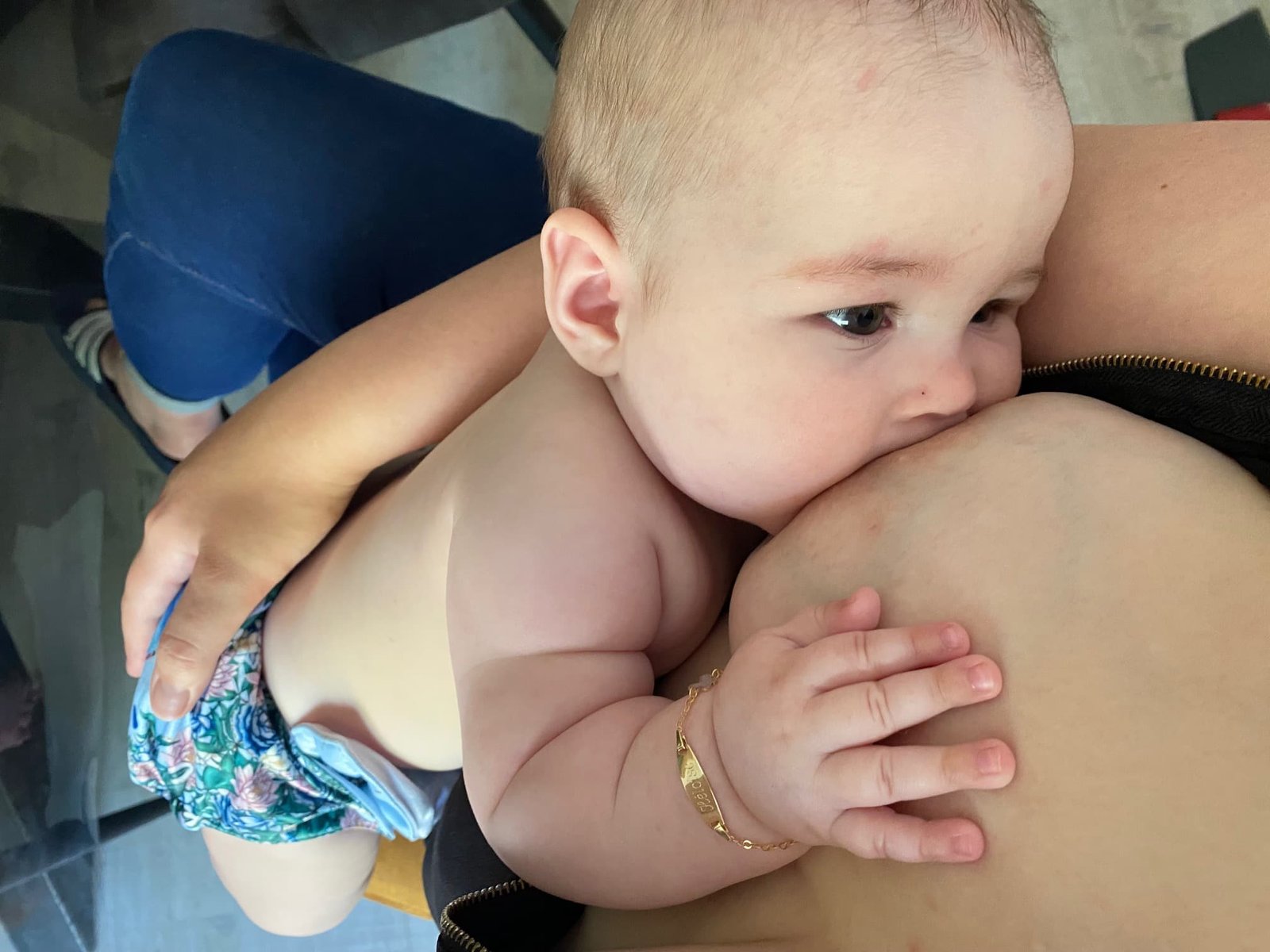
Defining breast feeding – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Defining breast feeding
Breast feeding is the best natural feeding and breast milk is best milk. The basic food of infant is mother’s milk. Breastfeeding is the most effective way to provide a baby with a caring environment and complete food.
[Ref-Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3/51]

or
Breastfeeding is the normal way of providing young infants with the nutrients they need for healthy growth and development. Virtually all mothers can breastfeed, provided they have accurate information, and the support of their family, the health care system and society at large.
Benefits of breastfeeding:
Breastfed babies experience lasting health benefits. This includes helping to prevent several diseases like:
- diabetes
- childhood cancers
- obesity
- infections
- diarrhea
- chest (respiratory) infections
- asthma
Women who breastfeed also derive several benefits in addition to protecting and nourishing their babies. These women, for example, have a lower cancer and ovarian cancer.
Exclusive breast – feeding:
When a baby is given only breast milk, not even a drop of water, upto 5 months of age it is called an absolute or exclusive breast feeding.
Exclusive breast feeding means that –
- No drinks or foods other than breast milk are given to a baby
- No pacifiers/ dummies or artificial teats are given to a baby.
- Most exclusively breastfed newborn babies breastfed at least 8-12 times in 24 hours, including night feeds
or
It implies feeding of breast milk is enough for the baby up to 6months of life and no other food is necessary during this time.
or
Exclusive breastfeeding means that the baby has no other food or drink but breast milk not even a ‘dummy’ If the baby sometimes has small amounts of another food or drink-such as drinks of water or vitamin drops he is almost exclusively breastfed.
or
When a baby is given only breast milk, not even a drop of water, upto 5 months of age it is called an absolute or exclusive breast feeding.
Cardinal principles of breastfeeding practice:
1. Initiation of breastfeeding within an hour after birth.
2 Exclusive breastfeeding up to 6 month of age.
3. Continuation of breastfeeding along with complementary feeding for up to 2 years of age
Milk is called ideal food for baby because –
1. Breast milk is safe, clean, hygienic, cheap, and available to infant.
2. It is available in prepared form in adequate temp.
3. It fulfills the nutritional requirement of the infant in the first 4-5 months of life.
4. It provides passive immunity to the infant, as it contains IgA, lysozyme, lactoferrin etc.
5. It protects the infant from diarrhoeal diseases, night blindness ARI, measles etc. for few months.
6. Easily digestable.
7. Sucking helps in development of jaws and teeth.
8. It prevents neonatal hypocalcemial & hypomagnesimia.
9. It prevents malnutrition.
10. It reduces IMR
11. It prevents obesity of the baby.
12. It promotes bonding between mother and infant.

Advantages of breast feeding:
A. For mother
1. Breast feeding prevents carcinoma of breastial
2. It prevents ovulation, thus acting as contraceptive method
3. Breast feeding causes release of oxytocin- contraction of uterus- expulsion of placenta..
4. Breast feeding reduces the body fat that was deposited during pregnancy.
5. It promotes psychological binding between the mother & infant.
B. For baby
1. Breast milk is safe, clean, hygienic, cheap, available to infant.
2. It is available in prepared form in adequate temp.
3. It fulfills the nutritional requirement of the infant in the first 4-5 months of life!
4. It provides passive immunity to the infant, as it contains IgA, lysozyme, lactoferrin etc..
5. It protects the infant from diarrhoeal diseases, night blindness ARI, measles etc. for few months.
6. Easily digestable.
7. Sucking helps in development of jaws and teeth.
8. It prevents neonatal hypocalcemial & hypomagnesimia.
9. It prevents malnutrition.
10. It reduces IMR
11. It prevents obesity of the baby.
12. It promotes bonding between mother and infant
Nutritive Value
1. Breast milk contains all the nutrients in the right, proportion which are needed for optimum growth and development of the baby up to 6 months.
2. It is essential for brain growth of the infant because it has high percentage of lactose and alactose which are important components of galactocerebroside.
3. It facilitates absorption of calcium which helps in bony growth.
4. It contains amino acids like taurine and cysteine which are important as eurotransmitters.
5. Breast milk fats are polyunsaturated fatty acids which are necessary for the myelination of the nervous system.
6. It has vitamins, minerals, electrolytes and water in the right proportion for the infant which are necessary for the maturation of the intestinal tract.
7. It provides 66 calories per 100 mL and contains 1.2 ‘g protein, 3.8 g fat, 7 g lactose and() vitamin A 170 to 670IU, vitamin ‘C’ 2to 6 mg, vitamin ‘D’ 2.2IU, calcium (35 mg,. phosphorus 15 mg in 100 mL. The total amount of milk secretion per day is about 600 to 700 mL, which is sufficient for the baby. Its composition is ideal for an infanta
8. It provides specific nutrition for preterm baby in preterm delivery.
Digestibility
1. Breast milk is easily digestable.
2. The protein of breast milk are mostly lactoalbumin and lactoglobulin which form a soft curds that is easy to digest
3. The enzyrme lipase in the breast milk helps in the digestion of fats and provides free fatty acids.
Protective Value
1. Breast milk contains IgA, IgM, macrophages, lymphocytes, bifidus factors, unsaturated. lactoferrin, lysozyme, complement and interferon. Thus breastfed body less likely to develop infections especially gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infectións, e.g. diarrhea and ARI.
2. It also provides protection against malaria and various viral and bacterial infections like skin infections, septicemia, etc.
3. Breastfeeding protects the infant from allergy and bronchial asthma. It also protects against neonatal hypocalcemia, tetany, necrotizing enterocolitis, deficiencies of vitamin E and zinc, neonatal comrrlsions and sudden infant death syndrome.
4. Exclusive breastfeeding baby has less chance of developing malnutrition, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, arteriosclerosis, ulcerative colitis, appendicitis, childhood lymphoma, liver disease; celiac disease and dental caries.
Psychological Benefits
1. Breastfeeding promotes close physical and emotional bondage with the mother. by frequent skin to skin contact, attention and interaction. It stimulates psychomotor rand social development. It leads to better parent child adjustment, fewer behavioral disorders in children and less risk of child abuse and neglect.
2. Breastfeeding promotes development of higher intelligence and feeling of security in infant.
Maternal Benefits
1. Breastfeeding reduces the chance of postpartum hemorrhage and helps in better uterine involution.
2. Lactational amenorrhea promotes in recovery of iron stores. It can protect from pregnancy for first 6 months if exclusive breastfeeding is carried out. tallin terra
3. Breastfeeding improves metabolic efficiency and satisfaction with sense of fulfillment of the mother.
4. It reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancer of the mother
5. It improves slimming of the mother by consuming extra fat which accumulated during pregnancy.
6. It is more convenient and time saving for the mother,
7. Mother can provide fresh, pure, readymade, clean uncontaminated milk to her baby lat right temperature without any preparations. Mother feels comfortable to feed the baby especially at night.
Family and Community Benefits
1. Breastfeeding is economical in terms of saving of money, time and energy.
2. Family has to spend less on milk, health care and illness.
3. Community expenditure on health care and contraception are reduced. It is economic for the families, hospitals, communities and for countries.
Importance of breast feeding:
1. Breast milk contains colostrums, which protect infants
2. Breast milk is cheap
3. Breast milk is freely available.
4. Breast milk is sterile.
5. Breast milk can be given at any time.
6. Breast milk increases the mother and child bond.
7. Breast milk is free from pathogenic organism.
8. Breast milk helps in involution of uterus.
9. Infants who cannot take breast milk are put on cow’s milk, Soya milk or thin milk
Contraindications of breast feeding:
Absolute contraindication (mother)
- Infection in the breast.
- Cracks fissure or inverted nipple.
- Mother taking anticancer drug.
- Mother having breast cancer
- Psehotic mother
Infant contraindication:
- Gross prematurity.
