Concept of Delegation of Authority – this book covers the entire syllabus of “Leadership & Management” prescribed by the BNMC for Diploma in Nursing Science & Midwifery Students.
We tried to accommodate latest information and topics. This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the pook students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Concept of Delegation of Authority
A manager alone cannot perform all the tasks assigned to him. In order to meet the targets, the manager should delegate authority. Delegation of Authority means division of authority and powers downwards to the subordinate. Delegation is about entrusting someone else to do parts of your job. Delegation of authority can be defined as subdivision and sub-allocation of powers to the subordinates in order to achieve effective results.

Definition of Delegation of Authority
According to F.C. Moore,
“Delegation means assigning work to the others and giving them authority to do so.”
According to O. S. Miner,
“Delegation takes place when one person gives another the right to perform work on his behalf and in his name and the second person accepts a corresponding duty or obligation to do that is required of him.”
Purposes of Delegation of Authority
- To reduce the excessive burden on the superiors i.e., executives and managers functioning at different levels.
- To provide opportunities of growth and self-development to junior executives.
- To create a team of experienced and matured managers for the Organization. It acts as a technique of management and human resource development.
- To improve individual as well as overall efficiency of the Organization
Process of Delegation of Authority:
process of delegation of authority comprises of four steps which are as follows:
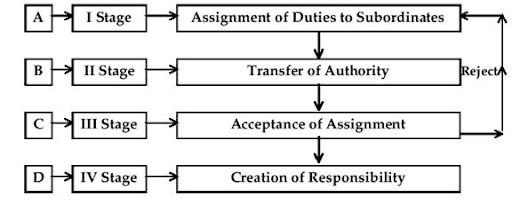
A. Assignment of Duties to Subordinates: Before the actual delegation of authority, the delegator must decide on the duties which he wants the subordinate or the group of subordinates to perform. Here, the manager lists the activities to be performed along with the targets to be achieved, and the same is spelled out to the subordinates. Thus, in the first stage, the duties are assigned to the subordinates as per their job roles.
B. Transfer of Authority to perform the duty: At this stage, an adequate authority is delegated to the subordinate which is essential to perform the duty assigned to him. A manager must make sure; that authority is strictly delegated just to perform the responsibility, as more authority may lead to its misuse by the subordinate.
C. Acceptance of the Assignment: At this stage, the subordinate either accepts or rejects the tasks assigned to him by his superior. If the subordinate or the delegate, refuses to accept the duty and the authority to perform it, then the manager looks for the other person who is capable of and is willing to undertake the assignment. Once the assignment gets accepted by the subordinate, the delegation process reaches its last stage,
D. Creation of Responsibility/Accountability: The process of delegation of authority ends at the creation of an obligation on the part of the subordinate to perform his responsibility within the powers assigned to him. Once the assignment is accepted by the subordinate, then he becomes responsible for the completion of the duty and is accountable to the superior for his performance.
What step can be taken for delegation authority effectively?
The following steps can be taken to ensure effective delegation:-
1. Plan a head in identifying task to be accomplished.
2. Identify the skill and education best level, necessary to complete the job…
3. Signal out the individual best able to complete the job, it term of capability as well as available.
4. Clearly communication exactly what is to be done?
5. The manager must be sure to delegate the authority as well as the responsibility, necessary to complete the task.
6. Timeframes should be set and monitor how the task is being accomplished.
7. If the subordinate having difficulty to carrying out the delegates, the manager should available as role model and resource in helping the subordinate identify other alternative solution.
8. Evaluate the performance of the subordinate after the task has been completed.
Discuss the types of authority that should not be delegated?
The following areas of authority should not be delegated:
1. Supervisory function.
2. Organization of staff development
3. Checking an individual’s results.
4. Communication to staff.
5. Planning and setting of staff objectives.
6. Ethical issue.
7. Economical/financial function.
8. Confidential work

