
1. To develop and retrain deficient muscles.
2. To restore as much normal movement as possible to prevent deformity.
3. To stimulate the function of various organ and body systems.
4. To build strength and endurance.
5. To promote relaxation.

Read more:
