Concept of Person in Nursing – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Person
Concept of Person in Nursing
Although the terms human being and human person are often used interchangeably, the term human person is used in Careful Nursing because the meaning of person encompasses more fully the nature of human life. Use of the word person evolved over several centuries in the ancient Greek and Roman worlds, gradually becoming associated with the spiritual dimension of human life.
By the 4th century CE the term person was used to denote the deeply relational aspect of human life and human persons were understood as ‘distinct possessors of intellectual and loving being’ (According to Clark 1992,).
Q. Define person? (BNMC-2019, DU-20, CU-12)
Q. What do you mean by person?
Answer:
Definition of Person:
A person is a being, such as a human, that has certain capacities or attributes constituting personhood, which in turn is defined differently by different authors in different disciplines and by different cultures in different times and places.
The word person is derived from the Latin word “persona”.
In ancient Rome, the word “persona” originally referred to the masks worn by actors on stage.
or
A person is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as –
- reason,
- morality,
- consciousness or self-consciousness, and
- being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility
Q. Define person in nursing perspective? (DU-19, 16, 13)
Answer:
Definition of Person in Nursing Perspective:
Person may be defined as the recipient of nursing care. It can include individuals, families and communities. The holism of person is the key to effective nursing practice. Nursing begins with the understanding of each individual client as a unique human being before considering the specific health problem.
Q. Describe person from different nursing perspective.
Answer:
Person from Different Nursing Perspective:
Patient/Client is defined as person, family, and/or community. Person is conceptualized as a holistic being encompassing the personal, social, and physical dimensions. The dimensions are examined as follows:
- The personal dimension illuminates the uniqueness of each person. The nursing assessment of this dimension is based upon theories of human development and communication. It is inclusive of the person’s self-concept, body image, self-awareness, and self-esteem. Assessment also involves meanings of sexuality, spirituality, and philosophical values particular to each person. Clients as persons, families, and/or communities are viewed as open systems that interact and interface with the environment.
- The social dimension focuses on the person in the context of family and environment and includes the cultural, moral, and political realms. Assessments within this dimension identify roles and patterns of behavior that impact on health maintenance and related behaviors.
- The biological systems form the basis of assessment within the physical dimension. These include the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary/reproductive, integumentary, musculoskeletal, neurologic and respiratory systems. The genetic patterns of inheritance are also characteristic of the physical dimension.
Q. Define personality?
Q. What do you mean by personality?
Answer:
Definition of Personality:
According to Munn NL
“Personality may be defined as the most characteristic integration of an individual’s structure, modes of behavior, interests, attitudes/capacities, abilities and aptitudes.”
According to Gordon Allport
“Personality is the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychosocial systems that determine his unique adjustment to his environment.”
According to Eysenck
“Personality is the more or less stable and enduring organization of a person’s character temperament, interact and physique which determines his unique adjustment to the environment.
Q. Classify personality?
Q. Write down the types of personality mentioned by Kretschmer and William Sheldon.
Q. Describe the introvert and extrovert types of personality?
Answer:
Types/Classification of Personality:
A. Types of Personality Based on Temperament
Hippocrates (about 400 BC), the father of medicine, classified people into four types as per temperament depending on which one of one’s bodily humors or fluids they believe to predominate.
a) Sanguine-cheerful, vigorous, confident, optimistic (blood).
b) Phlegmatic-calm, slow-moving, unexcitable, unemotional (mucus).
c) Choleric-irritable, hot-tempered (yellow bile).
d) Melancholic-depressed, morose (black bile).
