Definition of Autoclaving -Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Definition of Autoclaving
Sterilization which operate at high temperatures (In excess of 100°C) and pressure are called autoclaves.
Or,
Autoclaving is a method of sterilization by moist heat in which substances are sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes.
Types of Autoclave: They fall into two categories
1. Double chamber autoclave
2. Single chamber autoclave
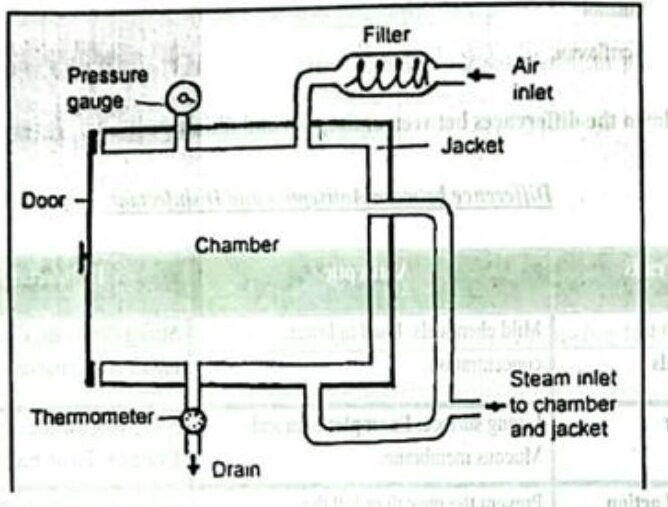
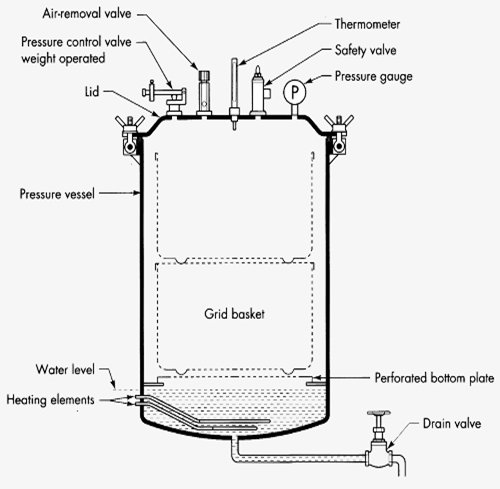
Principle of Autoclave:
- It is steam sterilization above 100°C in a pressure chamber
- With rise of pressure boiling of water also rises provided no air is present
- When autoclave is closed & made air tight, water starts boiling, the inside pressure increases & water boils above 100°C
- Steam under pressure unmixed with air has more temp than that mixed with air Steam under pressure has more penetrating power as steam condenses to water on contact with
- materials lowering pressure that draws more steam inside
- During condensation of steam to water, large amount of latent heat is liberated thus increasing the efficiency of sterilization.
(Ref by- Rashid, kabir, hydar/4/267+M.R. Choudhury/5/43+Park/23/128)
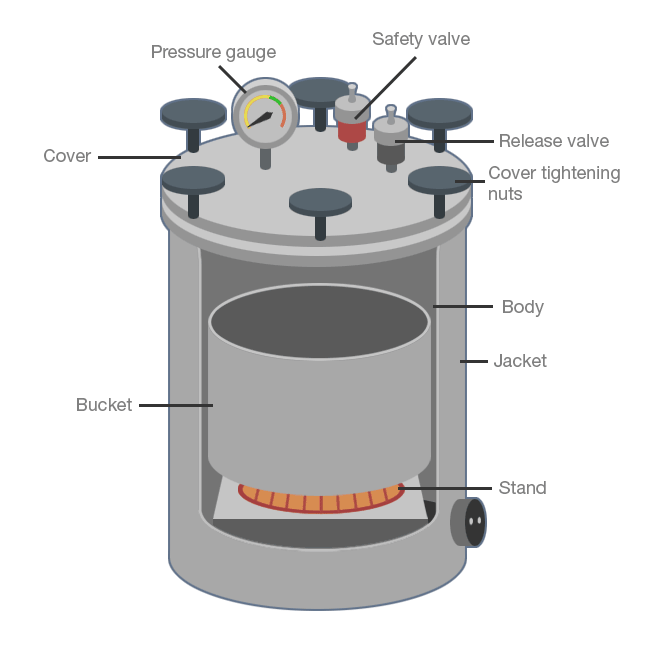
Advantages & Disadvantages of Autoclave
| Advantages of auto- clave: |
|
| Disadvantages of autoclave |
|
Autoclaving is the most efficient process of sterilization due to following reasons;
1. Autoclave is a moist heat procedure & moist heat kills organisms and spores at lower temperature and in shorter duration (20 hours at 100°C by dry heat is almost equal to 15 minutes at 121°C by moist heat)
2. Penetrating power of moist heat is better than dry heat due to-
- Low density of steam
- Condensation of steam and contraction of its volume creates negative pressure on the surface (1600 ml of steam condenses into 1 ml of water).
- Liberation of latent heat (518 calories for 1 ml of water) during condensation of steam.
HOT AIR OVEN
Hot Air Oven:
Hot air oven is a method of sterilization by dry heat above 100°C. The oven is heated by electricity and temperature is maintained by thermostat. This is usually a method of choice for sterilizing glassware.
- The temperature is 160° C for 1 hour.
- The variation of temperature is prevented by circulating air with a fan.