- Phenylketouria.
- Galactosuria.
Disadvantage of breast feeding:
a. Lactation may not be adequate.
b. Mother carinot remain away from her child for a long perioda
c. Social life may be upset,
d. Breast feeding may cause
- Cracked nipples
- Strepto and staphylococcal infection of breasts
- Breast abscess
e.Maternal infection may be transmitted to the baby.
Composition of breast milk:
| Component | Amount/concentration |
| Protein | 11gm/litre |
| Carbbhydrate | 70 gm/litre |
| Fat | 35 gm/litre |
| Non protein | 32 gm/litre |
| Minerals | 2 gm/ litre |
| Ca | 33 gm/ litre |
| P | 15 gm/ litre |
| Fe | .4-1.5mg/litre |
| Vitamin C Vit-D | 60 gm/ litre 50 UI |
| Water | 88gm/litre |
| Energy | 640-720 Kcal |
Nice to know
The composition of breast milk varies at different stages in the postnatal period to fulfil the needs of the baby
Colostrum.
1. It is secreted during first three days after delivery.
2. It is thick, yellow and small in quantities.
3. It contains more antibodies and cells with higher amount of proteins and fat soluble vitamin (A, D, K):
4. It is sufficient and protective for the baby and should not be discarded.
Transitional milk:
1. It follows the colostrums and secretes during first two weeks of postnatal period
2. It has increased fat ‘and sugar content and decreased protein and immunoglobulin content
Mature milk:
1 It is secreted usually from 10 to 12 days after delivery.
2. It is watery but contains all nutrients for optimal growth of the baby.
Preterm milk:
1. The breast milk secreted by a mother who has delivered a preterm baby is different from milk of a mother who has delivered a full term baby.
2. This milk contains more proteins, sodium, iron, immunoglobulins and calories appropriate for the requirements of the preterm neonates
Fore milk:
1. It is secreted at the starting of the regular breast feeding.
2. It is more watery to satisfy the baby’s thirst and contains more proteins, sugar, vitamins and minerals.
Hind milk:
1. It is secreted towards the end of regular breast feeding and contains more fat and energy.
Superiority of breast milk over cow’s milks:
Breast milk is considered superior to cow’s reasons:
1. Proteins in breast milk are easily digested as they form a very fine flocculent curd in the stomach. The curd of the cow’s milk is thick and hard to digest for the young stomach due to large proportion of casinogen.
2. Breast milk contains twice as much iron as in the cow’s milk. This iron is essential for the new born and meets his needs upto 3 months. Anaemia is commonly seen in babies fed on cow’s milk even before 3 months.
3. Calcium of breast milk is utilized better as it present in a more assimilable form.
4. Vitamin-A is present in larger quantities in colostrums. Mother’s milk contains more vitamin-A than that in cow’s milk.
5. Vitamin-C content of breast milk is related to vitamin-C content of mother’s diet, but in general it is higher. Cow’s milk looses its vitamin-C content due to boiling, dilution and exposure to air.
Comparison between human milk and cow’s milk:
| S/L | Composition | Breast milk | Cow’s milk |
| 1 | Protein | 11gm/litre | 33gm/ litre |
| 2 | Carbbhydrate | 70 gm/litre | 50 gm/litre |
| 3 | Fat | 35 gin/litre | 35 gm/litre |
| 4 | Non protein | 32 gm/ litre | .32 gm/ litre |
| 5 | Minerals | 2 gm/ litre | 8 gm/ litre |
| 6 | Ca | .33 gm/litre | 1 gm/ litre |
| 7 | p | .15 gm/ litre | 1 gm/ litre |
| 8 | Fe | .4-1.5mg/litre | .3.5mg/litre |
| 9 | Vitamin C | 60 gm/ litre | 20 gm/ litre |
| 10 | Vit- D | 50 UI | 25UI |
| 11 | Water | 88gm/litre | 7 gm/ litre |
| 12 | Energy | 640-720 Kcal | 650 Kcal |