Concept of Hepatitis – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Concept of Hepatitis
Definition of hepatitis:
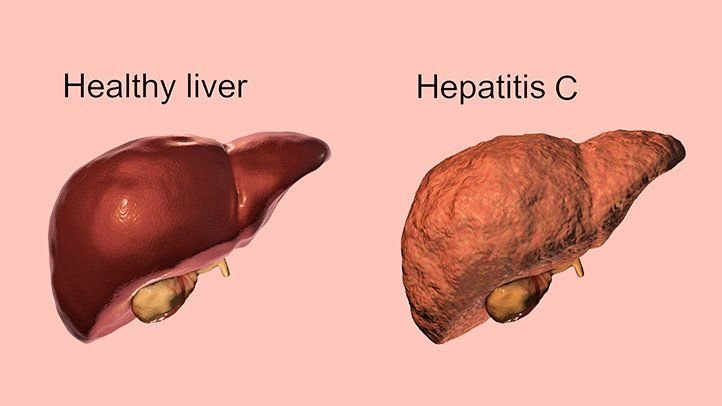
According to world Health organization (WHO), Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. The condition can be self-limiting or can progress to fibrosis (scarring), cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Or
Hepatitisis usually refers a disease characterized by inflammation of the liver. In particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease liver in hundreds of millions of people and, together, are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis and cancer.
Hepatitis during pregnancy:
Hepatitis is an infection and inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. There are several different kinds of hepatitis viruses, including hepatitis A, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Types of hepatitis:
a) Hepatitis A virus.
b) Hepatitis B virus.
c) Hepatitis C virus.
d) Hepatitis D virus.
e) Hepatitis E virus.
Hepatitis E is most common in pregnancy with A, B, C hepatitis virus.
Risk factors of hepatitis in pregnancy:
➤Workers in the health care professions.
➤Sewage and water treatment workers. People with multiple sexual partners
➤Intravenous drug users.
➤HIV patients.
➤People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors.
➤Travel or work in regions with high rates of hepatitis. Attend child care or work in a child care center.
➤Live with another person who has hepatitis.
➤Have oral-anal contact with someone who has hepatitis.
auses of hepatitis in pregnancy:
➤ Contaminated injecting equipment.
➤Sharing needles.
➤Blood contact on open wounds.
➤Drinking contaminated water.
➤Professional blood donor..
➤Insects and flies act as a carrier.
➤Unprotected sex and intercourse.
➤Homosexual and heterosexual.
➤Mother to fetus through placenta.
➤ Eating food handled by someone with the virus who doesn’t thoroughly wash his or her hands after using the toilet.
➤Drinking contaminated water.
➤Eating raw shellfish from water polluted with sewage.
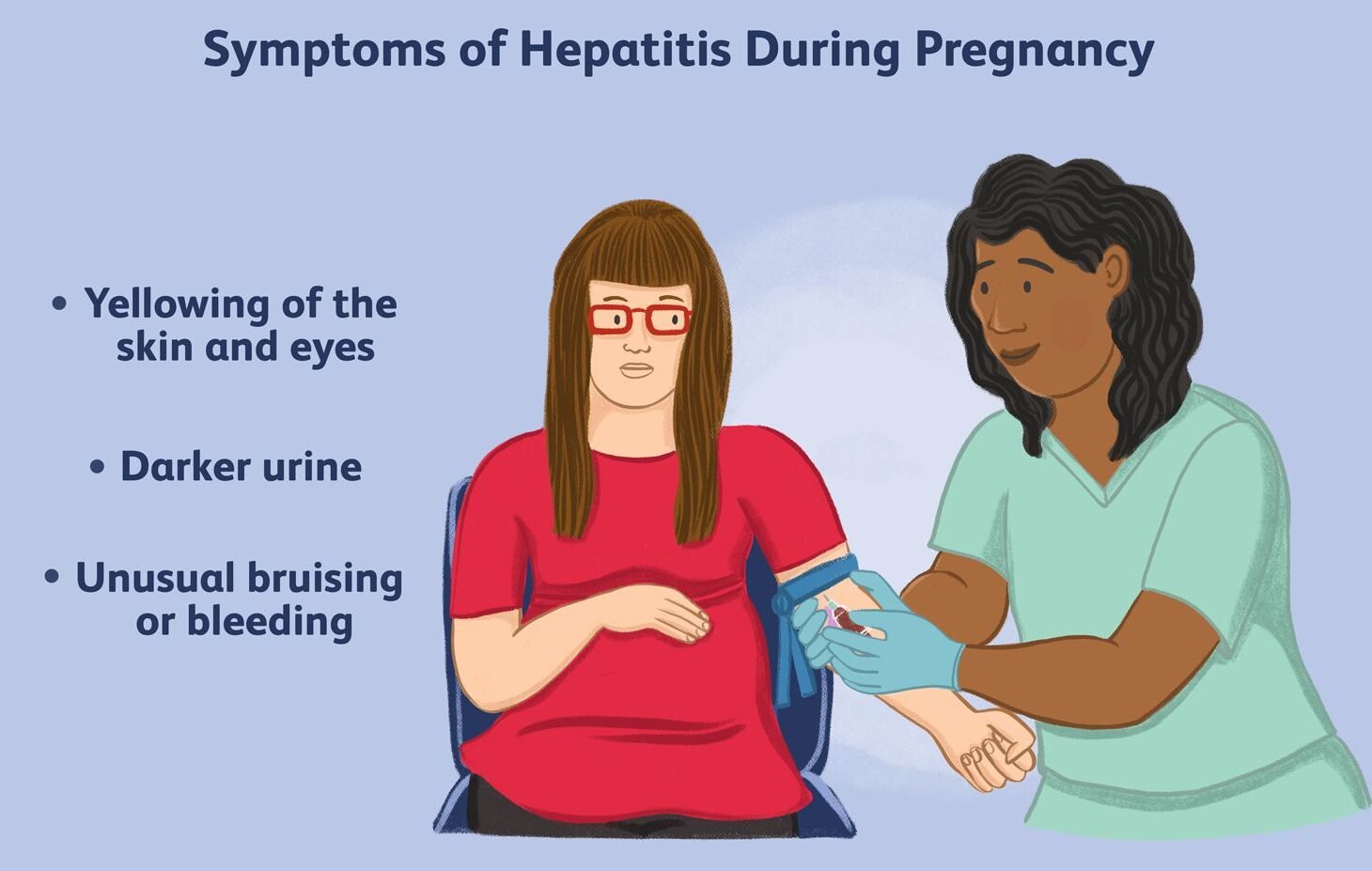
Signs and symptoms of hepatitis in pregnancy:
➤Flu-like symptoms, such as tiredness, aching in the abdomen and pains for up to ten days.
➤Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
➤Loss of appetite.
