Concept of Menorrhagia – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Concept of Menorrhagia
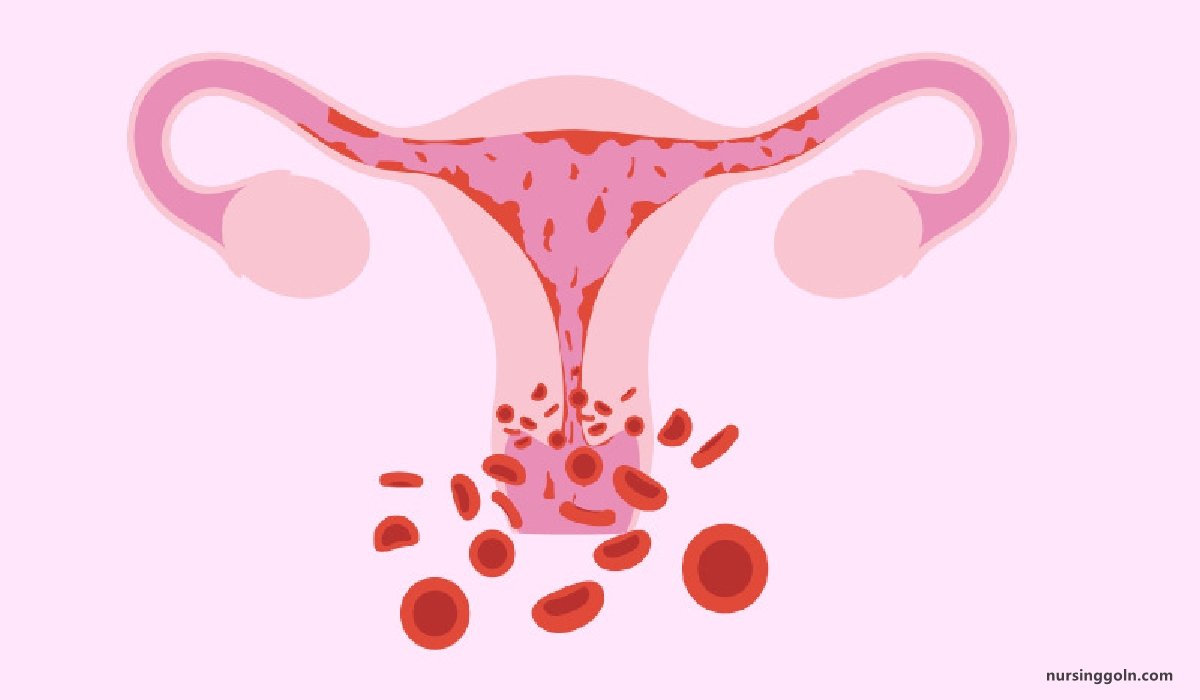
Definition of Menorrhagia:
Menorrhagia is a cycle bleeding at normal intervals which is excessive in amount (>80 ml) or duration or both, for example 5/28 (normal duration but excessive amount of bleeding) or 8/28 (normal or excessive amount of bleeding with excessive duration)
Causes of Menorrhagia:
A. Organic:
(a) Pelvic pathology:
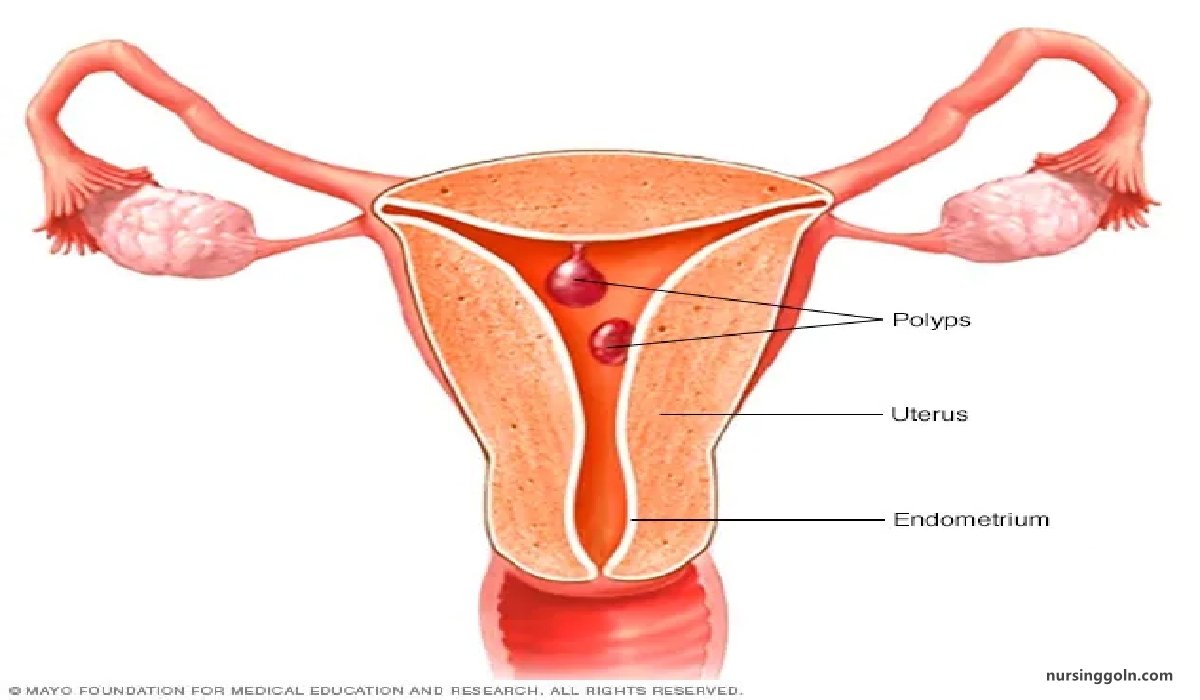
- Fibroids
- Adenomyosis
- Retroversion of uterus
- DUB Pelvic endometriosis
- Chronic tubo-ovarian mass
- Tubercular endometritis
- Granulosa cell tumor of the ovary
- IUCD
(b) Systemic diseases:
- CCF
- Liver dysfunction
- Severe hypertension
(c) Endocrine disorder:
- Hypothyroidism
- Early hyperthyroidism
- Early stage of acromegaly
(d) Blood dyscriasis:
- Leukemia
- Aplastic anemia
- ITP
(e) Emotional upset
B. Functional: Due to disturbed hypothalamus, pituitary, ovarian axis
Investigation of Menorrhagia:
1. History of the patient:
- Age of the patient
- Menstrual history: Continuous excessive vaginal bleeding preceded by a short period of amenorrhea. Bleeding is painless.
- Contraceptive history
- H/O weight change, cold or heat intolerance indicates thyroid disorder
- H/O any bleeding disorder
- Medical disease like liver or rend dissms
- Doug history like anticoagulant
- Family history like TB
2. Examinations
(a) General examination:
- Anemia
