Conduction system of Heart-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Conduction system of Heart
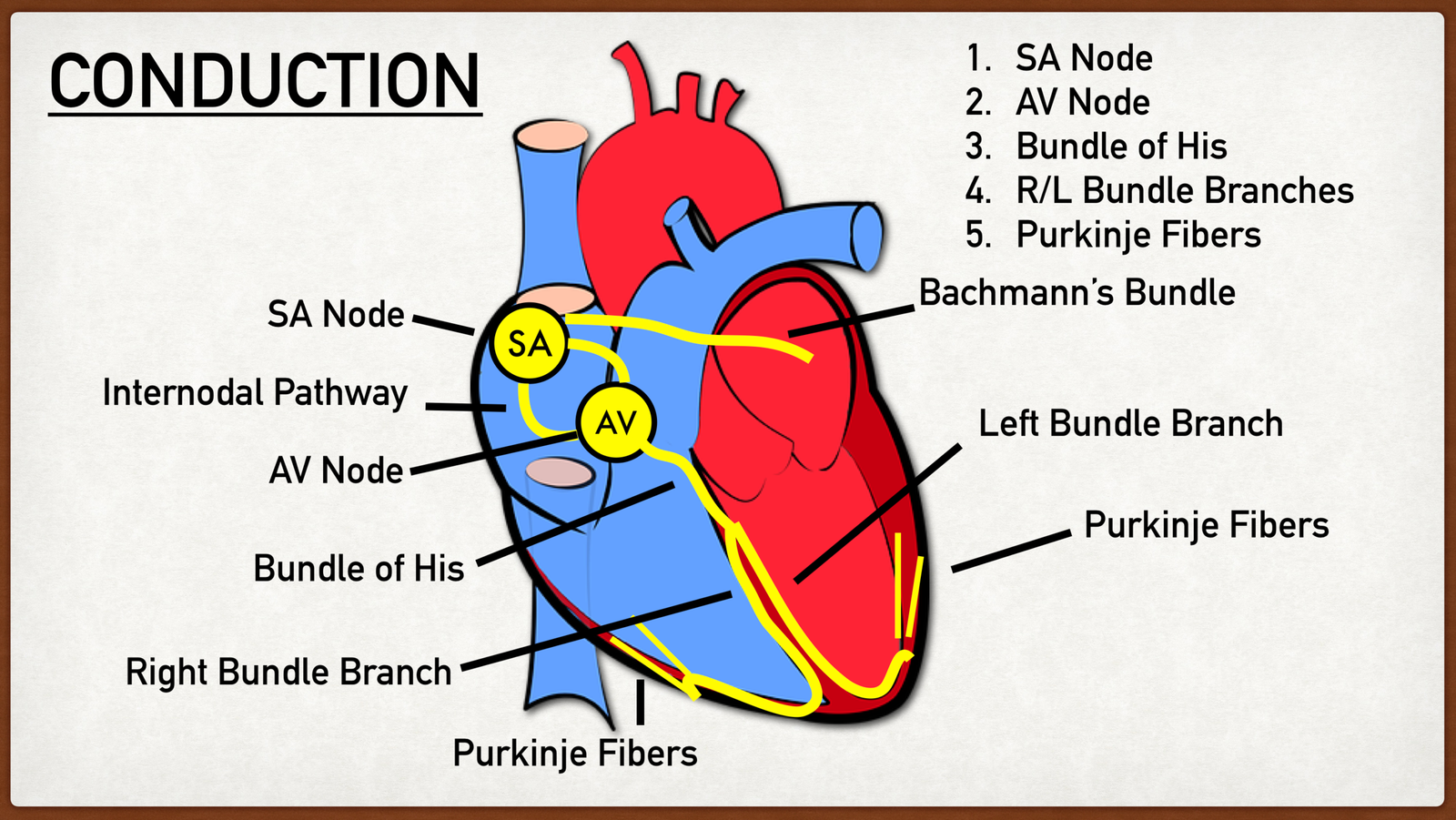
Electrical conduction system of Heart:
Specialized cardiac muscle cells that carry impulses throughout the heart musculature, sygnaling the chamben to contract in the proper sequence. This is also known as Junctional tissue of heart. About 1% of the cardiac muscle fibers are different from allothers because they can generate action potentials over and over and do so in a rhythmical pattern.
They continue tostimulate a heart to beat even after it is removed from thebody for example, to be transplanted into another person and all of its nerves have been cut. The nerves regulate theheart rate, but do not determine it These cells have twoumportant functions. They act as a pacemaker setting therhythm for the entire heart, and they form the conductionsystem.
Cardiac action potentials pass through the following components of the conduction system as
- Sino-atrial node (SA node).
- Atrio-ventricular node (AV node)
- Bundle of His
- Right & left branches of bundle of His
- Purkinje fibre
Sino-atrial node (SA node):-Normally, cardiac excitation begins in the sinoatrial (SA)node, located in the right atrial wall just inferior to theopening of the superior vena cava An action potentialspontaneously arises in the SA node and then conductsthroughout both atria via gap junctions in the intercalateddiscs of atrial fibers. Followingthe action potential, the two atria finish contracting atthe same time.
Atrio-ventricular node (AV node):-By conducting along atrial muscle fibers, the action potentialalso reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node, locatedin the interatrial septum, just anterior to the opening ofthe coronary sinus. At the AV node, the action potentialslows considerably, providing time for the atria to emprytheir blood into the ventricles.
Bundle of His-From the AV node, the action potential enters the atrioventricular(AV) bundle (also known as the bundle of His), inthe interventricular septum. The AV bundle is the onlysite where action potentials can conduct from the atria tothe ventricles.
Right & left branches of bundle of His:- After conducting along the AV bundle, the action potentualthen enters both the right and left bundle branchesthat course through the interventricular septum toward the apex of the heart.
Purkinje fibre:-Finally, large diameter Purkinje fibers rapidly conduct the action potential, first to the apex ofthe ventricles and then upward to the remainder of the ventricular myocardium. Then, a fraction of a secondafter the atria contract, the ventricles contract.
(Ref:-J. TORTORA The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8 edition-P-385)