Crypotococcus Neoformans – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Crypotococcus Neoformans
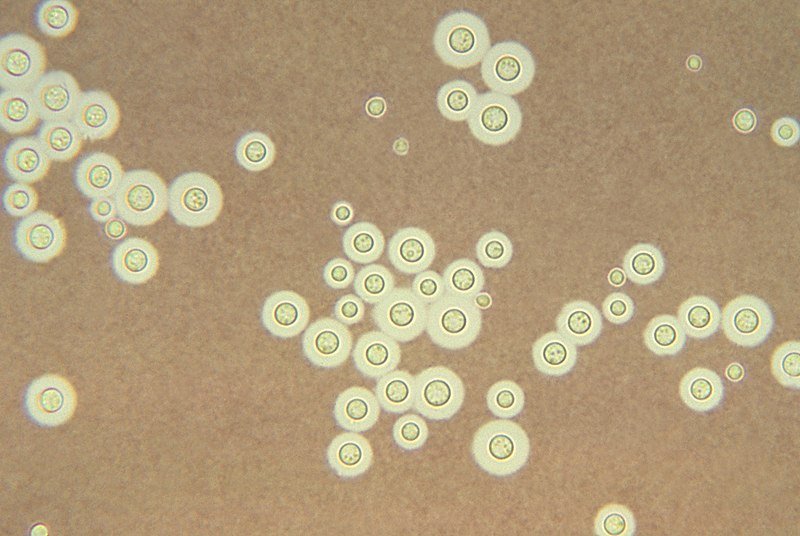
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals.
Properties:
- It is the only capsulated fungus.
- Round or oval in shape
- It is not dimorphic, i.e. no mold form.
Diseases: Cryptococcosis.
- Cryptococcal meningitis
- Asymptomatic lung infection
- Skin & bone marrow infection.
Pathogenesis of Cryptococcal Meningitis:
Inhalation of Cryptococcus neoformens -> Infection of the lungs -> Dissemination occurs in immunocompromised patients -> Goes to central nervous system -> Meningitis.
Lab, diagnosis:
Principle: Diagnosis is based on demonstration of causative organism by microscopic examination and isolation & identification by culture. Serological test is also helpful.
Steps:
➤ Specimen: CSF, serum, sputum.
➤ Microscopic examination: India ink preparation.
- Findings: Round or oval yeast cells surrounded by wide unstained capsule
➤ Culture: Culture is done in Sabouraud’s dextrose agar media at 37°C temp, for 2-3 days.
- Findings: Cream coloured mucoid colony.
➤ Serology: CSF & serum for Ag or Ab – Latex agglutination test.
Cryptococcosis
Definition of Cryptococcosis:
Cryptococcosis is infection with the fungi Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii
or
Cryptococcosis is a pulmonary or disseminated infection acquired by inhalation of soil contaminated with the encapsulated yeasts Cryptococcus neoformans or C. gattii
Risk Factors for Cryptococcosis Include
➤ AIDS
➤ Hodgkin lymphoma
➤ Other lymphomas
➤ Sarcoidosis
➤ Long-term corticosteroid therapy
➤ Solid organ transplantation
Symptoms
Symptoms of brain infection may include:
➤ Fever and headache
➤ Neck stiffness
➤ Nausea and vomiting
➤ Blurred vision or double vision
➤ Confusion
The infection can also affect the lungs and other organs. Lung symptoms may include:
➤ Difficulty in breathing
➤ cough
➤ Chest pain
Other symptoms may include:
➤ Bone pain or tenderness of the breastbone
➤ Fatigue
➤ Skin rash, including pinpoint red spots (petechiae), ulcers, or other skin lesions
➤ Sweating — unusual, excessive at night
➤ Swollen glands
➤ Unintentional weight loss
Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis
➤ Blood culture to differentiate between the two fungi
➤ CT scan of the head
➤ Sputum culture and stain
➤ Lung biopsy
➤ Bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage
➤ Spinal tap to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
➤ Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture and other tests to check for signs of infection
➤ Chest x-ray
➤ Cryptococcal antigen test (looks for a certain molecule that is shed from the cell wall of the Cryptococcus fungus into the bloodstream or CSF)
Treatment
Fungal medicines are prescribed for people infected with cryptococcus.
Medicines include:
➤ Amphotericin B (can have severe side effects)
➤ Flucytosine
➤ Fluconazole
