Definition Intramedullary (IM) Nail -An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Definition Intramedullary (IM) Nail
Standard intramedullary nails are cylindrical rods placed inside the medullary cavity of long bones.
(Ref-John Ebnezar’s, “Orthopedics for Nurses”, 4th edition, P-74]
Or
It is a surgical procedure by which a IM nail introduce into medulla of the bone to fix the bone correct place.
Indication s of IM nailing:
1) At the level of isthmus of femur in adults
2) Fracture of tibia.
3) Fracture of shaft of humerus.
4) Pathological fracture.
5) Non union, comminuted fracture.
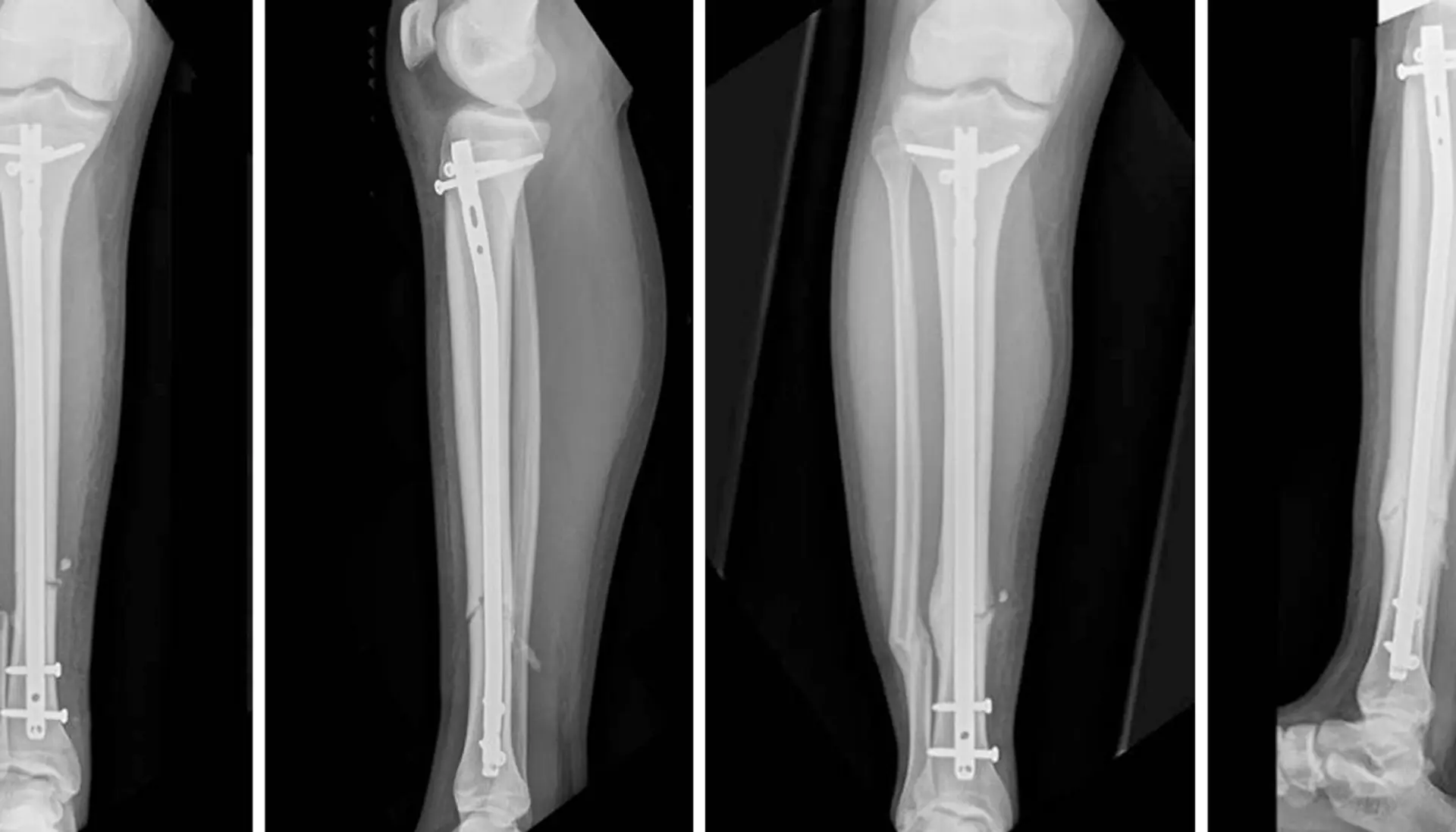
Different IM (Intramedullary) nail with where they used:
Broadly IM nail is 3 types:
A) Standard IM nail / Centromedullary nail:
1) Kuntscher nail.
2) Hansens nail.
3) Schneider nail.
4) Samson nail.
5) Lottes nail.
B) Interlocking nail.
C) Flexible medullary nail.
