Concept about Xerophthalmia – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Concept about Xerophthalmia
Xerophthalmia:
Xerophthalmia is a progressive eye disease caused by vitamin A deficiency. Lack of vitamin A can dry out the tear ducts and eyes.
Or
The term xerophthalmia covers all the ocular manifestations of vitamin A deficiency. Xerophthalmia can progress to irreversible blindness if left untreated.
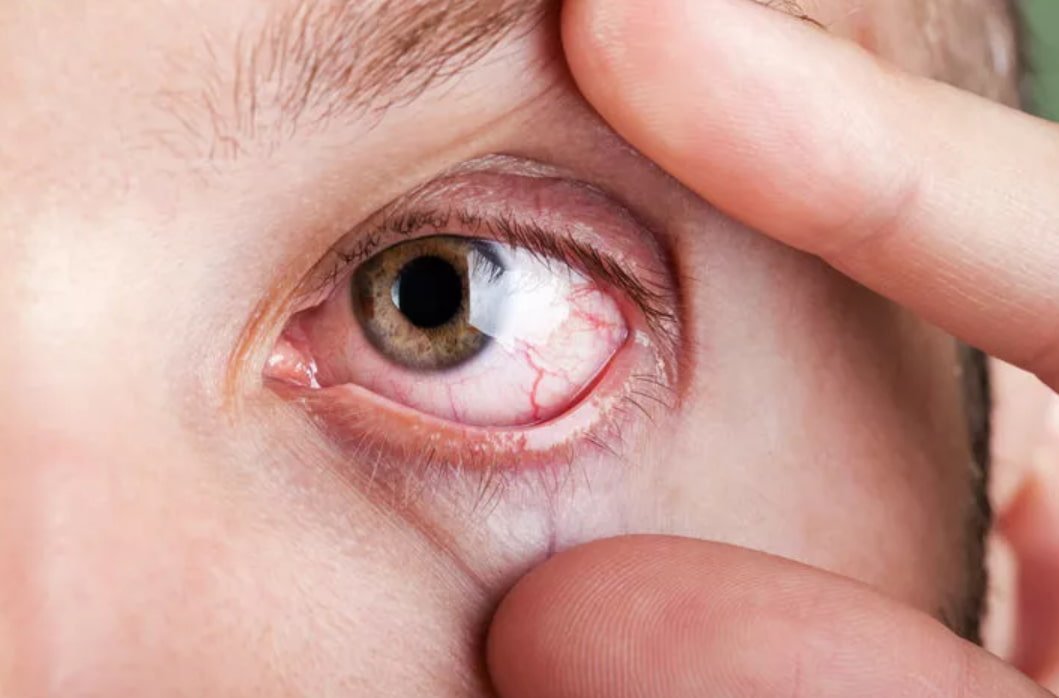
Xerophthalmia is a medical condition in which the eye fails to produce tears. It may be caused by vitamin A deficiency, which is sometimes used to describe that condition, although there may be other causes.
Risk factors of Xeronhthalmia:
1. Ignorance.
2. Faulty feeding practices.
3. Infection particularly diarrhea and measles.
4. PEM.
5. Faulty weaning.
(Ref: K. Park/234/617-618)
Ocular Changes Due to Vitamin A Deficiency:
1. Night blindness: Night blindness (nyctalopia) or inability to see in dim light is the earliest symptom of Vitamin A deficiency.
2. Conjuctival xerosis: The conjunctiva appears muddy and wrinkled, instead of looking clear and transparent. It becomes dry and unwetable. This is the first clinical sign of Vitamin A deficiency.
3. Bitot’s spots: These are triangular, pearly-white or yellowish, foamy spots on the bulbar conjunctiva on either side of the cornea. They are frequently bilateral.
4. Cornal xerosis: The corneal surface becomes dull, dry and non-wetable and eventually opaque.
5. Corneal ulceration / keratomalacia: There may be corneal ulceration with keratomalacia or liquefaction of the cornea. The cornea (a part or the whole) may become soft and may burst open.