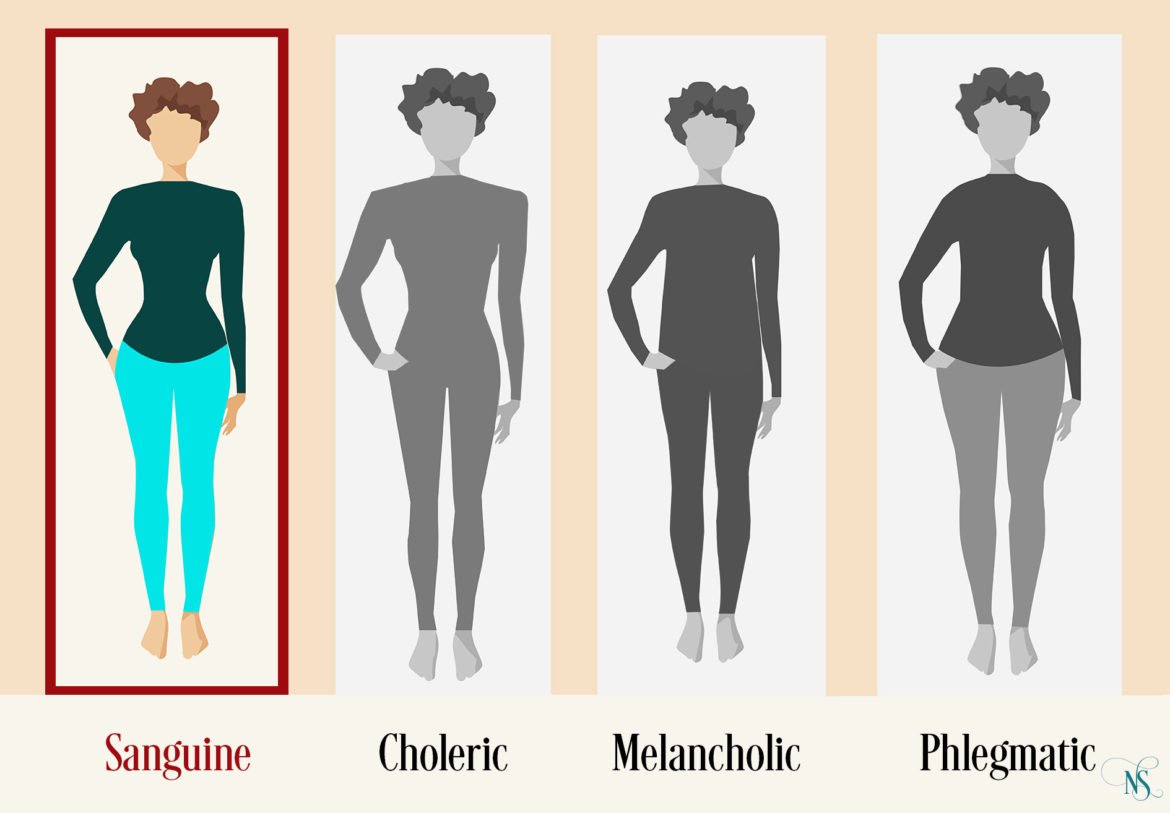
This is similar to dividing people into Vatha, Pitha and Kabham in Ayurveda.
B. Types Based on Body Build (Physiological Types):
- Kretschmer (Physic and character).
- William Sheldon (Based on different layers of skin).
a) Kretschmer (1925) divided people into 3 types based on body structure:
- Asthenic-introvert, tall, thin, sensitive.
- Athletic-active, aggressive, well-developed muscular body.
- Pyknic-extrovert, round and fat.
b) William Sheldon (1954) divided people into three types according to body build and behavior.
- Endomorph-plumb, soft, fat and round-sociable even tempered and
- Mesomorph-heavy set and muscular-physically active and noisy.
- Ectomorph-tall, thin and flat-chested-self-conscious, shy, fond of solitude and reserved (introverts).
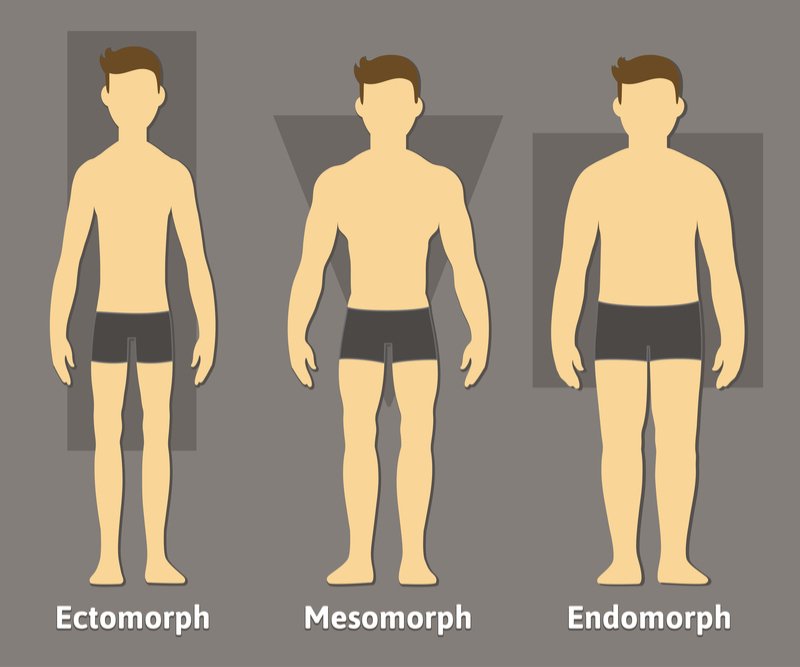
c) On the same basis, temperament too is classified into the following three classes:
- Visecerotonic (endomorphic) eating predominates. They love comforts and food also seek love of others. They also sleep deeply. They like others help them when they are in trouble.
