Congenital heart disease (CHD) – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric- nursing.
Pediatric-nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric-nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Congenital heart disease (CHD)
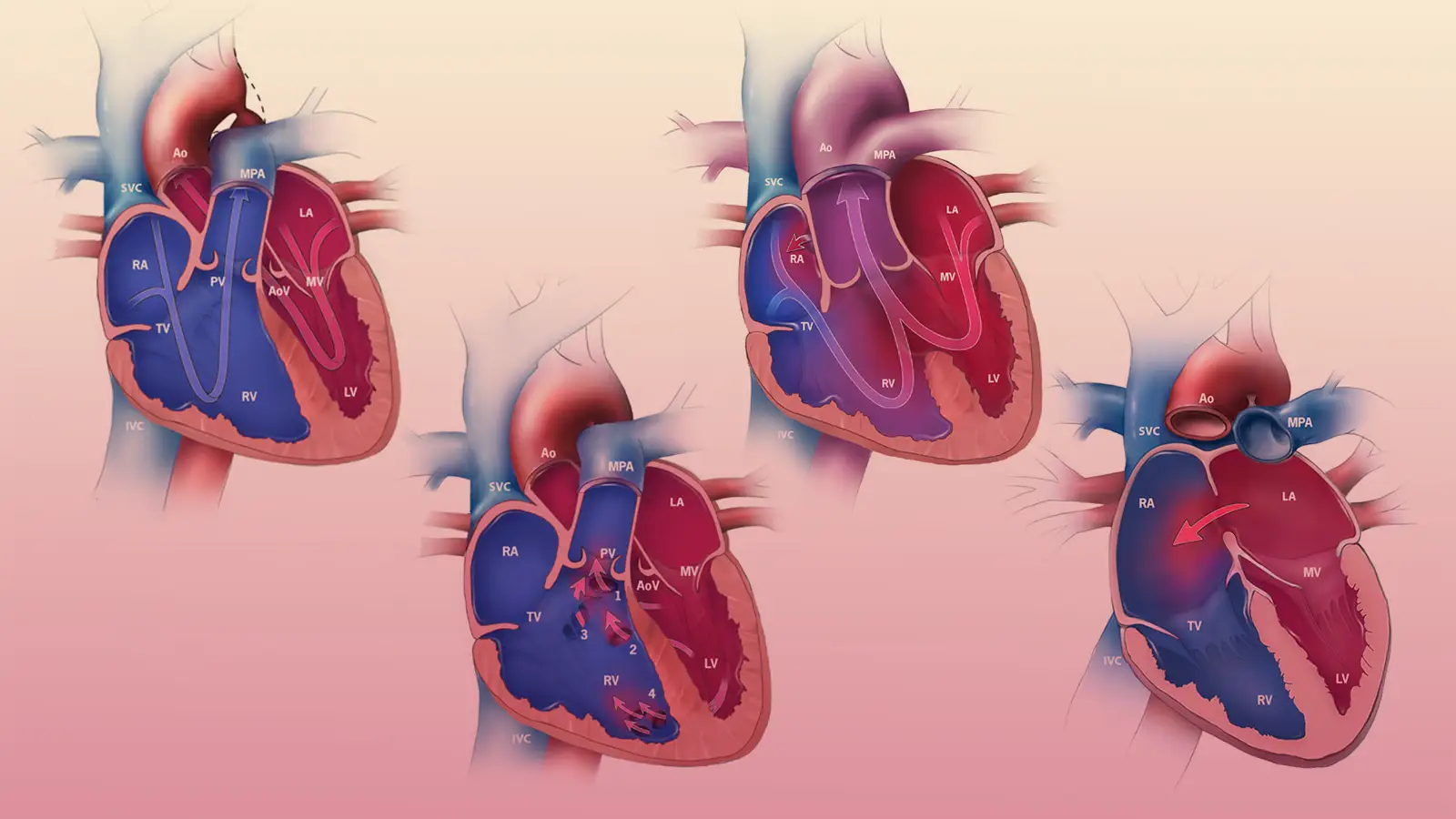
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem.
Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.
The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor.
Definition of Congenital Heart Disease:
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth.
Or
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the structural malformations of the heart or great vessels, present at birth. It is the most common congenital malformations.
(Ref: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3/303)
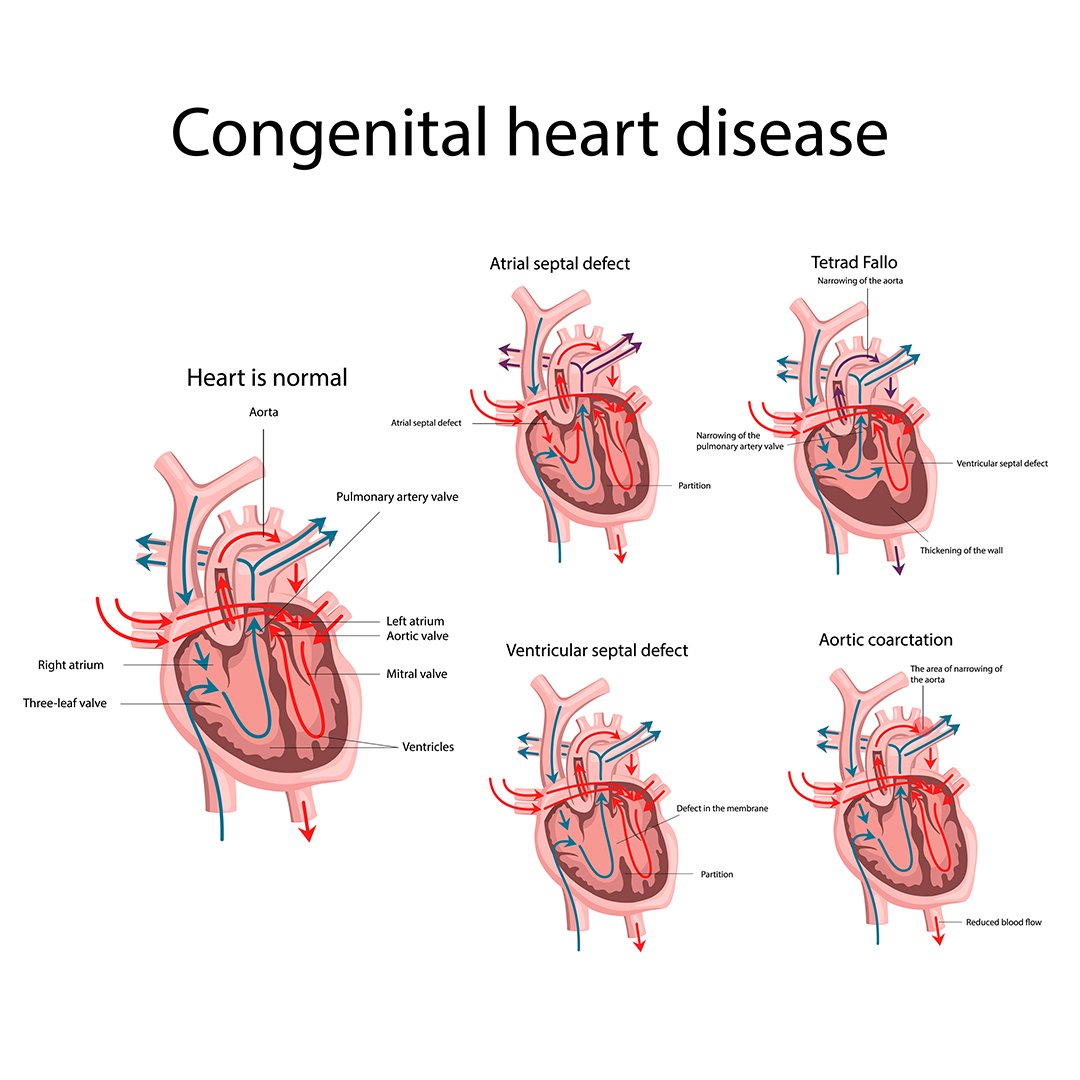
Classification of Congenital Heart Diseases:
| Acyanotic | Cyanotic |
| With shunts | With shunts |
| 1. Atrial septal defect 2. Ventricular septal defect 3. Patent ductus arteriosus 4. Partial anomalous venous drainage | 1. Fallot’s tetralogy 2. Transposition of the great vessels 3. Severe Ebstein’s anomaly |
(Ref by: Kumar & Clark/8th/755/Table-14.41)
Nice to know
Another classification of congenital heart disease
1. Cvanotic heart disease
A. Cyanotic heart disease (Right to left shunt):
a) Tetralogy of Fallot (5-7%)
- Ventricular septal defect.
- Overriding of aorta.
- Pulmonary stenosis.
- Right ventricular hypertrophy.
b) Pulmonary atresia.
B. Cyanotic heart disease with abnormal mixing:
a) Transposition of great vessels
b) Persistent truncus arteriosus
c) Ebstein’s anomaly.
d) Single atrium
e) Single ventricle
f) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
2. Acyanotic heart disease
A. Left to right shunt:
a) Atrial septal defect (ASD)
b) Ventricular sepetal defect (VSD) (25-30%)
c) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
B. Obstructive lesion:
a) Pulmonary stenosis
b) Aortic stenosis
c) Corctaction of aorta
C. Abnormal position of heart:
a) Dextrocardia
b) Levocardia.
Common Congenital Heart Diseases
1. Atrial septal defect (ASD)
2. Ventricular sepetal defect (VSD)
3. Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
4. Tetralogy of Fallot.
5. Pulmonary stenosis.
6. Eisenmenger’s syndrome.
An infant with congenital heart disease presents –
- Cyanosis
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmia
- Murmur
- Failure to thrive
(Ref- M. R. Khan 175/4th edition)
Causes of Congenital Heart-Disease:
- Heredityamu
- Consanguineous marriage
- Genetic disorders
- Chromosomal aberrations (Trisomy-21, Turner’s slmdrome)
- Fetal and maternal teratogenic infections (rubella)
- Teratogenic drug (thalidomide) intake Alcohol intake by the mother
- Irradiation in first trimester of pregnancy
- Maternal IDDM
- High altitude
- Fetal hypoxia
- Birth asphyxia