[Ref-John Ebnezar/4174)
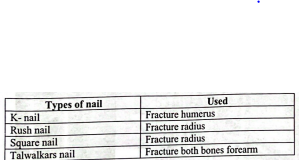
Different IM (Intramedullary) nail with where they used:
According to site:
1. Upper limbs:
2. Lower limbs:
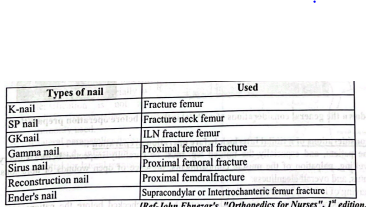
[Ref-John Ebnezar’s, “Orthopedics for Nurses”, I” edition, P-139,140)
Care of patients with IM nailing:
1) Take the patient in bed rest.
2) Patient can be permitted to move the operated limb on the next day.
3) Give analgesics to reduce pain.
4) Avoid weight bearing up to 6 weeks of operation.
5) Maintain personal hygiene.
6) Check X-ray.
7) Bedside standing with a walker can be permitted after the removal of sutures.
8) Walker support to be used for walking for at least 3 months.
[Ref-John Ebnezar/4 1735)
Interlocking nails:
Inter-locking nail is a metal rod forced into the medullary cavity of a bone. IM nails have long been used to treat fractures of long bones of the body.
Or
It is not exaggeration if say that interlocking nailing has revolutionized the treatment of long bone fractures.
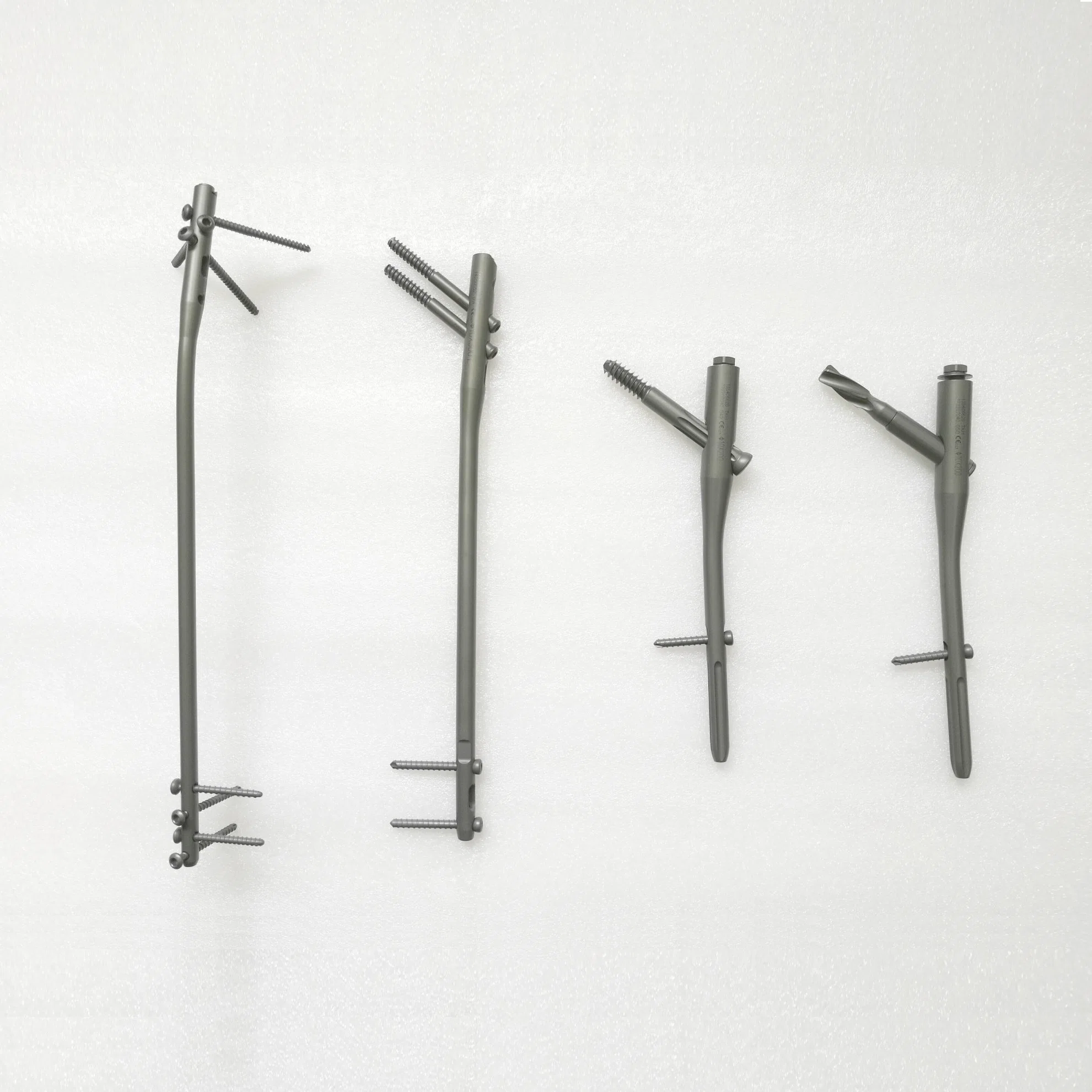

Indication of interlocking nailing:
1) Fracture of tibia at different s level.