- Jaundice
- Nutritional status
- Hirsutism
- Thyroid enlargement
(b) Specific examination:
1. Per-abdominal examination:
- If primary then no pathology will found
- If due to may specific cause then the findings will be according to the disease
2. Pelvic examination:
- Bimanual examination: If primary, normal or slightly bulky uterus, non-tender, fornices are free
- Per speculum examination: Cervix is healthy looking
- Per-rectal examination: Rectal mucosa free
3. Investigation:
(a) Routine investigation:
- Blood TC, DC, ESR, Hb%, platelet count, BT, CT, PT, APTT
- Tuberculin test
- Chest X-ray P/A view
- Hormones: Serum TSH, FT4, FSH, LH, prolactin
- Blood urea and serum creatinine
- Diabetes screening
- Ultrasonography of lower abdomen and pelvis to exclude any uterine or ovary pathology
(b) Special investigation:
- Diagnostic uterine curettage (D and C)
- Hysteroscopy
- Laparoscopy
- Historiography
Management of Menorrhagia:
General:
- Rest
- Adequate explanation and reassurance
- Psychological support
- Correction of the anemia (haematinics)
- Blood transfusion if required
Treatment according to cause:
A. Primary:
Hormone therapy:
(a) Norethisterone: Dose: 10-30 mg daily for 48 hours or until bleeding stops. After withdrawal Norethisterone 5 mg daily form 5 to 25th day of the cycle Repeated for 3-6 cycles (b) Combined oral pill: 1 tablet daily from 5th to 25th days of the cycle for 3 consecutive cycles
B. Secondary: Appropriate treatment according to cause