- Semantotonic (mesomorphic). They have a brittle, clear, competitive nature and a generally powerful, daring, authoritative and loud talkers. In troubles, they are more active.
- Cerebrotonic (ectomorphic). They are habituated in suppressing their emotions. They are self-controlled and withdrawing. They love solitude. Instead of seeking assistance in trouble, they keep to themselves. They speak slowly and their sleep is often disturbed. Although a person’s physique may have some influence on personality, the relationship is much more subtle. Research has shown little correlation between body build and specific personality characteristics.
C. Classification by Psychological Types:
On the basis of sociability Dr Karl G Jung classified people into two main groups namely.
1. Extroverts and
2. Introverts.
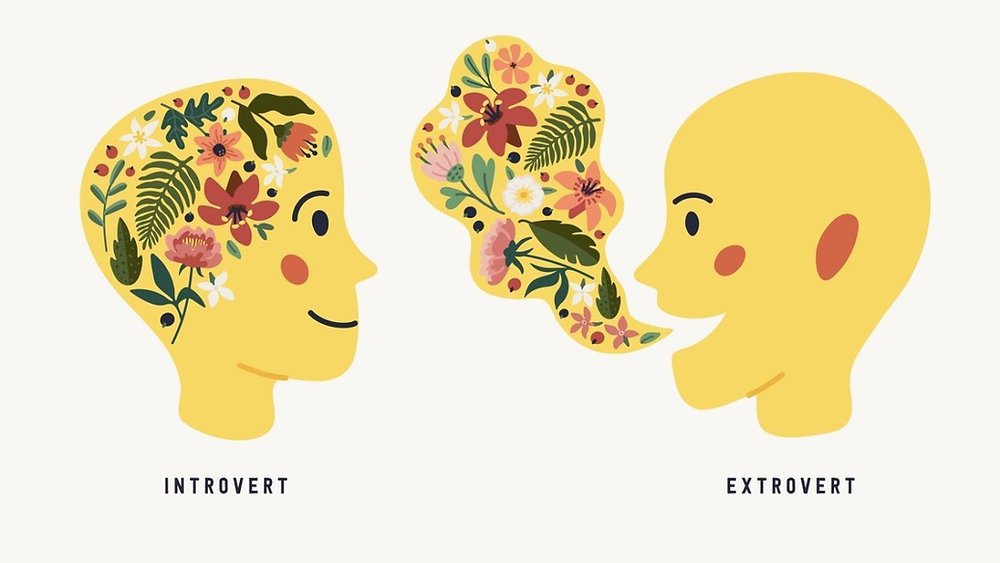

a) Extroverts are people who are sociable and take interest in others and like to move with people and are skilled in etiquette. They are friendly and sociable and not easily upset by difficulties. They are dominated by emotions, whereby they take decisions quickly and act on them without delay. They are realistic and face the problems of life.
b) Introverts are those who are interested in themselves, their own feelings, emotions and reactions. They are busy in their own thoughts and are self-centered. They are reserved and like to work alone.
They are very sensitive and are unable to adjust easily to social situations. They are inclined to worry and easily get embarrassed. Many poets, philosophers, scientists and artists belong to this group. There are very few people who are pure extroverts or introverts. Majority of the people are ambiverts having the qualities of extroverts and introverts in different proportions.
Q. What do you mean by personality trait?
Answer:
Personality Traits:
Personality traits reflect people’s characteristic patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Personality traits imply consistency and stability-someone who scores high on a specific trait like Extraversion is expected to be sociable in different situations and over time.
Q. Write down the personality trait of a nurse?
Q. What are the personality traits of a person?
Answer:
Personality Traits of a Nurse
- Discipline
- Responsibility
- Patience
- Commitment
- Dedication
- Punctuality
- Hard work
- Good physical stamina
- Alertness of mind
- Adaptability to follow difficult time schedules
- Ability to thirk in casis to take a quick decision
- Calm, pleasant, compassionate and understanding
- Good team spirit
- Ability to help and serve needy people without getting sentimentally attached.