2) Comminuted fractures.
3) Segmental fractures.
4) Proximal and distal third fractures.
General considerations of a tibilal interlock before operation preparation:
1) The patient, and especially the injured leg, must be carefully inspected before surgery for degree of swelling, palpation of the muscle compartments, presence of open wounds or abrasions, neurovascular status, and overall cleanliness.
2) Shaving of hair is not recommended.
3) In the operating room, surgical instruments should bechecked before the patient enters the operating theater.
4) The surgical site on the patient’s limb should be marked with an “X” and with the surgeon’s initials before entering the operating room.
5) On induction of an appropriate anesthetic, the surgical team must carry out a preoperative or preparatory pause to verify the surgical procedure to be performed and the side of injury as recommended by the World Health Organization.
6) The entire surgical team should be oriented to the nature of the procedure to be performed and the steps involved.
[Ref-Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Techniques in Orthopaedics Volume 24, Number 4, 2009)
Principle of method of tibial interlock operation:
1) Positioning:
After induction of anesthesia, the patient should be positioned on the operating table such that at least 110 degrees of knee flexion can be obtained. Many surgeons use a flannel blanket placed under the ipsilateral buttock. This serves to place the transcondylar axis of the distal femur parallel to the floor and assist with rotational alignment during IM nailing of multifragmentary tibial fractures. External rotation of the limb is also prevented by using such a roll.
Care must be taken not to place any pressure on the neurovascular bundle in the popliteal fossa.
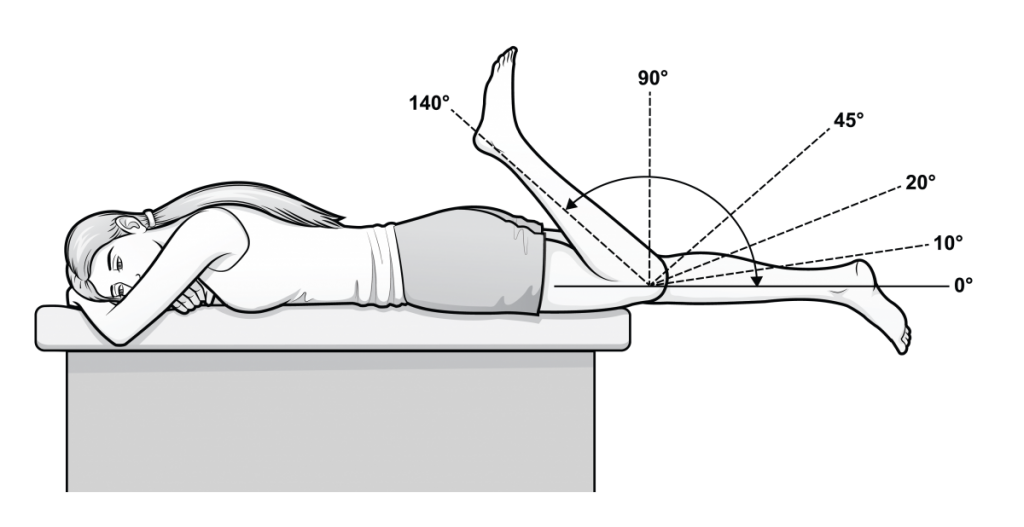
2) Gowning:
3) A central incision through the tendon:
a. Allows the proper placement of the bone entrance, especially when image intensification is not available. A medial parapatellar incision is
commonly used.
b. A lateral parapatellar incision.
c. It is used infrequently due to the potential for lateral meniscus injury.
4) Incision and Proximal Tibial Entry Point: There are different recommendations regarding where bone entrance point should be placed. In general, the more proximal the fracture, the more lateral the ent point should be. Some believe that the entry point should be medial to the lateral tibia spine. 12 Anatom dissections reveal the lateral meniscus to be at risk with a lateral parapatellar approach and care is requin to avoid injury.
Tornetta states that “the safe zone is located 9.1 millimeters lateral to the center of f plateau and 3 millimeters lateral to the center of the tibial tubercle.”14 The surgeon cannot use the landmarks without imaging. The patella tendon is palpated with the knee in flexion. A central longitudir incision through the tendon allows a predictable and accurate placement of the bone entrance.
5) Reaming. Always make sure that the fracture is reduced prior to passing the reamers.
6) Reattach the Target Arm
7) Insert the small drill guide into the cannula:
8) Distal tibial blocking screws placed on the concavelateral side prevent the distal tibia from falling into valgus.
Care after application of interlocking nailing:
1) Patient can be permitted to move the operated limb on the next day.
2) Active and active assisted exercises for knee are done next.
3) Bedside standing with walker can be permitted after 2-3 days.
4) Walker support to be used for walking for at least 2-3 weeks.
5) Weight bearing can be permitted at the end of 6 weeks.