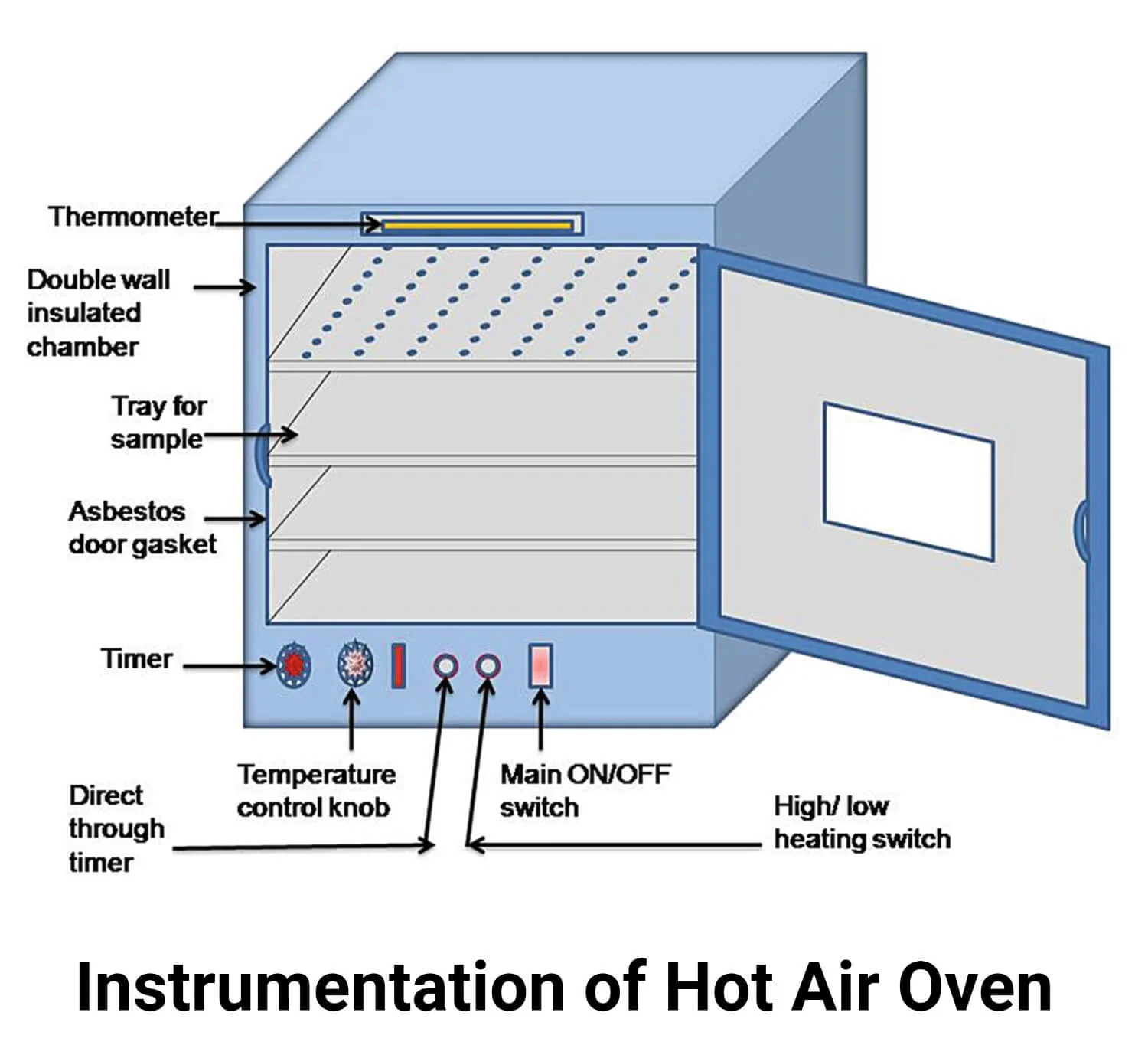
Example of articles sterilized by hot air oven:
- Glass wares: Petridishes, test tubes, flasks, beaker, cylinder, glass pipettes, swab sticks etc.
- Oily fluids like grease & powder.
Advantages of hot air oven:
- Glass wares like petridishes, swab sticks, and glass syringes can be sterilized.
- Powder, fats, grease etc. can be sterilized.
- Sharp cutting surgical instruments can be sterilized
Disadvantage of hot air oven:
- Need more temperature
- Time consuming
- Plastic materials cannot be sterilized in this process.
- Natural and synthetic fibers cannot be sterilized.
- Destroy the constituents of normal media.
Differences between Autoclave & Hot Air Oven:
| Traits | Autoclave | Hot Air Oven |
| 1. Time needed | Less time consuming | More time consuming |
| 2. Penetrating power | Moist heat has more penetrating power. | Dry heat has less penetrating power. |
| 3. Latent heat | Latent heat of evaporation is release. | Latent heat of evaporation is not released. |
| 4. Fats, Oils & powders | Can’t be sterilized. | Can be sterilized |
| 5. Natural & synthetic fliers | Can be sterilized. | Can’t be sterilized |
| 6. Uses | Dressing, apron, glove, catheter, surgical instruments (except sharp cutting instruments) can be sterilized. | Glass wares like petridishes, swab sticks & glass syringes, and powder, fats, grease, sharp cutting surgical instruments etc. can be sterilized |
