Concept of Neuritis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Concept of Neuritis
Definition of Neuritis:
Neuritis is a broad term use to describe various diseases involving the inflammation of a nerve or a group of nerves. It is often associated with pain, changes in sensations, weakness, numbness, paralysis or muscle wasting.
Or,
Neuritis is inflammation of a nerve or the general inflammation of the peripheral nervous system. Symptoms depend on the nerves involved but may include pain, paresthesia (pins-and-needles), paresis (weakness), hypoesthesia (numbness), anesthesia, paralysis, wasting, and disappearance of the reflexes.
Types of Neuritis
Several types of neuritis have been identified. The most common types of neuritis are peripheral neuritis and optic neuritis. There are several other less common varieties of neuritis including:
1. Brachial neuritis
2. Polyneuritis multiplex
3. Intercostal neuritis
4. Ulnar neuritis
5. Lumbosacral neuritis
6. Occipital neuritis
7. Vestibular neuritis
8. Cranial neuritis
9. Arsenic neuritis
10. Sensory motor polyneuropathy
11. Granulomatous neuritis of leprosy
Causes of Neuritis:
- Physical injury
- Infection
✔ Diphtheria
✔ Herpes zoster (shingles)
✔ Leprosy
✔ Lyme disease
- Chemical injury such as chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Underlying conditions
- Alcoholism
- Autoimmune disease, especially multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Beriberi (vitamin B, deficiency)
- Cancer
- Celiac disease
- Diabetes (Diabetic neuropathy)
- Hypothyroidism
- Porphyria
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Vitamin B6 excess
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of neuritis depend on the nerve or group of nerves affected. The common symptoms of neuritis usually localized to the affected area include:
- Pain – stabbing or pricking type
- Muscle weakness (paresis)
- Paresthesia (abnormal sensation) can be in the form of tingling or a burning sensation
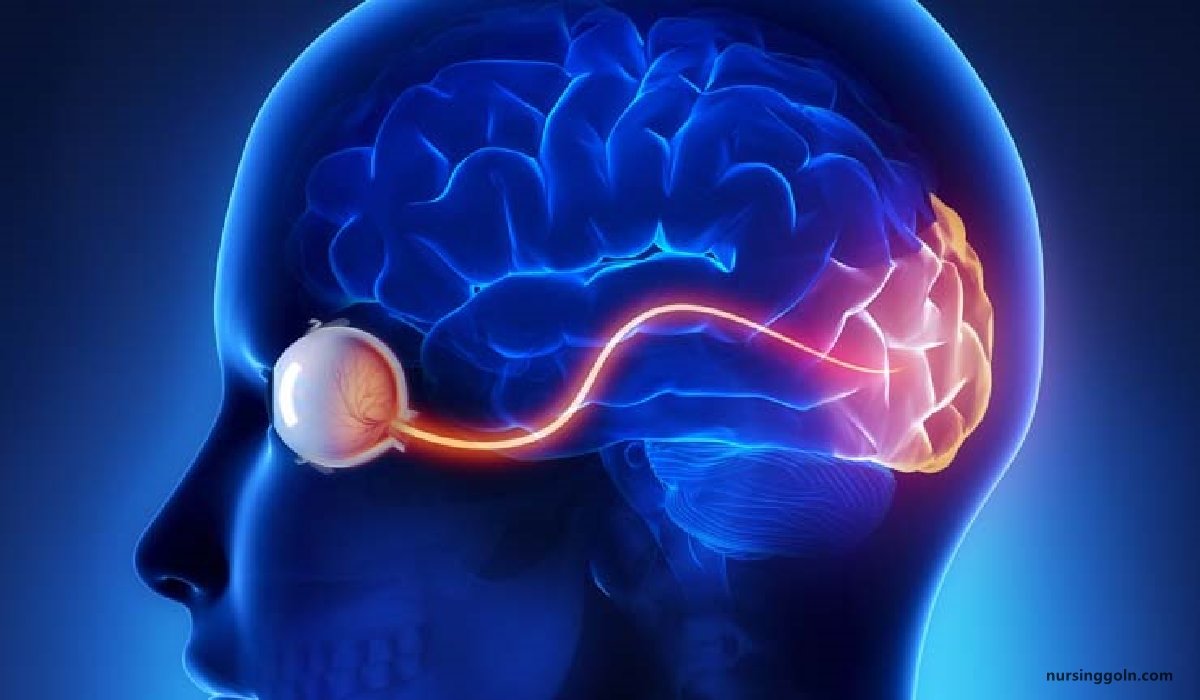
In patients with severe forms of neuritis
- Numbness,
- Loss of sensation (anesthesia),
- Swelling,
- redness of skin,
- Paralysis,
- Muscle wasting and
- Loss of muscle reflexes may be seen.