6. Corneal scar: The corneal ulceration may heal leaving a corneal scar which can affect vision.

WHO classification
| Classification Code | Clinical Description |
| 1. XN |
|
| 2. ΧΙΑ |
|
| 3. XIB |
|
| 4. X2 |
|
| 5. X3A |
|
| 6. X3B |
|
| 7. XS |
|
| 8. XF |
|
Pathology of Xerophthalmia:
- Vitamin A is necessary for light appreciation in the eye. The photosensitive pigments opsin and iodopsin are bound to retinal (oxidised retinol) which retains the cis-form in the dark and the transform in the light. The change from cis- and the trans- form releases energy and stimulates never endings. So, in vitamin A deficiency the earliest sign is impaired dark adaptation resulting in Xerophthalmia.
- Dryness of the cornea (corneal xerosis) and conjunctiva (conjunctival xerosis) is due to hyperplasia and metaplasia of the epithelium
- The Bitot’s spots are due to metaplasia of epithelium with collection of Meibomian secretion on it.
- Corneal ulceration/keratomalacia is due to necrosis of carneal substance.
(Ref: K. Park/23rd/617-618)
Causes of Blindness:
| Main causes in developed countries |
|
| Main causes in developing countries: |
|
(Ref: K. Park/234/617-618)
Preventive Measures Of Vitamin A Deficiency Disorder:
- Periodic administration of high-doses of vitamin A (2,00000 IU) is an effective measure of controlling vitamin A deficiency.
- Adequate treatment and supplementation for mal-nutrition, diarrhea infection and, measles.
- Long term measures including nutrition education such as local sources of the vitamin A or carotenoids, production anti consumption of foods rich in vitamin A or pro-vitamin A and fortification of foods with vitamin A.
- Programs to encourage breast feeding increased consumption of dark green leafy vegetables, carrot, egg, liver, fish and meal cod liver oil, small fish etc. can be provided when parents can afford.
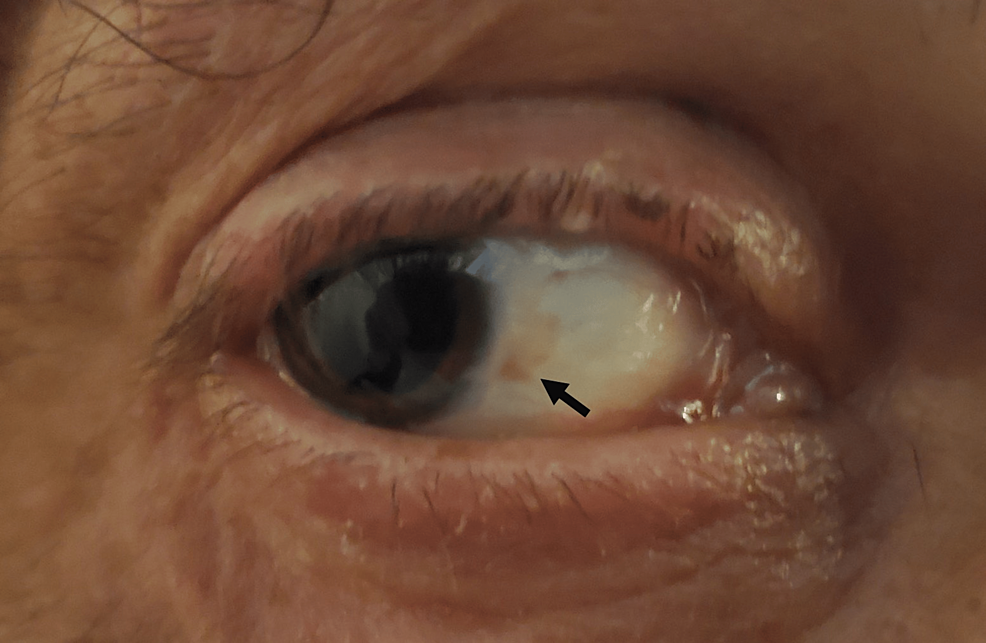
Treatment of Xerophthalmia:
A. Vitamin A supplementation should be done on day 1st, 2nd and 8th days (3 doses) according to the following dose:
| Age of the child | Dose of vitamin A |
| <6 months | 50000 IU |
| 6 months to 12 months | 100000 IU |
| >1 year | 200000 IU |
B. Treatment of underlying conditions such as PEM, diarrhea, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance and infection.
C. Antibiotic if secondary bacterial infections
D. Local treatment of eye, if disorganized
Read more:
