Concept of Gland – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept of Gland
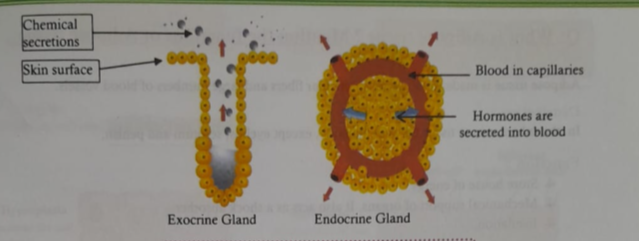
Glands are groups of epithelial cells that produce specialized secretion. There are usually two categories of glands.
A. Exocrine glands (from the Greek exo = outside) secrete chemicals through a duct that leads to the outside of a membrane, and thus to the outside of a body surface. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, lacrimal, sebaceous, and mucous.
Functions Of Exocrine Glands
They perform the following functions:
- Regulate body temperature
- Lubrication
- Lactation
- Helps in digestion
- Helps in reproduction
Classification of exocrine gland:
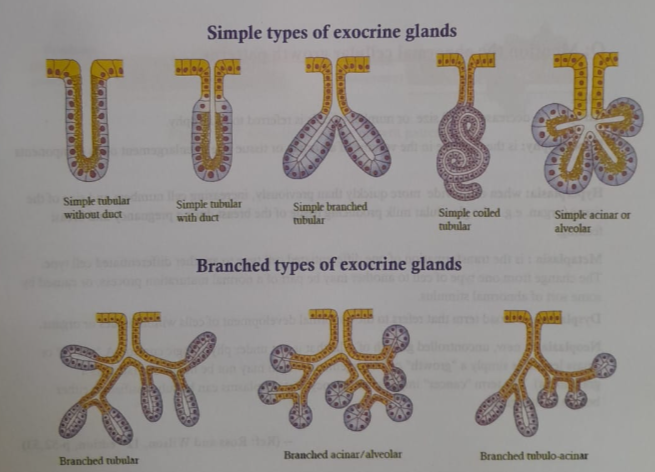
Exocrine glands are classified in the following way:
According to Duct Structure
- SIMPLE-single unbranched duct (glands of large intestine)
- COMPOUND – branched duct (salivary glands)
According to Shape of Secretory Units
- TUBULAR (alveolar) – (sweat glands)
- ACINOUS (acinar) – shaped like a grape (salivary glands)
According to Mechanism of Secretion
- Merocrine-product released by exocytosis (most sweat glands). The most common type of secretion.
- Holocrine- whole cell ruptures during release of product (sebaceous glands).
A third type of secretion: apocrine was also once described, but these glands are in fact mostly merocrine.
B. Endocrine glands (from the Greek endon = within) secrete chemicals called hormones into the blood. The gland that makes hormones that are released directly into the blood and travel to tissues and organs all over the body is known as endocrine gland.
Examples of endocrine glands include thyroid, adrenal and pituitary glands.
N.B : There are some glands having both exocrine and endocrine functions, these glands are called Mixed Gland.
Examples of Mixed gland: Pancreas, Liver
