Concept of Pharmacokinetic – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Pharmacology” prescribed by BNMC- for diploma in nursing science & midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics. This book is an examination set up according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions.
At the end of the book, previous questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourish. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
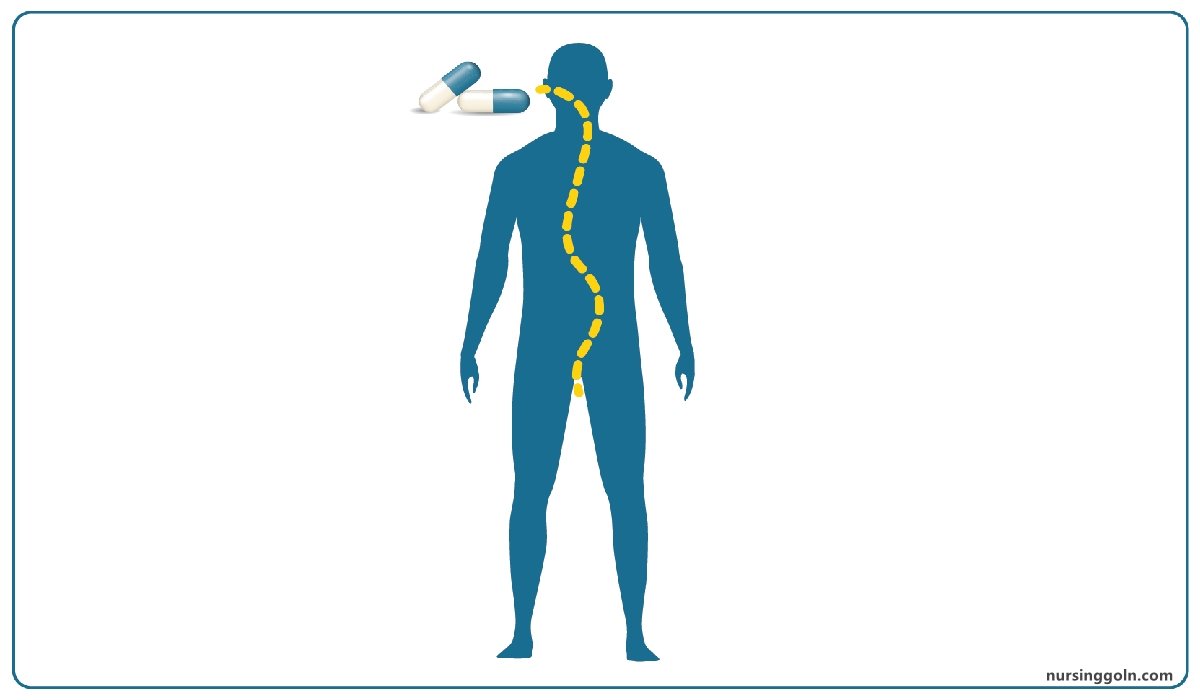
Concept of Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics
The word pharmacokinetics is derived from two Greek words, Pharmacon means: drug, kinein means: to move. Pharmacokinetics refers to what the body does to a drug.
The study of drug absorption, distribution, Biotransformation and elimination is called Pharmacokinetics.
Four pharmacokinetic properties determine the onset, intensity, and duration of drug action
1. Absorption: First, absorption from the site of administration permits entry of the drug (either directly or indirectly) into plasma.
2. Distribution: Second, the drug may then reversibly leave the bloodstream and distribute into the interstitial and intracellular fluids.
3. Metabolism: Third, the drug may be bio-transformed by metabolism by the liver or other tissues.
4. Elimination: Finally, the drug and its metabolites are eliminated from the body in urine, bile, or feces.

Importance of Pharmacokinetics:
Using knowledge of pharmacokinetic parameters, clinicians can design optimal drug regimens, including the route of administration, the dose, the frequency, and the duration of treatment.
Principles/Objects of Drug Administrations
1. For treatment/cure:
- Antibiotics for infections (bacterial)
- Antipyretics for pyrexia (fever).
- Diuretics for oedema
2. For symptomatic relief:
Propranolol for cardiac arrhythmia
Analgesics for pain.
Sedatives for pain.
Salbutamol for bronchial asthma
Insulin for diabetes
Anti-hypertensive drug for hypertension
Anticoagulant drugs for blood disorders

3. For prophylactic (preventive) use:
- Primaquine lor malaria
- Contraceptives for contraception
4. For diagnosis:
- Barium sulphate for peptic ulcer
- Endrophonium for myasthenia gravis
Read more:
