Cranial nerves-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
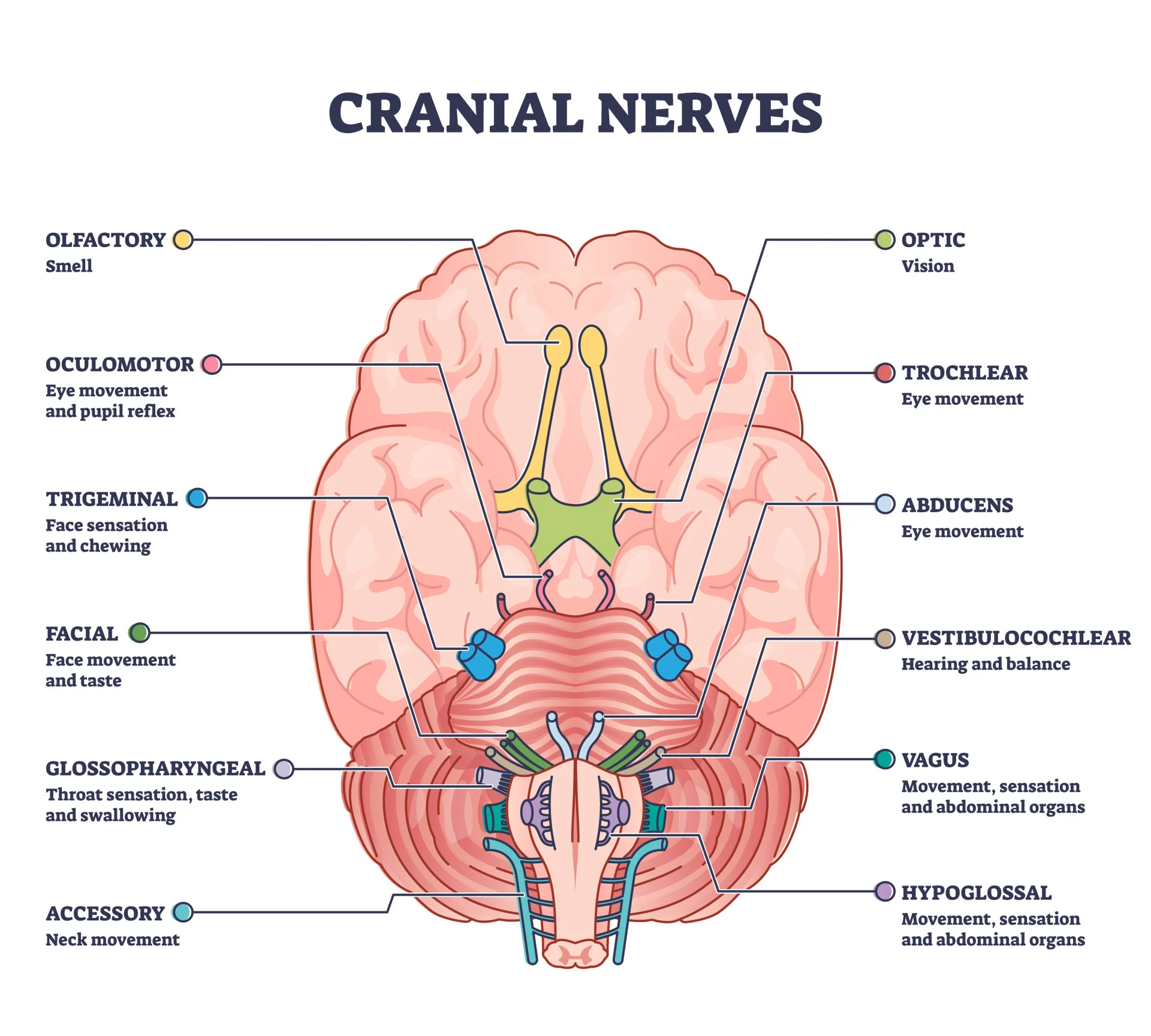
Cranial nerves
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves. The cranial nerves are designated with roman numerals and with names. The roman numerals indicate the order (anterior to posterior) in which the nerves emerge from the brain. The names indicate the distribution or function.
Cranial nerves come into view from:
- The nose (cranial nerve I).
- The eyes (cranial nerve II),
- The inner ear (cranial nerve VIII),
- The brain stem (cranial nerves III-XII), and
- The spinal cord (cranialnerve XI).
Three cranial nerves (I, II, and VIII) carry axons of sensory neurons and thus are called sensory nerves.
Five cranial nerves (III, IV, VI, XI, and XII) contain only axons of motor neurons as they leave the brain stem and are called motornerves.
The other four cranial nerves (V, VII, IX, and X) are mixed nerves because they contain axons of both sensory and motor neurons.
The cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in ganglia outside the brain. The cell bodies of motor neurons lie in nucles within the brain.
Cranial nerves III, VII, IX, and Xinclude both somatic and autonomic motor axons. The somaticaxons innervate skeletal muscles; the autonomic axons, which are part of the parasympathetic division, innervateglands, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
12 pairs of cranial nerves are
I. Olfactory nerve (Sensory)
II. Optic nerve (Sensory)
III. Oculomotor nerve(Motor)
IV. Trochlear nerve (Motor)
V. Trigeminal nerve(Mixed)
VI. Abducent nerve(Motor)
VII. Facial nerve(Mixed)
VIII. Vestibulocochlear nerve (Sensory)
IX. Glossopharyngeal nerve(Mixed)
X. Vagus nerve(Mixed)
XI. Accessory nerve(Motor)
XII. Hypoglossal nerve(Motor)
(N.B:– A mnemonic device that can be used to remember the names of the nerves is: “Oh, oh, oh, to touch and feel very green vegetables-AH !!!” Each boldfaced letter corresponds to the first letter of a pair of cranial nerves.)
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th ed, P-166-169+ Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12 ed)
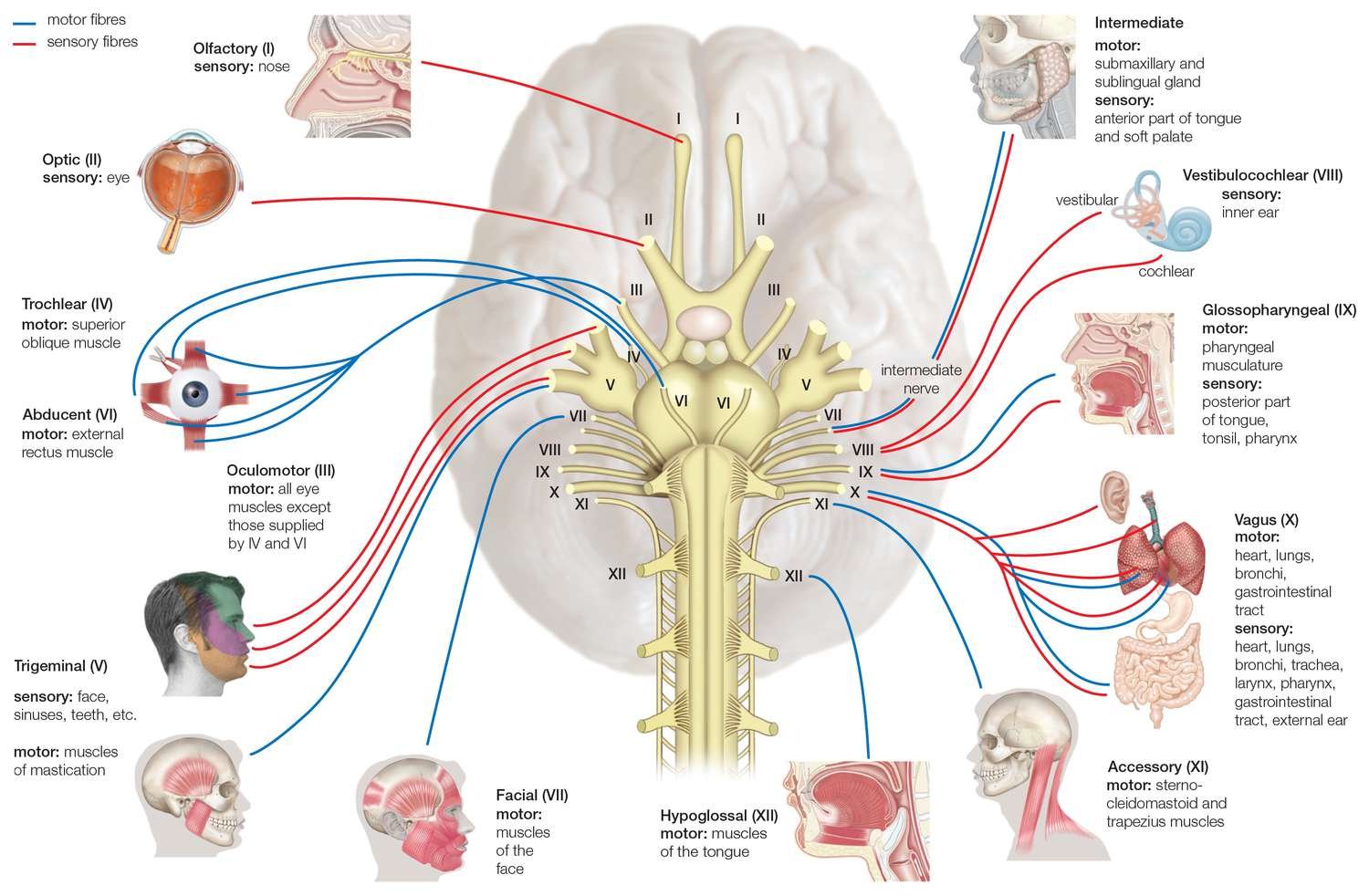
The cranial nerves, along with their components(sensory, motor, or mixed) and functions are mentioned below:
| Number | Name of cranial nerves | Type | Functions |
| I | Olfactory nerve (olfact = to smell) | Sensory | Smell |
| II | Optic nerve( opti = eye, vision) | Sensory | Vision |
| III | Oculomotor nerve (oculo eye, motor = mover) | Motor | Movement of upper eyelid and eyeball; alters shape of lens for near vision and constricts pupil. |
| IV | Trochlear nerve (trochle a pulley) | Motor: | Movement of the eyeball |
| V | Trigeminal nerve (triple for its three branches) | Sensory part: Consists of three branches the ophthalmic nerve, the maxillary nerve, the mandibular nerve Motor part: Axons of somatic motor neurons: | Touch, pain, and temperature sensations and muscle sense (proprioception). Chewing |
| VI | Abducent nerve (ab = away, ducens to lead) | Motor part: Axons of somatic motor neurons: | Movement of the eyeball |
| VII | Facial nerve (face) | Sensory part: Axons from taste buds on tongue Motor part: Axons of somatic motor neurons | Taste: muscle sense (proprioception); touch, pain. and temperature sensations. Facial expressions: secretion of tears and saliva |
| VIII | Vestibulocochlear (vestibulo =small cavity; cochlear = a spiral, snail-like) | Sensory | Equilibrium. Hearing |
| IX | Glossopharyngeal nerve (glosso tongue, pharyngeal = throat) | Sensory part: Axons from taste buds and somatic sensory receptors on part of tongue, Motor part: Axons of somatic motor neurons that stimulate swallowing | Taste and somatic sensations (touch, pain, and temperature) from tongue Swallowing, speech, secretion of saliva |
| X | Vagus nerve (vagus= vagrant or wandering) | Sensory part: Axons from taste buds in pharynx(throat) and epiglottis, Motor part: Axons of somatic motor neurons | Taste and somatic sensations (touch, pain, temperature) from pharynxand epiglottis Swallowing, coughing, and voiceproduction; |
| XI | Accessory nerve (assisting) | Motor: Axons of somatic motor neurons | Movements of head and shoulders. |
| XII | Hypoglossal nerve (hypo below, glossal = tongue) | Motor: Axons of somatic motor neurons | Movement of tongue during speech and swallowing |