➤ Nausea and vomiting.
➤ Fatigue for one to three weeks.
➤ Dark urine and light colored stools.
➤Weakness.
➤Fever
➤Abdominal pain.
Diagnosis of hepatitis in pregnancy:
➤ Clinical sign and symptoms not suggestive, unless through history and labs.
➤ Serum anti-HIV antibodies test (IgM and IgG).
➤ ALT (Alanine Amino-Transferase) test.
➤ Liver biopsy: for cirrhosis, prognosis.
➤ Serologic tests.
➤ RNA-hased detection tests.
Nursing management/intervention of hepatitis during pregnancy:
➤ Ensure appropriate isolation and precautions.
➤ If a pregnant woman has confirmed hepatitis infection such as especially A, B, C in pregnancy there is a risk of transmission to her baby.
➤ If pregnant mother has antibody, then give hepatitis (A, B, C) vaccine soon after birth and then at months 1, 2 and 12 with lifelong dosages.
➤ If pregnant mother has no antibody or the mother acquired hepatitis infection during pregnancy, the baby should receive hepatitis vaccine as above plus hepatitis B immunoglobulin as soon after birth as possible.
➤ Diet according to the patient preference, parental if necessary Antiemetics: Phenothiazines may be used according to doctor advice.
➤ Immuno-prophylaxis of infant if HBV is present.
➤ Baby will need a blood test at 12 months to ensure that he/she has not become infected.
Complication of hepatitis during pregnancy:
➤ Acute fatty liver of pregnancy,
➤ Severe preeclampsia.
➤ HELLP syndrome (Hemolysis, Elevated liver enzymes, and Low platelets).
➤ Obstetric complication such as obstetric labor during birth.
➤ Malformation of the fetus.
➤ Premature labor.
➤ Fetal demise/still birth.
➤ Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
➤ Major obstetric complication including PROM, IUGR.
Prevention of hepatitis during pregnancy:
➤ Wash your hands after going to the bathroom and before fixing food or eating.
➤ Use latex condoms, which may lower the risk of transmission.
➤ Don’t share drug needles & injecting equipment
➤ Don’t share personal items such as toothbrushes, razors and nail clippers with an infected person
➤ Avoid blood contact on open wounds.
➤ Avoid drinking contaminated water.
➤Professional blood donor should be discourage.
➤ Avoid unprotected sex and intercourse.
➤Discourage people to have homosexual and heterosexual activities.
➤ Not to become pregnant after exposure to hepatitis disease.
