Concept of Skeleton-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Concept of Skeleton
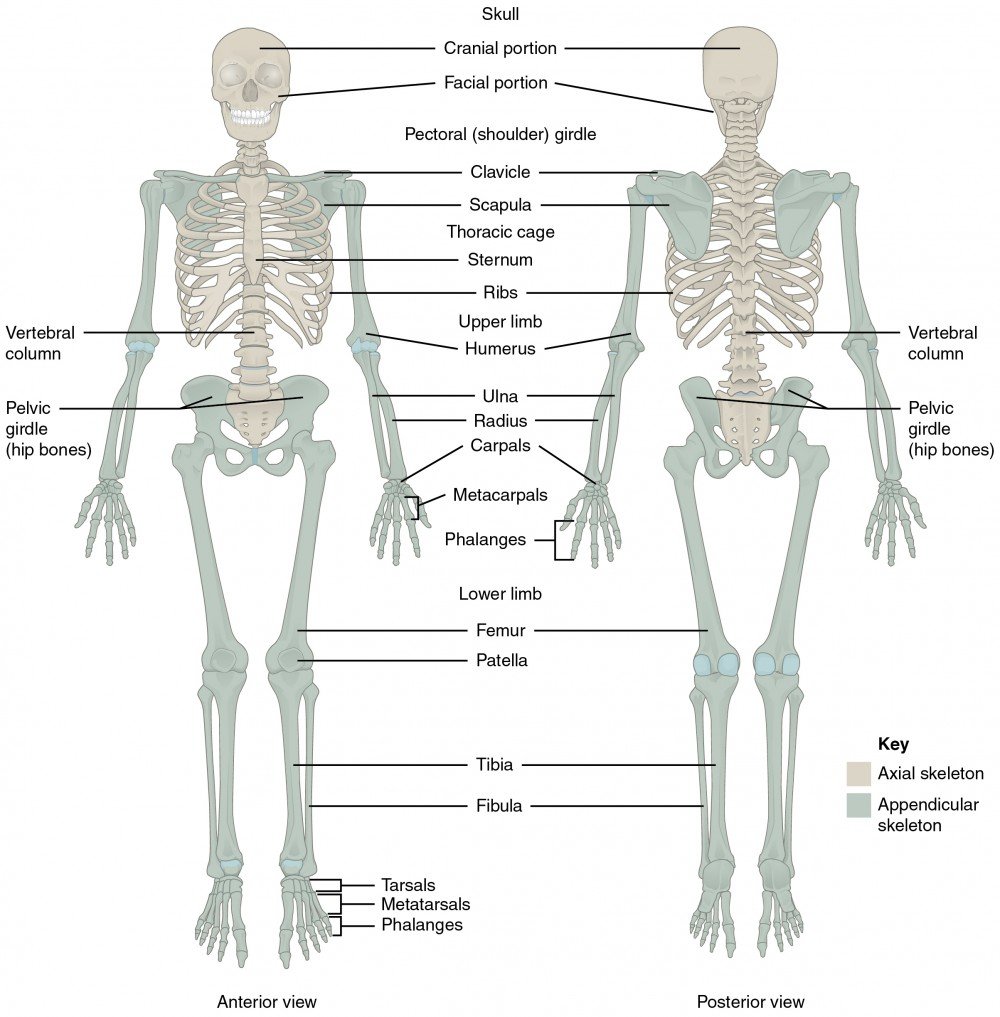
Skeleton
The skeleton is the bony framework of the body providing support and protection for some of the soft organs, particularly in the skull, chest, and pelvis, acting as levers in movement and providing surfaces for the attachment of the skeletal muscles. The adult human body has total 206 bones.
Though endoskeletons are the best known, the animal kingdom features three other types of skeleton: exoskeletons, cartilaginous exoskeletons, and hydrostatic skeletons. Endoskeletons have evolved to suit their owner’s lifestyle.
(Ref:- Evelyn C. Pearce, Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses, 16th edition, P-63)
The human skeleton is divided into two main groups or categories. They are called:
- The axial skeleton (80 bones) and
- The appendicular skeleton (126 bones)
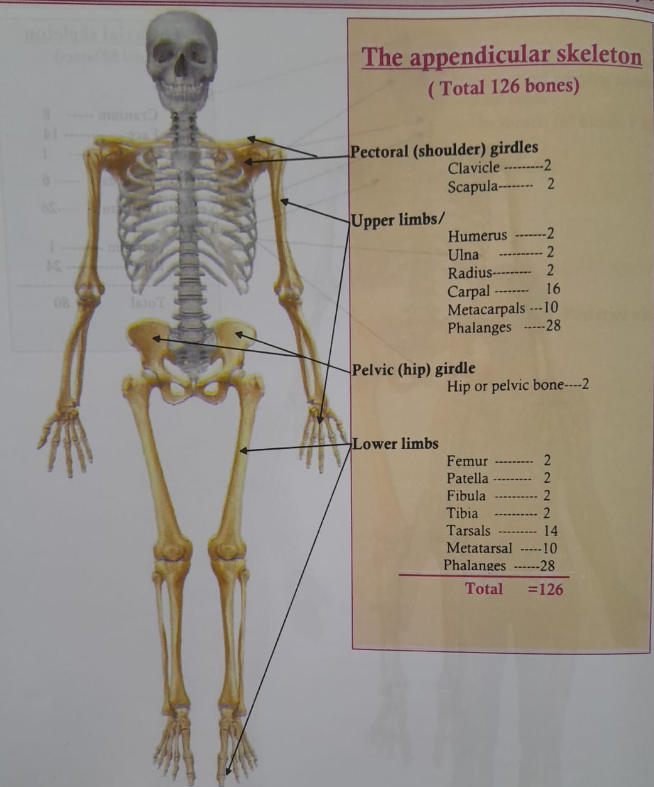
The appendicular skeleton (Total 126 bones)
Pectoral (shoulder) girdles
Clavicle-2
Scapula 2
Upper limbs
Humerus-2
Ulna- 2
Radius- 2
Carpal- 16
Metacarpals -10
Phalanges-28
Pelvic (hip) girdle
Hip or pelvic bone-2
Lower limbs
Femur -2
Patella -2
Fibula -2
Tibia -2
Tarsals -14
Metatarsal-10
Phalanges-28
Total =126
Total bones of human skeleton are
The axial skeleton = 80 bones and the appendicular skeleton = 126 bones
Total = 206 bones
(Ref: Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13 ed)
